Artificial intelligence is no longer confined to the cloud or expensive software suites. Many powerful AI tools are available as open-source software, allowing you to harness the power of AI right on your own computer. This accessibility stems partly from academia, where open licensing fosters collaboration and development. This article explores nine free AI tools utilizing various AI techniques—neural networks, machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing—that you can run locally on your Windows PC.
The availability of pre-trained models and training data has been instrumental in making these practical AI applications possible. Developing these models often involves years of work and terabytes of data. However, advancements in PC hardware, coupled with open-source frameworks like Facebook and Microsoft’s PyTorch and Google’s TensorFlow, have democratized AI development, enabling smaller teams to contribute and innovate.
AI-Powered Image Enhancement and Manipulation
Final 2x: Upscaling Images with Neural Networks
Traditional image upscaling often leads to pixelation and quality loss. Final 2x leverages neural networks to enlarge images while preserving detail and smoothness. It offers various algorithms (Real Cugan, Real Esrgan, Waifu 2x, and SRMD) suited for different image types, effectively improving even pixelated or noisy photos.
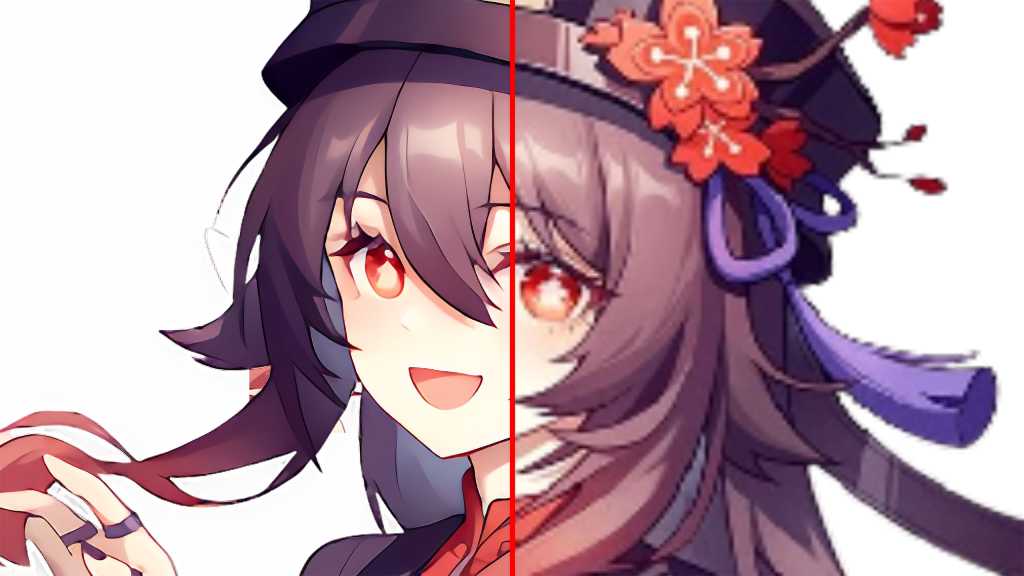
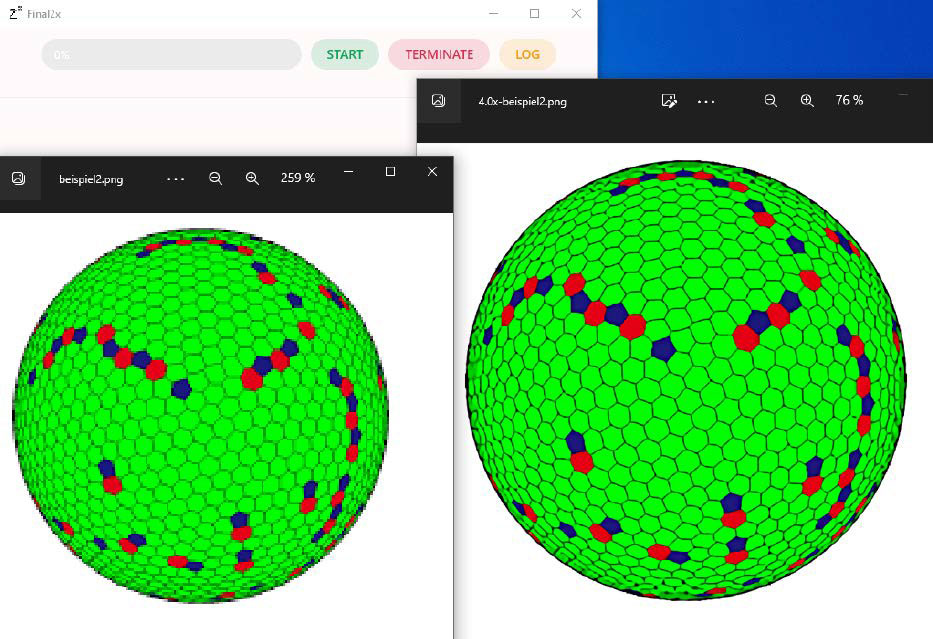 Upscaled Image with Final 2x: The left image is pixelated, while the right image shows the result after upscaling with Waifu 2x.
