Want to upgrade your processor but unsure what CPU you currently have? Checking your CPU is quick and easy, regardless of whether you’re running an Intel or AMD processor, on a brand new PC, or a machine that’s a decade old. This guide will show you how to find your CPU information in just a few clicks.
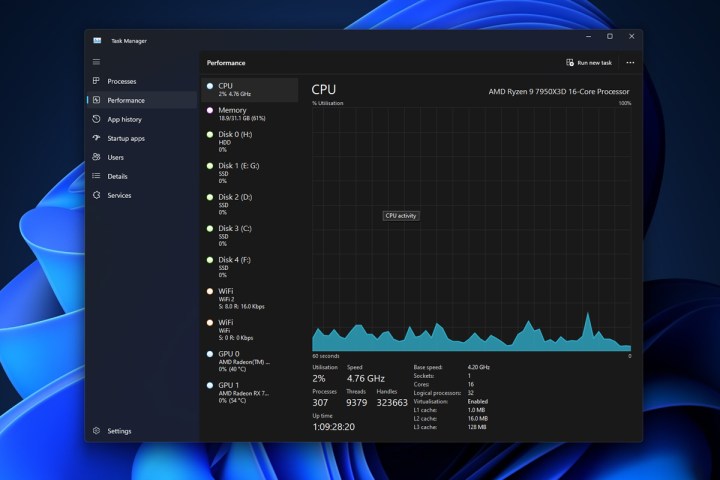 Task manager in Windows 11. This image shows the Task Manager window with the CPU tab selected. The CPU name and model are visible in the top right corner.
Task manager in Windows 11. This image shows the Task Manager window with the CPU tab selected. The CPU name and model are visible in the top right corner.
Checking Your CPU with Task Manager
Task Manager offers the quickest way to identify your CPU.
Step 1: Right-click the taskbar and select “Task Manager.”
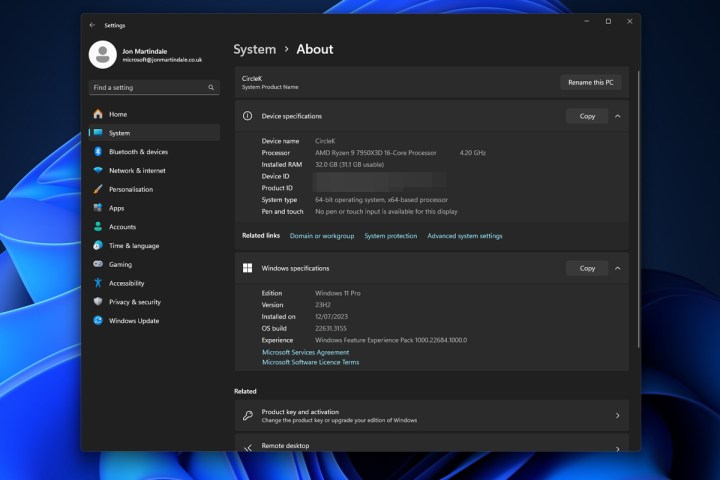 Checking the CPU in Windows Settings. This image shows the Windows Settings app open to the System > About page. The processor information, including name and speed, is highlighted.
Checking the CPU in Windows Settings. This image shows the Windows Settings app open to the System > About page. The processor information, including name and speed, is highlighted.
Step 2: Navigate to the “Processes” tab in the left-hand menu. If necessary, select “CPU” at the top of the component list.
Your processor’s name and model number will be displayed in the top-right corner. You’ll also find detailed information like base speed, cache size, core count, and current usage at the bottom of the window.
Identifying Your CPU through Windows Settings
The Windows Settings menu provides comprehensive system information, including your CPU details.
Step 1: Press the Windows key + I to open the Windows Settings menu.
Step 2: Select “System” from the left-hand menu.
Step 3: Scroll down and click on “About.” Here, you’ll find your processor’s name, model, and base clock speed listed next to “Processor.” This section also provides additional information about your computer and Windows installation.
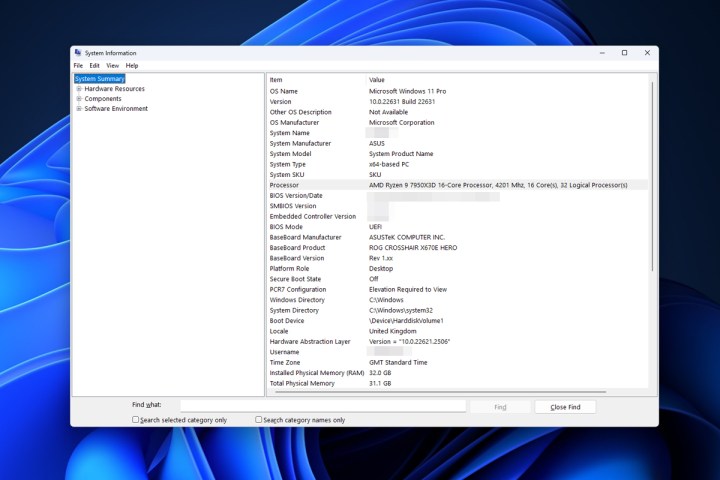 Checking system information in Windows 11 to find CPU name. The system information window is shown, displaying the processor details such as name, number of cores, and speed.
Checking system information in Windows 11 to find CPU name. The system information window is shown, displaying the processor details such as name, number of cores, and speed.
Finding Your CPU via System Information
System Information offers a more detailed view of your hardware specifications.
Step 1: Search for “System Information” in the Windows search bar and select the corresponding result.
Step 2: The default “System Summary” tab displays a wealth of information about your PC. Locate the “Processor” entry to find your CPU name, number of cores, and base clock speed.
Next Steps After Identifying Your CPU
Now that you know how to check your CPU, you can use this information to research potential upgrades, monitor CPU temperature, or even explore overclocking. Learning about CPU architecture, performance metrics, and cooling solutions can further enhance your understanding of your system’s capabilities.