Experiencing random crashes, blue screens, or slow performance? Faulty RAM might be the culprit. While RAM failure is relatively uncommon, it can cause a range of frustrating problems. Whether your high-end RAM’s overclock is set too aggressively, there’s a BIOS conflict, or the memory modules themselves are failing, diagnosing RAM issues is crucial for a stable system. This guide provides effective methods to test your RAM and potential solutions if problems are detected.
 Windows Memory Diagnostic in the Windows search bar.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
Windows Memory Diagnostic in the Windows search bar.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
Using Windows Memory Diagnostic
Windows includes a built-in RAM testing utility called Windows Memory Diagnostic. This tool offers a simple yet often effective way to identify memory problems. Remember to save your work before proceeding, as a system restart is required.
-
Open Windows Memory Diagnostic: Type “Memory diagnostic” in the Windows search bar and select the application.
-
Restart and Run Test: Choose the “Restart now and check for problems (recommended)” option. Your PC will restart automatically and initiate the memory test.
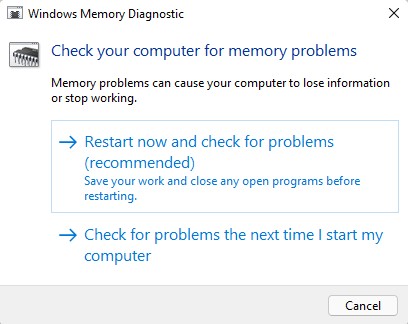 Windows Memory Diagnostics options.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
Windows Memory Diagnostics options.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
-
Testing Process: Upon restarting, a blue screen will appear, indicating the RAM test is in progress. This typically takes 15-30 minutes.
-
Review Results: After the test completes and Windows restarts, a notification will inform you of the results. A failure indicates unstable RAM, requiring further troubleshooting or replacement.
Comprehensive Testing with MemTest86
If Windows Memory Diagnostic doesn’t reveal any issues, but you still suspect faulty RAM, MemTest86 offers a more thorough diagnostic. This tool by PassMark runs outside of Windows, requiring a bootable USB drive. Ensure the USB drive is empty or contains no essential data, as it will be formatted.
- Download MemTest86: Download the free version of MemTest86 from the official PassMark website. Extract the downloaded .zip file to a new folder.
 MemTest86 in the Windows download folder.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
MemTest86 in the Windows download folder.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
- Prepare Bootable USB: Insert a USB drive and run the
imageUSB.exefile from the extracted MemTest86 folder. Confirm the drive selection and proceed with writing the image to the USB drive. This will format the drive.
 MemTest86 .zip file contents.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
MemTest86 .zip file contents.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
- Boot from USB: Save all your work and restart your PC. Access the boot menu (usually by pressing F2, F12, Del, or Esc during startup) and select the USB drive as the boot device. The specific key depends on your motherboard manufacturer.
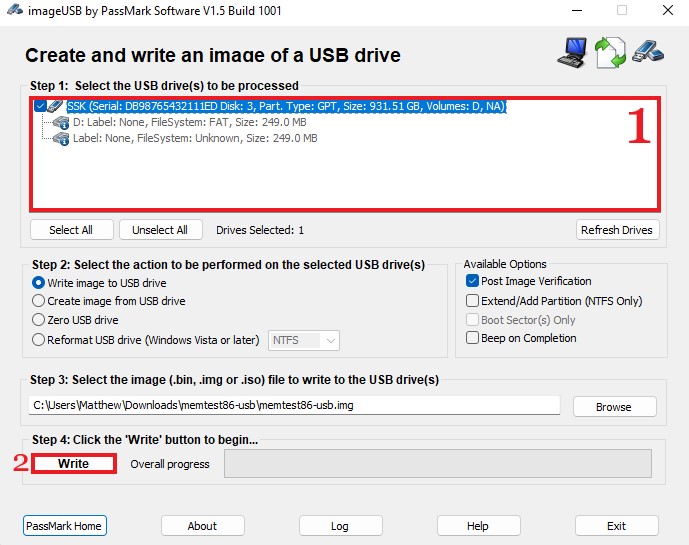 MemTest86 installation instructions.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
MemTest86 installation instructions.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
-
Run MemTest86: MemTest86 will load automatically and begin testing your RAM. This process can take up to three hours.
-
Interpret Results: Upon completion, MemTest86 will display the test results. Any errors indicate potential RAM issues.
 The restart button in the advanced startup option menu.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
The restart button in the advanced startup option menu.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
Troubleshooting Unstable Memory
If either test reveals RAM instability, several solutions can be explored.
-
Reduce Overclock: If you’ve overclocked your RAM, try reducing the frequency or timings. Resetting to default settings or slightly lowering the overclock can often resolve instability.
-
BIOS Reset/XMP Profile: Resetting your BIOS to default settings or re-enabling the XMP/EXPO profile can sometimes resolve compatibility issues.
-
Check Compatibility: Ensure your RAM is compatible with your motherboard. Consult your motherboard’s documentation for a list of validated RAM kits.
-
Underclock RAM (Last Resort): As a last resort, try underclocking your RAM to improve stability. This will reduce performance but might be necessary if other solutions fail.
-
RMA or Replacement: If none of the above steps work, and your RAM is still under warranty, consider requesting a replacement from the manufacturer. If you have a pre-built system or laptop, contact the vendor for support.
Conclusion
Testing your RAM is a crucial step in diagnosing system instability. By utilizing the built-in Windows Memory Diagnostic or the more comprehensive MemTest86, you can identify potential memory issues and take appropriate action. Whether adjusting overclock settings, checking compatibility, or ultimately replacing faulty modules, these troubleshooting methods can help ensure a stable and reliable computing experience. Remember to consult your motherboard’s documentation and RAM manufacturer’s warranty information for specific guidance.
 Advanced startup in the Windows search bar.Image used with permission by copyright holder.
Advanced startup in the Windows search bar.Image used with permission by copyright holder.