We’ve all encountered them: those ubiquitous CAPTCHA tests requiring us to identify traffic lights, bicycles, or distorted characters. These tests, once a constant source of online frustration, have become less frequent. But how do they work, and can AI actually bypass them? Let’s unravel the mystery behind CAPTCHAs.
What is a CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHA stands for “Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart.” Essentially, it’s an automated Turing test designed to differentiate between human users and bots. The Turing test, conceived by British mathematician and computer scientist Alan Turing, assesses a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human. It’s also used to evaluate AI for creativity and awareness.
The term CAPTCHA, coined around 2000, intentionally resembles “capture.” Its primary function is to intercept and filter out bots on websites, preventing spam and automated purchases.
How CAPTCHAs Work
CAPTCHAs present simple tasks requiring human interaction. These tasks often involve deciphering distorted text or identifying patterns in images, such as the presence of traffic lights, bridges, or animals. The tests are randomized, presenting different challenges upon each website reload to prevent bots from learning and circumventing the system. While early CAPTCHAs posed a challenge for computers lacking sophisticated pattern recognition algorithms, advancements in artificial intelligence have enabled bots to solve these tests more easily.
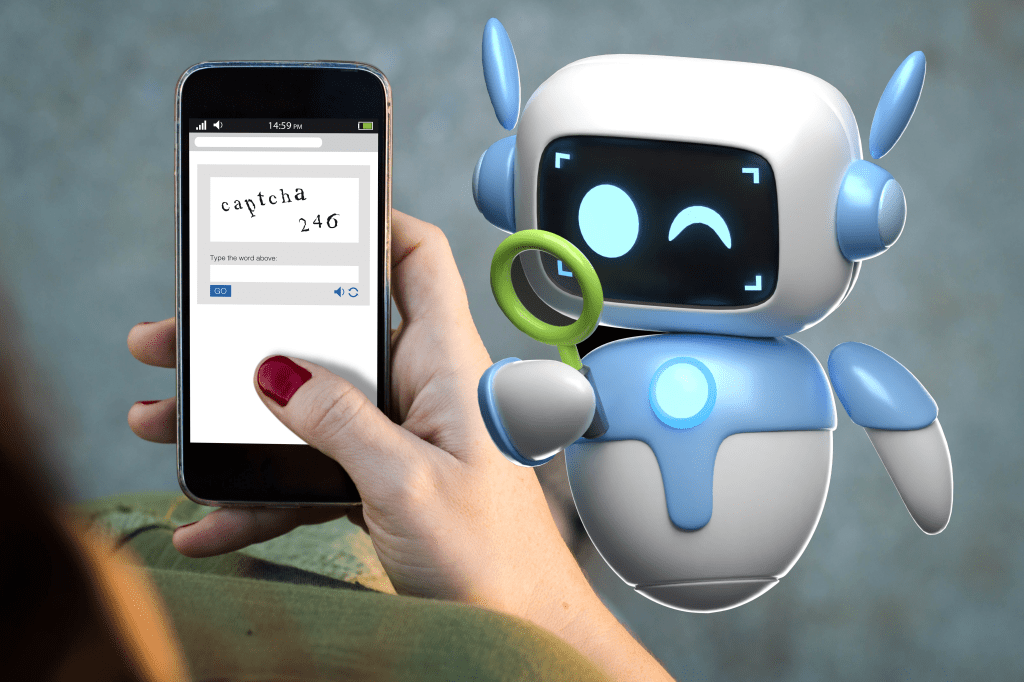
 captcha test robotSimple CAPTCHA tests like these are increasingly solvable by advanced bots.
captcha test robotSimple CAPTCHA tests like these are increasingly solvable by advanced bots.
Distinguishing Humans from Bots: Mouse Movements
Despite advancements in AI, CAPTCHAs remain effective due to a clever solution: mouse tracking. Modern CAPTCHAs monitor cursor movement. Human mouse movements are inherently erratic, varying in speed and trajectory. Conversely, bots typically execute clicks in perfectly straight lines or predictable patterns. Websites detect this robotic behavior and block access.
Occasionally, a simple “I am not a robot” checkbox might be followed by a more complex image-based CAPTCHA. This often occurs when mouse movements appear too “robotic.” So, adding a bit of natural irregularity to your mouse movements can help confirm your human status.
Conclusion: The Evolving Landscape of CAPTCHAs
CAPTCHAs have evolved significantly since their inception. While they are less prevalent than before, they continue to play a crucial role in protecting websites from bot activity. By leveraging sophisticated techniques like mouse tracking, CAPTCHAs effectively differentiate between human users and automated bots, ensuring a more secure and user-friendly online experience.