Nearly all software contains coding errors (bugs) and security vulnerabilities. Larger codebases naturally have more. While many flaws are discovered and patched by users or developers, some are first found by malicious hackers. These hackers often exploit these vulnerabilities for personal gain, either by infiltrating systems or selling the information for substantial sums.
What is a Zero-Day Flaw?
Newly discovered vulnerabilities are called zero-days or 0-days. This refers to the time the developer has to fix the issue—zero days. Hackers actively exploit the vulnerability before the developer is even aware of it. This exploitation involves a zero-day exploit, a method designed to take advantage of the specific vulnerability, leading to a zero-day attack.
Once the vulnerability becomes known, the software developer can create a patch to fix the affected code or release an updated version of the program. Once the patch or update is available, the exploit becomes ineffective, and the zero-day threat is officially over. However, since many users delay installing patches, the vulnerability can remain a threat for a period of time.
Zero-day attacks are exceptionally dangerous because they exploit unknown vulnerabilities, leaving manufacturers and users unprepared. Attackers can infiltrate systems undetected for days, weeks, or even months, gaining access, stealing data, or installing malware. While antivirus software aims to detect such activity, attackers often employ sophisticated methods to remain undetected.
The Lucrative Black Market of Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
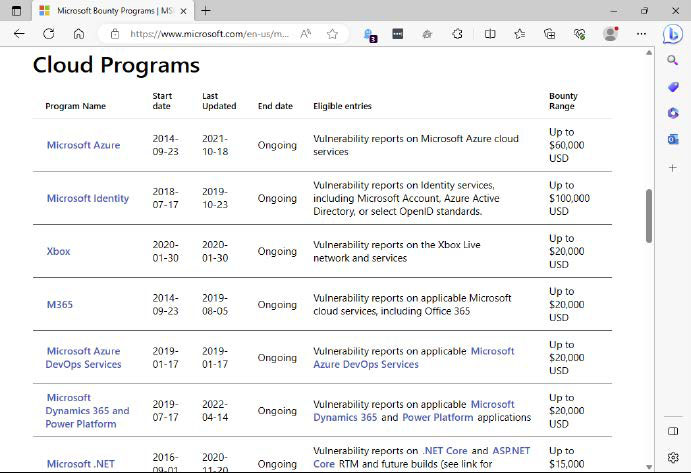 Microsoft's bug bounty website lists the maximum payouts for newly discovered security vulnerabilities. Some can earn finders up to $100,000.
Microsoft's bug bounty website lists the maximum payouts for newly discovered security vulnerabilities. Some can earn finders up to $100,000.
Zero-day vulnerabilities are highly valued on the black market. Six- and seven-figure sums are offered on the dark web for vulnerabilities in popular software like Windows. Beyond criminals, intelligence agencies have also exploited these flaws to target databases and infrastructure of other nations.
The Stuxnet computer worm, reportedly developed by Israel and the US, exemplifies this. Stuxnet infiltrated the Iranian nuclear program’s systems by exploiting unknown Windows vulnerabilities. The worm manipulated centrifuge controls, causing malfunctions without triggering error messages.
Governments and corporations also use zero-day vulnerabilities for industrial espionage, targeting development plans, company data, and contact information. Hacktivists may also employ these methods to advance their political or social agendas.
Recognizing the high risk and potential payouts, several major software companies have implemented bug bounty programs. These programs offer rewards for reporting newly discovered vulnerabilities and other bugs, with payouts often reaching six figures depending on the severity.
Detecting Zero-Day Attacks
Modern antivirus programs utilize virus signatures, heuristics, and artificial intelligence to detect malware. These programs are trained on known malware behavior patterns to identify new variants. However, zero-day exploits often use novel attack methods, making detection challenging.
Behavior-based security solutions, like intrusion detection systems (IDS), are frequently employed by businesses. IDS monitor log files and system information, such as CPU usage, to identify suspicious network and computer activity. They then issue alerts or send emails to administrators. Intrusion prevention systems (IPS) take this further by automatically initiating countermeasures, like firewall configuration changes. However, these solutions are costly and primarily suited for businesses.
Finding Information about New Security Vulnerabilities
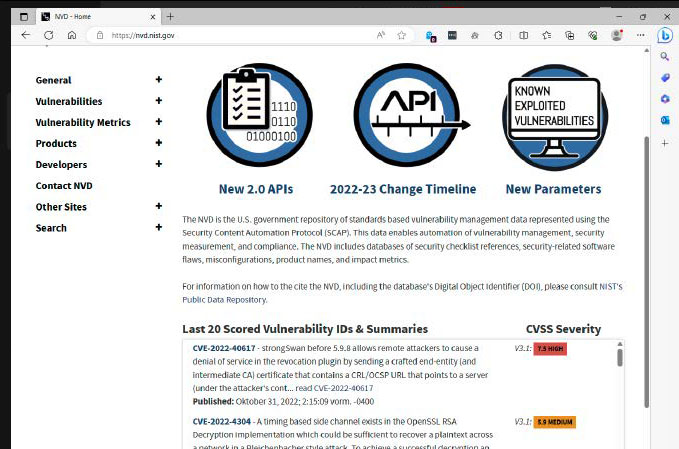 The US National Vulnerability Database displays the 20 most recent vulnerabilities, their CVE numbers, and information about their impact and available patches.
The US National Vulnerability Database displays the 20 most recent vulnerabilities, their CVE numbers, and information about their impact and available patches.
The CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) system, introduced in 1999, provides a standardized method for cataloging security vulnerabilities. Each vulnerability receives a CVE number (CVE-XXXX-XXXXX), where XXXX represents the year and XXXXX is a sequential number. The CVE system is now an internationally recognized standard.
The Mitre Corporation, a non-profit organization funded by the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), maintains the CVE database at www.cve.org. Users can search for specific CVE numbers or keywords. The entire database is also available for download.
The National Vulnerability Database (NVD), closely linked to the CVE website, lists the 20 most recently identified vulnerabilities, along with explanations and links to patches. The NVD also provides a risk assessment (Low, Medium, High, Critical) for each vulnerability.
Microsoft adheres to the CVE standard but also maintains its own list of vulnerabilities for its products. Microsoft distributes patches automatically through its monthly security updates.
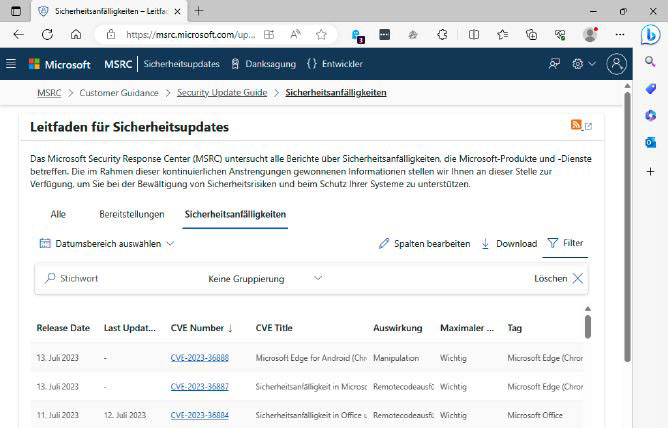 Microsoft publishes newly discovered security vulnerabilities in its products on the Microsoft Security Response Center. Patches are installed automatically.
Microsoft publishes newly discovered security vulnerabilities in its products on the Microsoft Security Response Center. Patches are installed automatically.
Protecting Yourself from Zero-Day Exploits
Zero-day attacks aren’t limited to corporations. Individuals are also targeted through phishing emails or tricked into installing software containing zero-day exploits, sometimes through malicious Google ads.
You can protect yourself by:
- Installing updates promptly: Windows typically does this automatically. Use tools like Sumo to check for updates for other applications.
- Downloading software from trusted sources: Stick to official websites.
- Minimizing installed software: Reduce potential vulnerabilities.
- Using a firewall: The Windows firewall is enabled by default and should remain active.
- Educating yourself about phishing scams: Learn to recognize common tactics.
Troubleshooting Windows Update Issues
 Ensure your drivers are up-to-date. Tools like Driver Booster Free can help you find outdated versions.
Ensure your drivers are up-to-date. Tools like Driver Booster Free can help you find outdated versions.
Install Windows security updates and patches immediately to mitigate vulnerabilities. However, update installations can sometimes fail. If this happens:
- Clear the update cache: Use the Windows troubleshooter (Settings > System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters > Windows Update). Restart Windows (Windows key + R, type
shutdown /g). Retry the update. - Check C: drive space: Ensure at least 32GB free. Enable storage optimization (Settings > System > Storage). Clean up large files and unused apps. Empty the Recycle Bin.
- Manually install the update: Find the KB number of the failed update (Settings > System > Windows Update > Update history). Search for it in the Windows update catalog (www.catalog.update.microsoft.com). Download and install manually.
- Temporarily uninstall third-party antivirus software: Restart Windows and retry the update.
- Disconnect USB devices: Retry the update.
- Uninstall devices with question marks in Device Manager: Restart Windows, which will reinstall drivers.
- Update drivers: Use a tool like Driver Booster Free.
 Samsung 980 pro ssd windows 11
Samsung 980 pro ssd windows 11
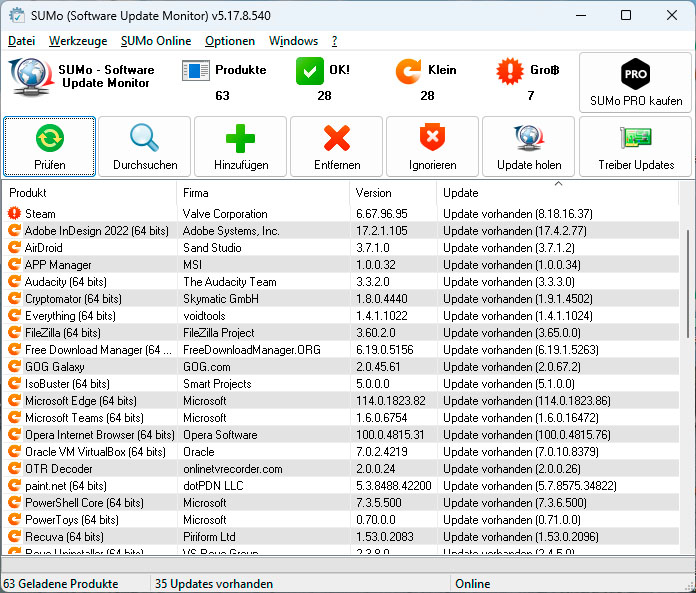 With the free tool Sumo, you can find out for which of your programmes updates are available and then install them specifically.
With the free tool Sumo, you can find out for which of your programmes updates are available and then install them specifically.