Network security isn’t just for large corporations. Protecting your home network is crucial for safeguarding your privacy, devices, and data from external threats like hackers and malware, as well as preventing unauthorized access to your connected devices. This guide provides practical steps to bolster your home network security without adding complexity to your daily life.
Securing Your Router: The First Line of Defense
Your router acts as the central hub of your home network and the gateway to the internet. All data flowing between your devices and the internet passes through it, making router security paramount.
 Router Configuration
Router Configuration
Robust Passwords and Usernames
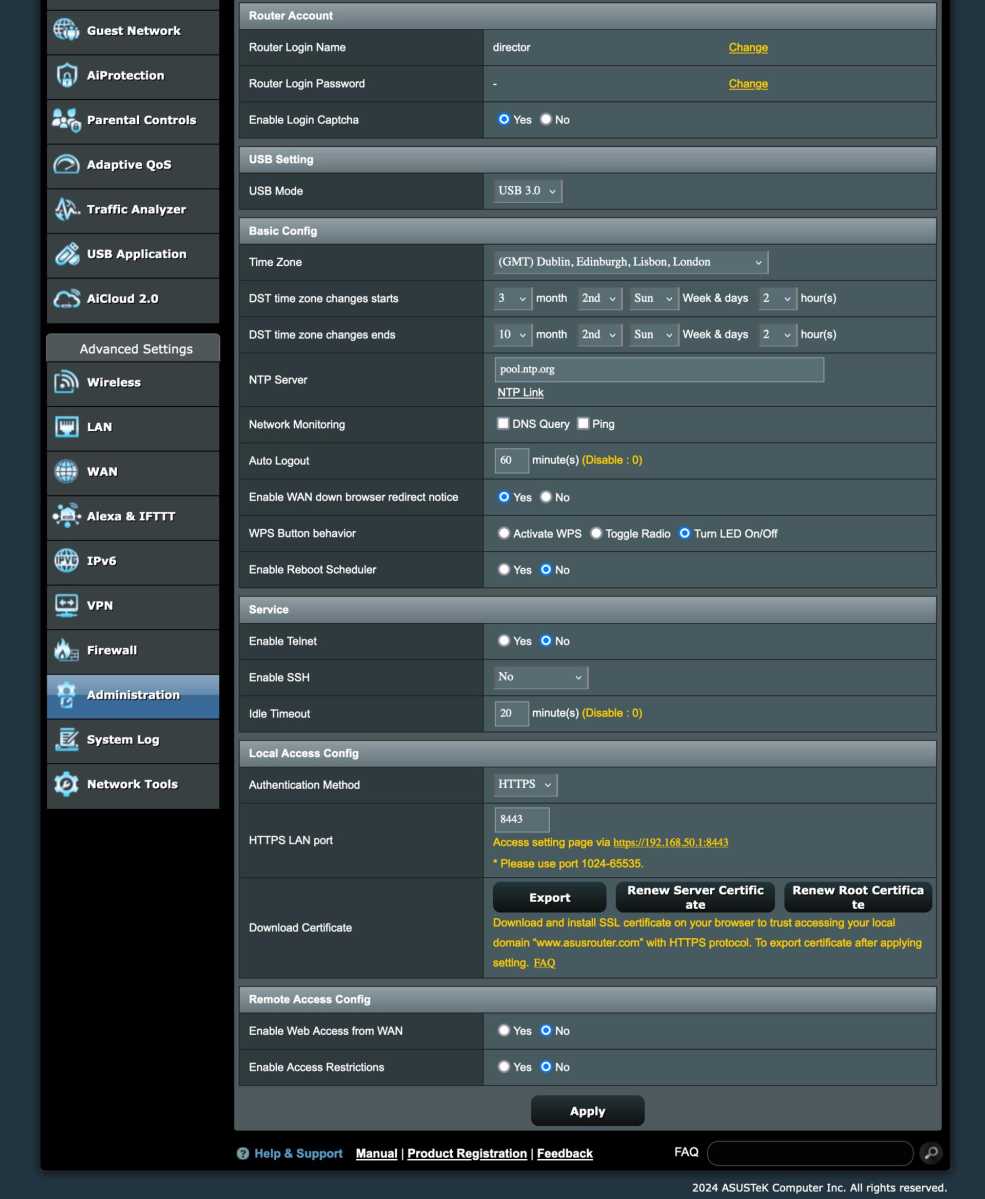
Start by setting a strong, unique password for your router’s admin interface. If possible, change the default username as well. This adds an extra layer of protection against automated login attempts exploiting router vulnerabilities.