Upscaled Image with Final 2x: The left image is pixelated, while the right image shows the result after upscaling with Waifu 2x.
Installation and Usage: Final 2x is easy to install on Windows and runs on Nvidia, AMD, and Intel GPUs, even integrated ones. While ample RAM is beneficial for AI tools, Final 2x is relatively lightweight. Download the installer from the developer’s GitHub page. After installation, drag and drop image files (JPG or PNG) into the program, choose the appropriate algorithm and scaling factor in the settings, and click “Start.”
Meshroom: Turn Photos into 3D Models
Meshroom utilizes photogrammetry to create 3D models from a series of photographs. This open-source software analyzes images to reconstruct the shape of an object, generating a mesh file suitable for CAD and animation programs.
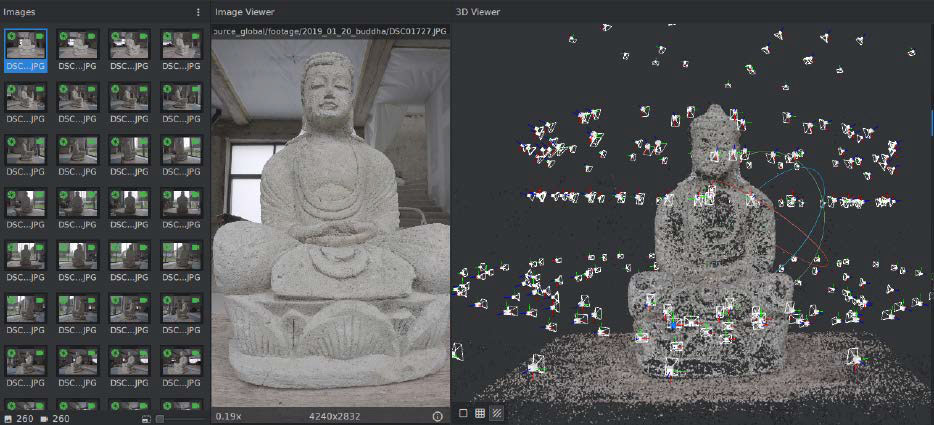 Meshroom creates 3D models from photos. This image shows a 3D mesh generated from photographs of a real-world object, ready for use in CAD software or 3D modelling tools like Blender.
Meshroom creates 3D models from photos. This image shows a 3D mesh generated from photographs of a real-world object, ready for use in CAD software or 3D modelling tools like Blender.
Installation and Usage: Meshroom requires an Nvidia GPU with CUDA support for optimal performance. Install the CUDA drivers followed by Meshroom. Photograph the object from various angles with good lighting and depth of field. Drag the images into Meshroom’s “Images” area to initiate the 3D reconstruction process. Further refinement can be done in 3D modeling software like Blender.
AI for Video Editing and Audio Processing
Kdenlive: AI-Powered Object Tracking
Kdenlive, a free video editor, integrates AI for motion tracking. This feature allows you to automatically track objects in video clips, apply masks, and add targeted effects like pixelation for blurring faces or objects.
