Hard drives, while capable of lasting for years under optimal conditions, are susceptible to various factors that can significantly impact their lifespan. These include manufacturing quality, handling, temperature, humidity, and power fluctuations. This guide provides essential steps to maximize the longevity of your hard drive.
Protecting Your Drive from Physical Damage
Physical shocks, such as drops, can severely damage a hard drive. The impact can cause the read/write head to collide with the rotating platters, resulting in scratches or damage. Internal components can also be dislodged, potentially harming the read head or drive motor. Therefore, handle external drives with care and avoid dropping your laptop. When purchasing drives online, opt for reputable shipping services known for their careful handling of electronics.
Static electricity also poses a threat to sensitive hard drive components. When handling internal drives, wear a grounded antistatic wrist strap to prevent static discharge. Avoid placing drives on static-generating materials like synthetic fabrics or clothing. Utilize an anti-static mat and handle the drive by its edges whenever possible. Store unused or external drives in anti-static bags for added protection.
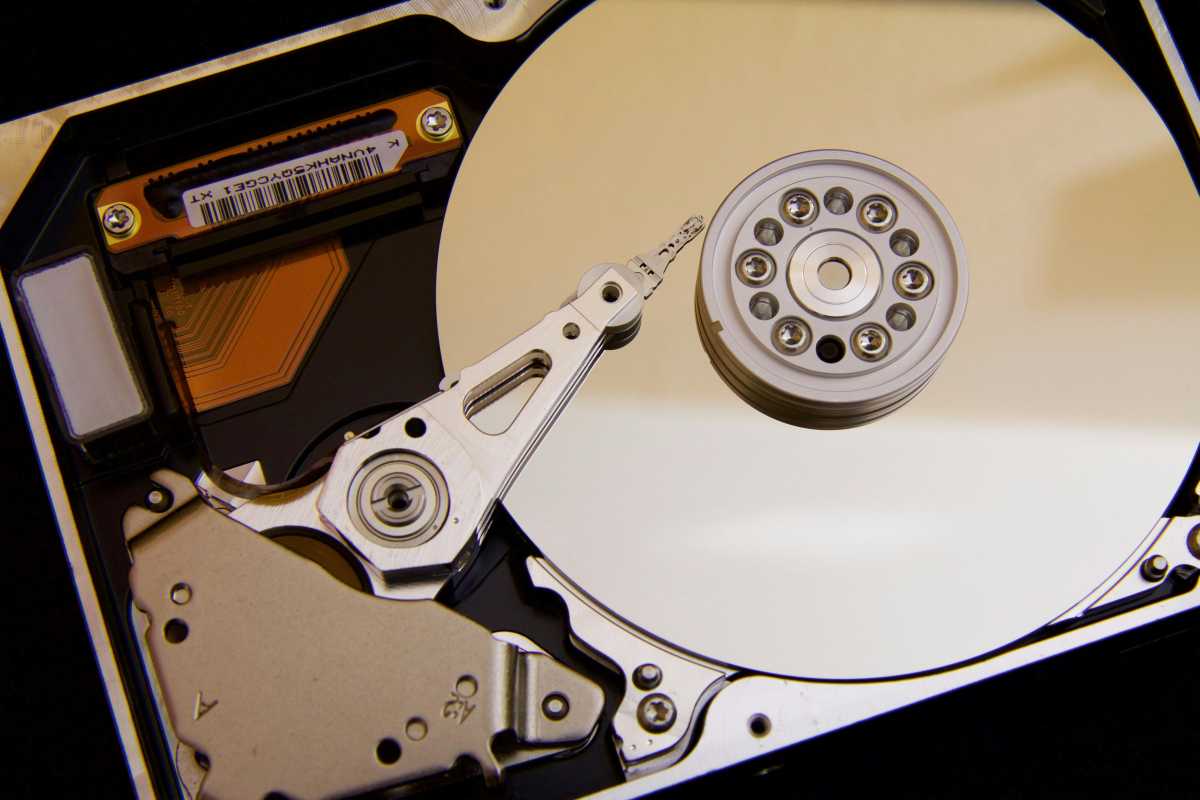 Hard Drive Read/Write Head (IDG)
Hard Drive Read/Write Head (IDG)
Safe Ejection Practices
Always safely eject external hard drives through the operating system before disconnecting them. This prevents data loss and ensures the read/write head is parked correctly, minimizing the risk of crashes. Abruptly removing a drive can cause voltage fluctuations and electrical spikes, potentially damaging the drive’s electronics. Safe ejection allows the operating system to disconnect the drive properly and stabilize moving parts like the spindle motor.
Power Supply Considerations
A high-quality power supply unit (PSU) is crucial for hard drive health. Reputable PSUs provide stable power and incorporate protective features like overvoltage, undervoltage, short-circuit, and overcurrent protection. These features safeguard against voltage fluctuations that can damage hard drive electronics. High-quality PSUs are constructed with durable materials and undergo rigorous testing to ensure reliability.
 Seagate BarraCuda Pro (Price When Reviewed: $299.99)
Seagate BarraCuda Pro (Price When Reviewed: $299.99)
Managing Temperature and Humidity
Overheating significantly reduces hard drive lifespan. The operating temperature should ideally remain below 55 degrees Celsius, even under heavy load. Ensure adequate computer ventilation by regularly cleaning dust and dirt from vents. Avoid overcrowding the computer case with components and monitor the hard drive temperature. If the drive runs too hot, relocate it to a cooler area or upgrade the cooling system.
High humidity and temperatures are also detrimental. Maintain humidity levels between 40% and 50%. In humid environments, consider using a dehumidifier or placing silica gel packets inside the computer case. Store external drives in sealed, weatherproof cases in dry locations.
Internal Hard Drive (IDG)
Surge Protection
Reliable surge protection safeguards sensitive computer components from power surges. Even with whole-house surge protection, using a local surge protector at the outlet is recommended. Choose a surge protector with a high Joule rating, fast response time, and features like indicator lights and resettable circuit breakers. Regularly check the indicator lights to ensure proper functionality.
Conclusion
By following these guidelines, you can significantly extend the life of your hard drive and protect your valuable data. Remember to prioritize careful handling, maintain a stable operating environment, and invest in quality components like power supplies and surge protectors. These preventative measures will contribute to the long-term health and performance of your hard drive.