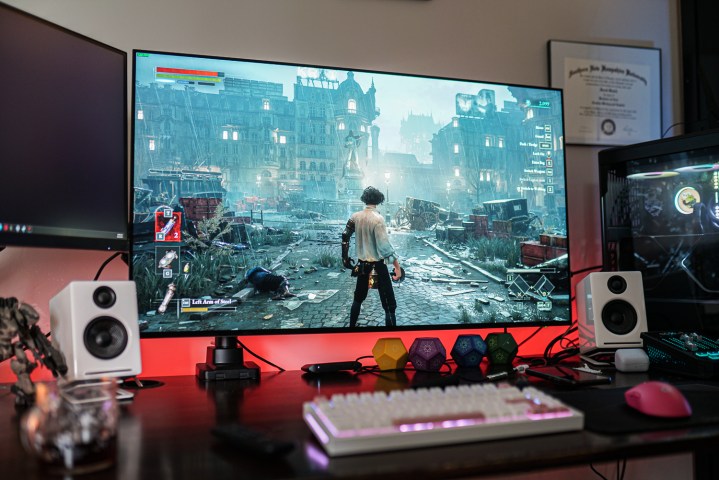
Alt text: A screenshot from the video game Lies of P, showcasing the game's graphics and visual effects on a KTC G42P5 monitor.
Alt text: A screenshot from the video game Lies of P, showcasing the game's graphics and visual effects on a KTC G42P5 monitor.
Anti-aliasing is a crucial graphics setting in PC gaming, impacting visual fidelity significantly. From its origins decades ago to the diverse options available today, understanding anti-aliasing is essential for optimizing your gaming experience. This article explores various anti-aliasing techniques, from TAA and FXAA to more advanced methods, providing a clear understanding of how they function and how to utilize them effectively. Almost every PC game offers anti-aliasing options, often with different types and quality modes that impact both performance and image quality. This guide breaks down these various forms to empower you to make informed decisions when configuring your graphics settings.
What is Aliasing and How Does Anti-Aliasing Work?
 Alt text: An example of aliasing in Photoshop, demonstrating the jagged edges that occur when curved lines are represented digitally.
Alt text: An example of aliasing in Photoshop, demonstrating the jagged edges that occur when curved lines are represented digitally.
Before delving into anti-aliasing, it’s important to understand aliasing itself. Aliasing arises from the inherent limitations of displaying curved lines on a grid of square pixels. Since each pixel displays a single color, curved lines appear jagged, resembling a staircase effect. Anti-aliasing techniques aim to mitigate these jagged edges, creating smoother, more visually appealing lines.
This “staircase effect” is prominent in games and image editing software. Observe the example from Destiny 2 below. The railing, rendered across multiple pixels, exhibits a jagged edge where pixels transition.
 Alt text: A screenshot from Destiny 2, highlighting the jagged edges (aliasing) on a railing within the game environment.
Alt text: A screenshot from Destiny 2, highlighting the jagged edges (aliasing) on a railing within the game environment.
Anti-aliasing aims to smooth these jagged edges. Various techniques achieve this, and you likely encounter anti-aliasing daily, even outside gaming. Web browsers, for instance, utilize anti-aliasing to render smooth text.
Exploring Different Anti-Aliasing Techniques
 Alt text: A comparison of two anti-aliasing techniques in Forza Horizon 5: FXAA on the left and MSAA on the right, showcasing their visual impact on the game's graphics.
Alt text: A comparison of two anti-aliasing techniques in Forza Horizon 5: FXAA on the left and MSAA on the right, showcasing their visual impact on the game's graphics.
While numerous anti-aliasing techniques exist, they fall into two primary categories: supersampling and post-processing. Supersampling renders the image at a higher resolution, then downsamples it to the native resolution, smoothing edges in the process. Post-processing techniques analyze the rendered image and apply algorithms to soften jagged edges. This article focuses on the most prevalent types found in modern games.
Supersample Anti-Aliasing (SSAA)
 Alt text: A comparison of SSAA in Metro 2033 Redux, showing the difference between enabled and disabled SSAA and its impact on image quality.
Alt text: A comparison of SSAA in Metro 2033 Redux, showing the difference between enabled and disabled SSAA and its impact on image quality.
SSAA renders the image at a higher resolution, then downsamples it, averaging color values to smooth edges. SSAA 4x, for example, renders each pixel as four, then combines them. While visually impressive, SSAA is computationally expensive and rarely found in modern games.
Multisample Anti-Aliasing (MSAA)
 Alt text: A comparison of MSAA in Forza Horizon 4, demonstrating its effect on edge smoothing and overall visual clarity.
Alt text: A comparison of MSAA in Forza Horizon 4, demonstrating its effect on edge smoothing and overall visual clarity.
MSAA optimizes SSAA by only supersampling areas with potential aliasing (edges). This reduces the performance impact while still improving image quality. However, MSAA remains more demanding than post-processing methods.
Fast Approximate Anti-Aliasing (FXAA)
 Alt text: A comparison of FXAA in Destiny 2, illustrating its effect on edge smoothing and its relatively lower performance impact.
Alt text: A comparison of FXAA in Destiny 2, illustrating its effect on edge smoothing and its relatively lower performance impact.