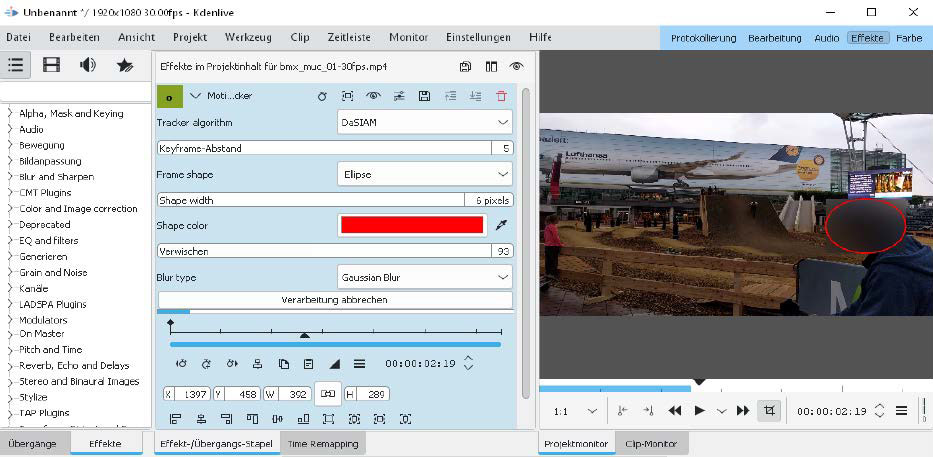 Kdenlive's motion tracker. This image shows the DaSIAM motion tracker in Kdenlive, used to track an object and apply a blur effect for privacy.
Kdenlive's motion tracker. This image shows the DaSIAM motion tracker in Kdenlive, used to track an object and apply a blur effect for privacy.
Installation and Usage: Install Kdenlive and download the necessary motion tracking model files. Place these files in the designated “opencvmodels” folder within the Kdenlive installation directory. In Kdenlive, apply the “Motion Tracker” effect to a clip, select the “DaSIAM” algorithm, position the tracking frame around the object in the first frame, and click “Analysis.”
Spleeter: Separate Vocals and Instruments from Music Tracks
Spleeter uses AI to deconstruct music into individual tracks, isolating vocals, bass, drums, and other instruments. Developed by Deezer, it leverages TensorFlow and Ffmpeg to analyze and separate audio streams.
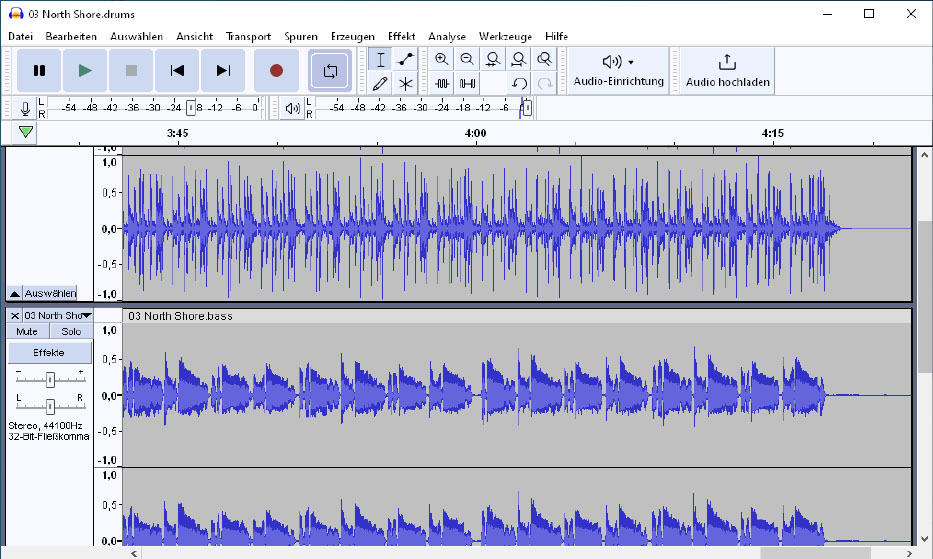 Spleeter separates music into individual tracks. This image displays the separated tracks in Audacity, showing Spleeter's ability to isolate vocals and instruments, though some high frequencies might be lost.
Spleeter separates music into individual tracks. This image displays the separated tracks in Audacity, showing Spleeter's ability to isolate vocals and instruments, though some high frequencies might be lost.
Installation and Usage: Install Spleeter via the Chocolatey package manager on Windows. Download the pre-trained models using the provided batch file. Use the command line to specify the input MP3 file and the desired number of stems (2, 4, or 5). Spleeter will create separate MP3 files for each isolated track.
AI-Powered Tools for Everyday Tasks
Microsoft Edge: Enhance Images in Your Browser
Microsoft Edge offers an AI-powered image enhancement feature that upscales images displayed in the browser. This feature leverages Microsoft’s servers for processing.
