Windows 11 boasts a range of new features compared to Windows 10, but these advancements sometimes come at a cost: increased RAM usage. While Windows 11 might consume more RAM than its predecessor, the actual amount isn’t fixed. This article will explain what RAM is, explore how much RAM Windows 11 typically uses, and suggest ways to reduce that usage if your PC is struggling.
 Person using Windows 11 laptop on their lap by the window.
Person using Windows 11 laptop on their lap by the window.
Windows 11’s RAM usage can vary considerably, often between 2GB and 8GB, sometimes even more. However, this doesn’t mean all that RAM is unavailable for other applications. Windows 11 employs a service called SysMain (formerly Superfetch) to optimize performance. SysMain preloads frequently used apps and files into RAM, resulting in faster loading times.
This preloading by SysMain contributes to the potentially high idle RAM usage in Windows 11, which can sometimes reach up to half of your total system memory. However, if that RAM is needed elsewhere, Windows intelligently releases the SysMain cache, allocating the memory to the demanding task. Therefore, you generally won’t encounter situations where you can’t run a program due to SysMain, unless your PC has insufficient RAM to begin with.
On a system with 8GB of RAM, Windows 11 processes might consume 2GB to 4GB or more. With 32GB of RAM, this figure can rise to 8GB or 10GB. The more RAM available, the more Windows 11 may utilize for optimization.
Checking RAM Usage in Windows 11
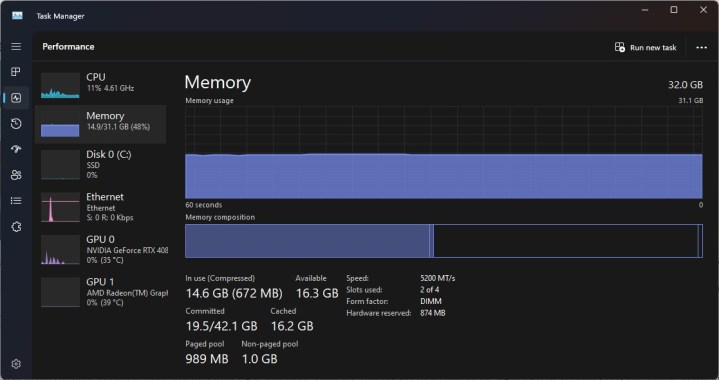 RAM usage in Windows 11.
RAM usage in Windows 11.
Accessing the Task Manager is the key to monitoring RAM usage. Right-click the taskbar and select “Task Manager,” or press Ctrl + Alt + Delete and select “Task Manager” from the lock screen.
Within the Task Manager, navigate to the “Performance” tab and select “Memory.” This provides an overview of total RAM, speed, and current usage. For a clearer picture of Windows 11’s consumption, close all third-party applications and as many background processes as possible before checking.
Alternatively, the “Processes” tab lists individual processes and their RAM usage. While less straightforward, this allows a detailed breakdown of memory allocation. Remember that not all RAM usage is attributable to Windows 11 itself; background processes and pre-installed software also contribute. Utilities like Nvidia Control Panel or AMD Software: Adrenalin Edition can also consume memory, especially when active.
Recommended RAM for Windows 11
 RAM inside the Starforge Navigator.
RAM inside the Starforge Navigator.
Microsoft officially recommends a minimum of 4GB of RAM for Windows 11. While technically installable on systems with less RAM, it’s strongly discouraged. Performance issues and instability are likely.
While 4GB meets the minimum requirement, it’s not ideal. It might suffice for light browsing, but resource-intensive tasks like gaming will likely suffer. 8GB is recommended for everyday browsing and work, while 16GB or 32GB is ideal for gaming and demanding multitasking.
Windows 11 vs. Windows 10: RAM Consumption
 Windows 11 and Windows 10 operating system logos are displayed on laptop screens.
Windows 11 and Windows 10 operating system logos are displayed on laptop screens.
Windows 11’s higher RAM requirements compared to Windows 10 (1GB for 32-bit and 2GB for 64-bit) are due to its enhanced features. The modernized user interface, new animations, updated taskbar and Start Menu, Widgets panel, Snap Layouts, and Snap Groups contribute to increased memory usage even without running additional applications.
Reducing RAM Usage in Windows 11
 A gaming PC with RGB synced lights running Apex Legends.
A gaming PC with RGB synced lights running Apex Legends.
Closing unnecessary third-party processes can effectively reduce RAM usage. In the Task Manager’s “Processes” tab, sort by “Memory” to identify the most RAM-intensive programs. Common culprits include web browsers like Google Chrome, which consume resources even when minimized.
Background processes like Phone Link, game clients like Steam or Epic Games, and hardware-related applications also contribute to RAM usage. Close any unnecessary programs. If unsure about a process, research it online before terminating.
This process needs repeating with each PC reboot. To avoid this, disable unnecessary startup programs. For gaming performance improvements, explore Windows gaming optimization options.
Finally, remember that high RAM usage isn’t necessarily detrimental, as long as performance remains unaffected. Windows 11 efficiently manages memory, releasing resources as needed. However, persistent high RAM usage accompanied by slow performance could indicate underlying issues requiring further troubleshooting.