FXAA is a post-process technique, applying a filter to smooth edges after the image is rendered. This is computationally inexpensive but can result in slightly blurred edges.
Temporal Anti-Aliasing (TAA)
 Alt text: A comparison of TAA in Tiny Tina's Wonderlands, showcasing its ability to smooth edges while maintaining a relatively sharp image.
Alt text: A comparison of TAA in Tiny Tina's Wonderlands, showcasing its ability to smooth edges while maintaining a relatively sharp image.
TAA utilizes temporal information, blending current and previous frames to smooth edges. This leads to good image quality with moderate performance impact, but can introduce ghosting artifacts. TAA is a core component of modern upscaling techniques like DLSS and FSR.
Subpixel Morphological Anti-Aliasing (SMAA)
 Alt text: A comparison of SMAA in Destiny 2, demonstrating its edge smoothing capabilities.
Alt text: A comparison of SMAA in Destiny 2, demonstrating its edge smoothing capabilities.
SMAA is a post-processing technique similar to FXAA but uses more sophisticated edge detection and blending, offering a balance between quality and performance.
DLAA, FSR Native AA, and Modern Anti-Aliasing
 Alt text: A screenshot showcasing DLAA in Diablo 4, highlighting the improved image quality and reduced aliasing.
Alt text: A screenshot showcasing DLAA in Diablo 4, highlighting the improved image quality and reduced aliasing.
Modern upscaling technologies like DLSS and FSR often incorporate their own anti-aliasing, typically TAA, which is highly optimized and often combined with sharpening filters. This can simplify anti-aliasing settings, sometimes even removing separate controls. DLAA (Deep Learning Anti-Aliasing) and FSR Native AA leverage the anti-aliasing capabilities of DLSS and FSR without the upscaling component, providing improved image quality at native resolution. Intel’s XeSS also offers a similar native AA mode.
Enabling Anti-Aliasing in Games and Graphics Settings
Anti-aliasing settings are usually found within a game’s graphics menu, either as a general “Anti-Aliasing” option or with specific technique names (FXAA, MSAA, etc.). Some techniques like MSAA include quality multipliers (e.g., MSAA 2x, 4x).
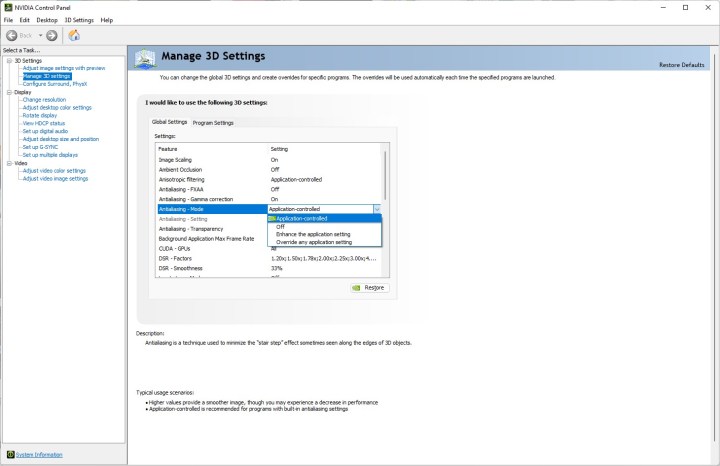 Alt text: A screenshot of the anti-aliasing settings within the Nvidia Control Panel.
Alt text: A screenshot of the anti-aliasing settings within the Nvidia Control Panel.
Graphics drivers also offer global anti-aliasing controls. Nvidia’s Control Panel and AMD’s Radeon Software allow you to force or enhance in-game settings. These controls provide options to override application settings, offering flexibility in fine-tuning anti-aliasing across different games.
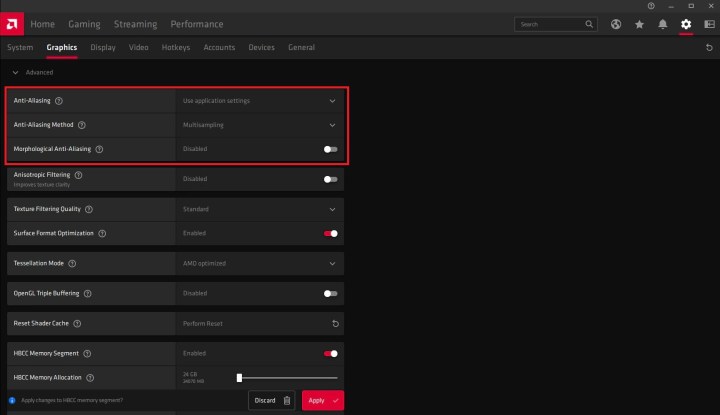 Alt text: A screenshot of the anti-aliasing settings within AMD Radeon Software.
Alt text: A screenshot of the anti-aliasing settings within AMD Radeon Software.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is aliasing detrimental to graphics?
Aliasing creates jagged edges, diminishing visual quality and potentially distracting players.
Does anti-aliasing enhance graphics?
Correctly applied anti-aliasing smooths jagged lines, improving overall visual fidelity.
Should anti-aliasing be enabled?
Generally, enabling anti-aliasing improves graphics. Customize settings within games or driver software to balance visual quality and performance based on your system’s capabilities.