Installation and Usage: Install the developer version of Microsoft Edge. Enable the “Enhance images” option in the browser settings.
Vosk: Offline Speech Recognition
Vosk is an offline speech recognition engine based on the Kaldi toolkit. It can transcribe audio and video files, making it useful for creating subtitles or generating text from spoken content.
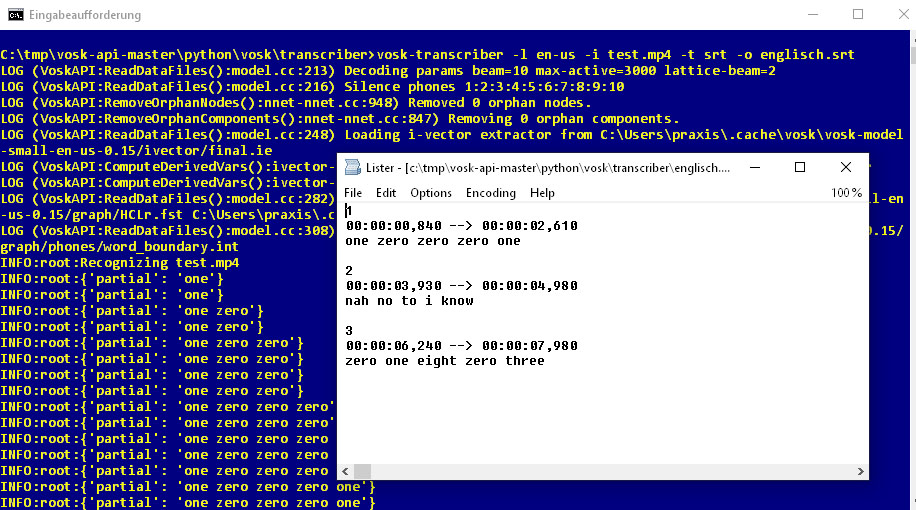 Vosk generates subtitles from audio. This example shows an SRT file created by Vosk after analyzing the audio track of a YouTube video.
Vosk generates subtitles from audio. This example shows an SRT file created by Vosk after analyzing the audio track of a YouTube video.
Installation and Usage: Install Python 3.11, Ffmpeg, and Vosk using pip. Download and place the necessary language models. Use the command-line tool to specify the input audio/video file, language, and output format (e.g., SRT).
Digikam: Face Recognition for Photo Management
Digikam, a photo management tool, utilizes AI for face recognition, helping you organize and tag photos based on detected individuals.
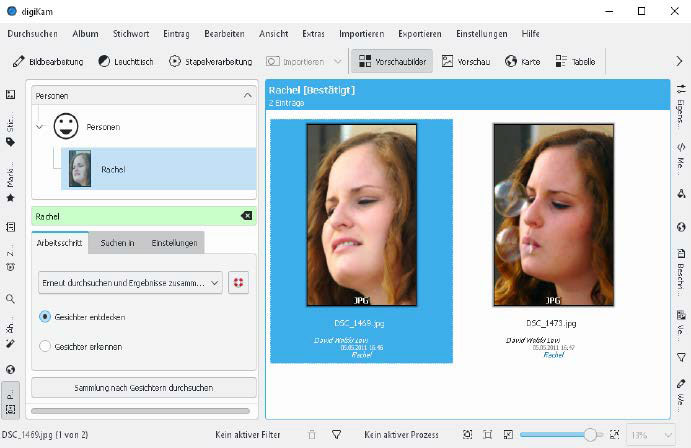 Digikam performs facial recognition. This image showcases Digikam's ability to recognize faces and create a database for tagging and searching individuals within a photo collection.
Digikam performs facial recognition. This image showcases Digikam's ability to recognize faces and create a database for tagging and searching individuals within a photo collection.
Installation and Usage: Install Digikam and download the face recognition model data. Manually tag faces in a few photos, and Digikam will learn to recognize those individuals in your photo collection.
Hugin: Create Panoramic Images
Hugin stitches together multiple overlapping images to create seamless panoramas. While not strictly AI-based, its advanced algorithms utilize pattern recognition for image alignment.