Enable HTTPS for Admin Access
Ensure HTTPS (encrypted connection) is enabled in your router settings, usually found in the same area as the password settings. HTTPS prevents unauthorized users on your local network from intercepting your password and gaining control of your router.
Update Your Wi-Fi Credentials
Factory-default Wi-Fi names (SSIDs) and passwords are often not as random as they appear. Change them to unique names and passwords. A strong password using randomly chosen common words is easier to remember and type than a complex string of characters.
Choose WPA2/WPA3 Security
Select WPA3 or WPA2/WPA3 for Wi-Fi security. WPA1 is outdated and less secure. If some devices can’t connect with WPA3, switch to WPA2/WPA3 or WPA2 only. Enable “protected management frames” if available.
Activate the Firewall
Enable your router’s built-in firewall. This essential security feature helps block unauthorized access to your network.
Disable Unnecessary Features
Disable outdated and potentially insecure features like hidden SSID, UPnP, WPS, and MAC filtering. These features offer minimal security benefits and can complicate network management.
Disable Remote Login
Disable remote login to your router from the internet. This feature significantly increases your vulnerability to unauthorized access.
 Guest Network
Guest Network
Advanced Network Management
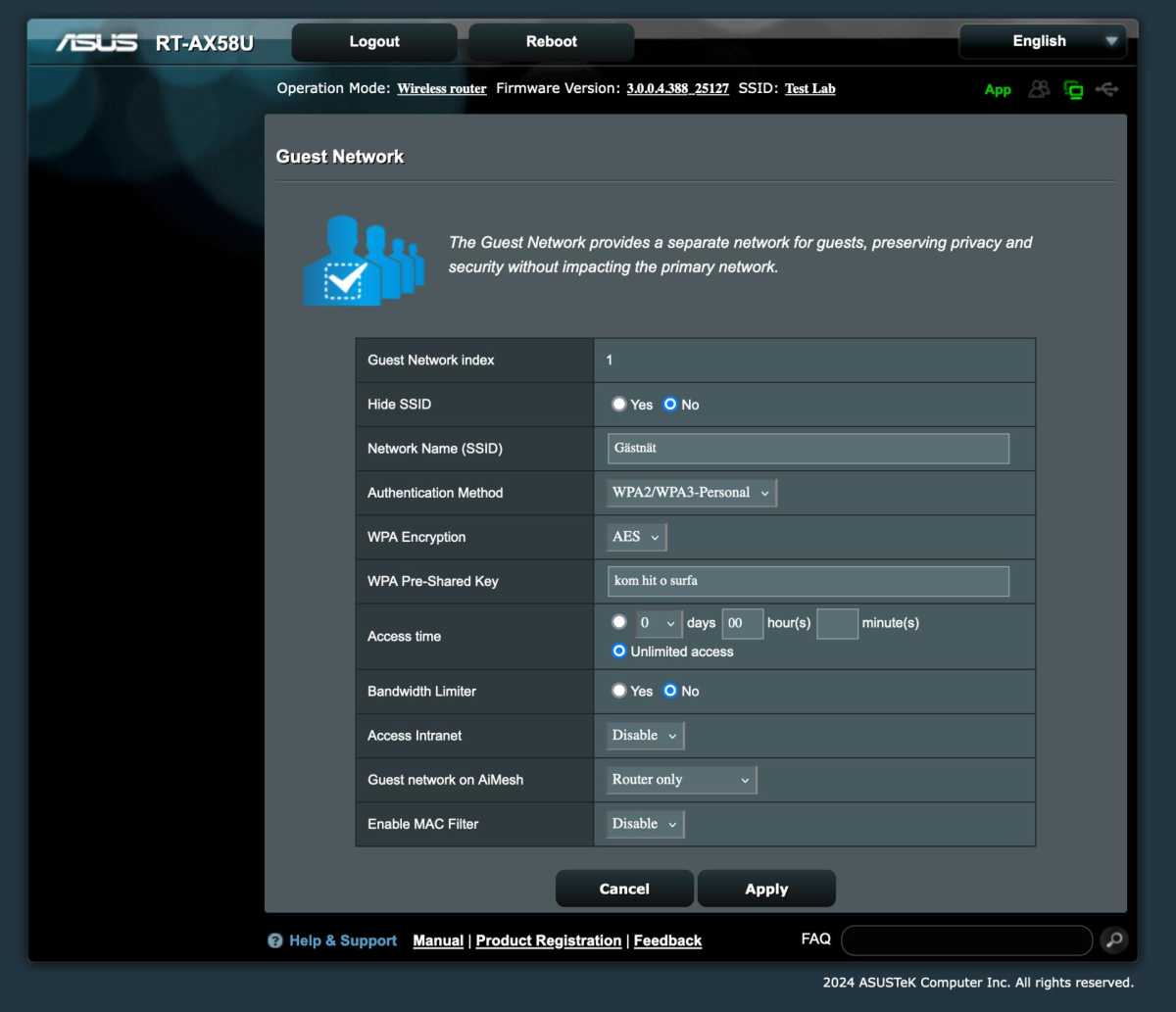
Leverage Guest Networks
Use guest networks to isolate devices connected to the internet from your primary network. This prevents hacked smart home devices from accessing your computers and other sensitive devices.
Segment Your Network
Consider network segmentation using VLANs on more advanced routers or with custom firmware like OpenWRT. This allows for granular control over network access, for example, isolating smart home devices from the internet while still allowing control through platforms like Home Assistant.
 Encrypted DNS
Encrypted DNS