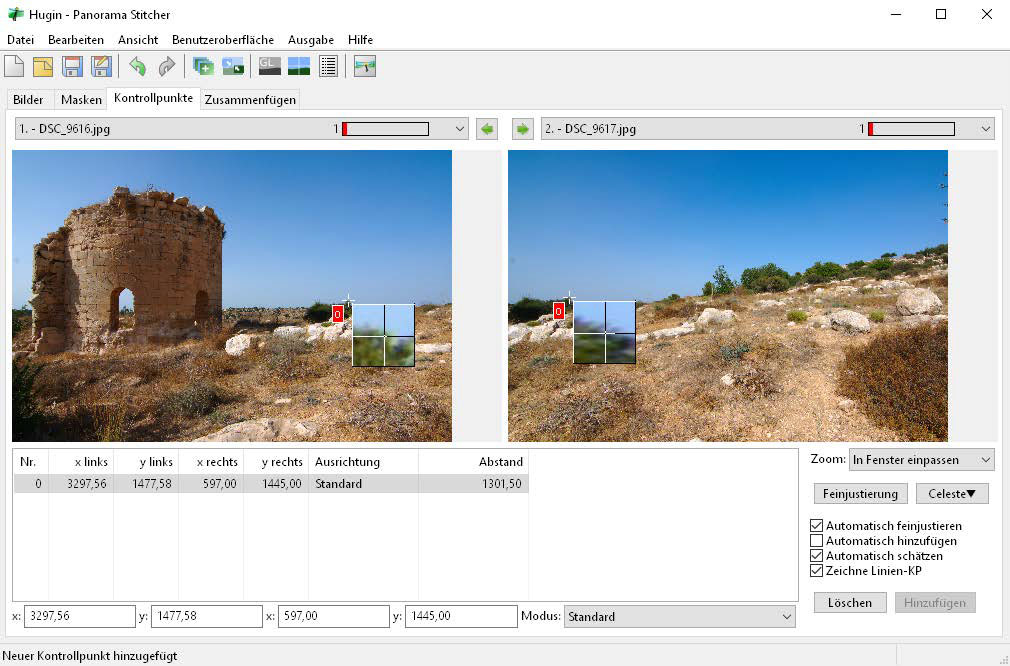 Hugin stitches images into panoramas. This image demonstrates Hugin's ability to combine multiple overlapping images into a single panoramic image, using control points for precise alignment.
Hugin stitches images into panoramas. This image demonstrates Hugin's ability to combine multiple overlapping images into a single panoramic image, using control points for precise alignment.
Installation and Usage: Download and extract the Hugin archive. Add images to the “Images” tab, specify focal length, and manually add control points for optimal alignment.
Subsync: Synchronize Subtitles with AI
Subsync utilizes speech recognition to synchronize subtitle files with video files, ensuring that the subtitles accurately match the dialogue.
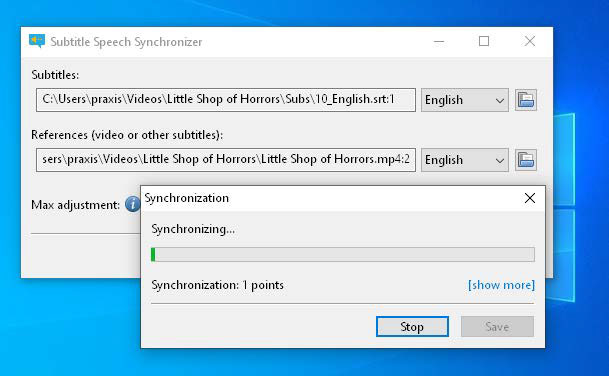 Subsync synchronizes subtitles. This image illustrates how Subsync uses speech recognition to analyze a video file and adjust the timestamps of an SRT subtitle file, ensuring accurate synchronization.
Subsync synchronizes subtitles. This image illustrates how Subsync uses speech recognition to analyze a video file and adjust the timestamps of an SRT subtitle file, ensuring accurate synchronization.
Installation and Usage: Download and install Subsync. Specify the subtitle and video files, along with their respective languages. Subsync will automatically download the necessary language models and adjust the subtitle timings.
These nine free AI tools empower you to experience the capabilities of artificial intelligence without relying on cloud services or proprietary software. From image enhancement and 3D modeling to video editing, audio processing, and even subtitle synchronization, these tools offer a diverse range of functionalities readily accessible on your local PC.