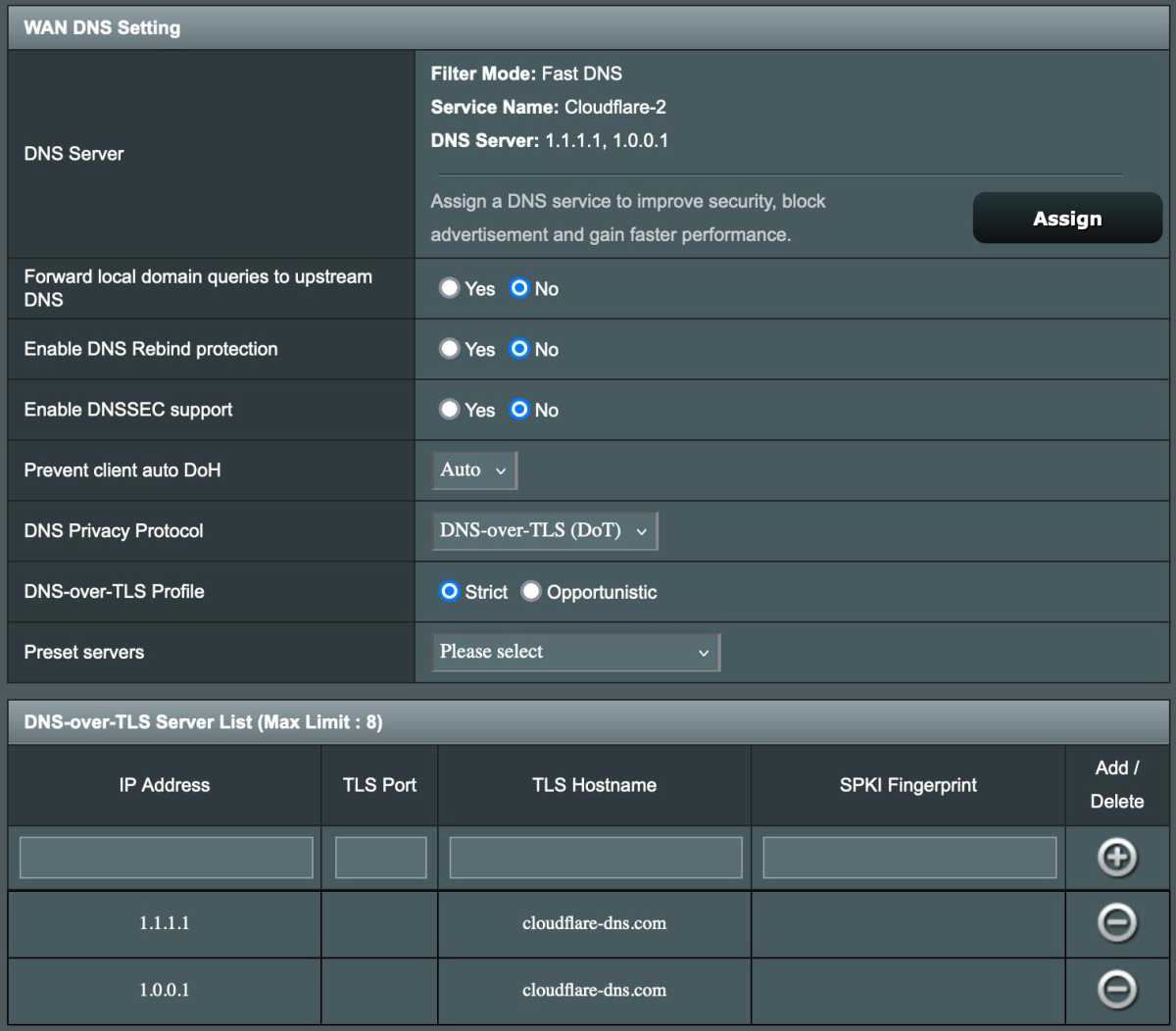
Implement Encrypted DNS
Use encrypted DNS (DNS-over-TLS or DNS-over-HTTPS) to prevent your internet service provider from tracking your browsing history. Cloudflare is a popular provider of encrypted DNS services.
Maintaining Network Security
Regular Router Updates
Enable automatic firmware updates for your router. If not available, manually check for updates at least monthly to patch security vulnerabilities and protect against botnet recruitment.
Keep Devices Updated
Regularly update all connected devices, including computers, smartphones, tablets, printers, TVs, and smart home products, to address security flaws.
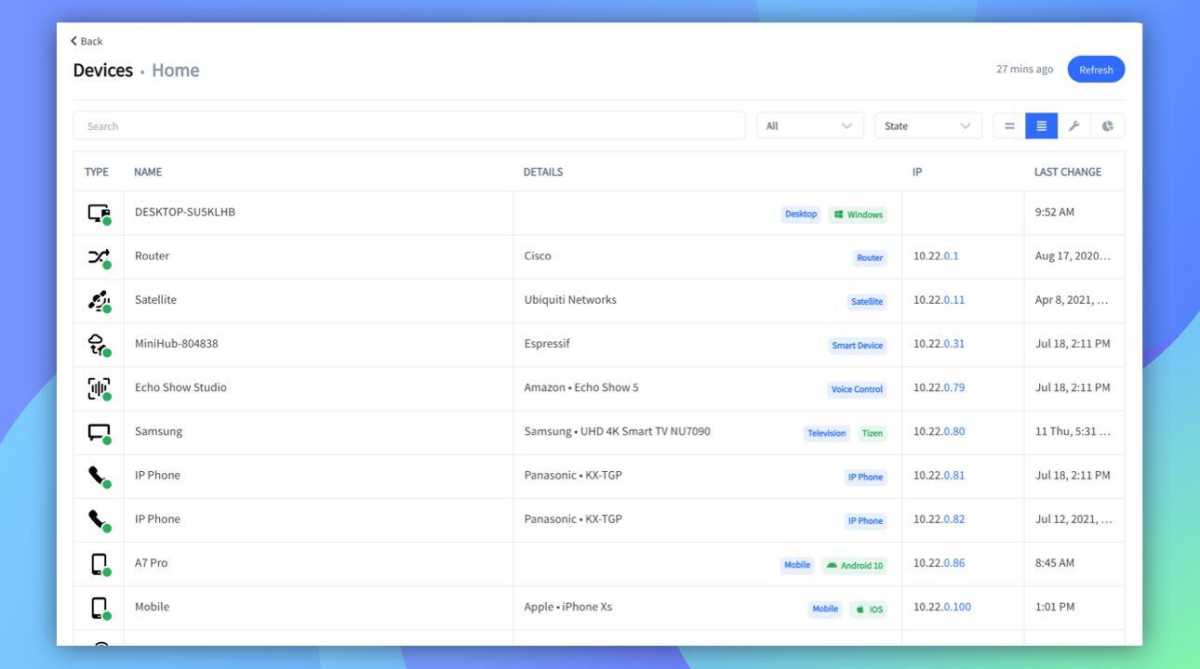 Network Monitoring
Network Monitoring
Monitor Connected Devices
Periodically scan your network to identify all connected devices. This helps you detect unauthorized access and reminds you of devices that might need updates. Tools like Fing can assist in identifying devices by manufacturer.
 Power Down
Power Down
Power Down When Away
Turn off your router when away from home for extended periods to prevent unauthorized access attempts. Exceptions include security cameras or alarm systems requiring remote access.
Explore Additional Security Features
Utilize additional security features offered by your router, such as AI protection and parental controls. These features can enhance network security and provide granular control over internet access for specific devices.
 Secure Accounts
Secure Accounts
Securing Connected Devices and Accounts
Protect Device Accounts
Secure accounts associated with connected devices with strong, unique passwords and two-factor authentication. This is crucial for preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data, especially from devices like connected cameras.
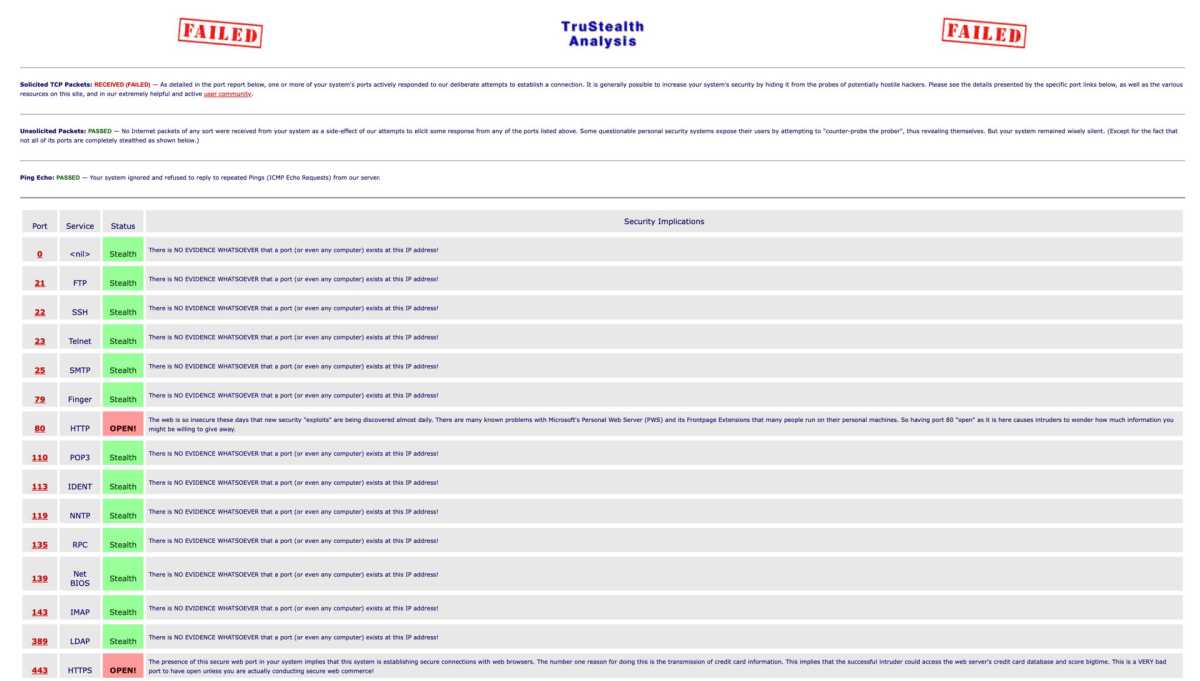 Port Security
Port Security
Avoid Unnecessary Port Forwarding
Modern applications rarely require port forwarding. Review your router’s port forwarding settings and remove any unnecessary entries. Tools like Shields Up or nmap can help you check for open ports.
By following these guidelines, you can significantly enhance your home network security and protect your digital life.