NASA is turning to the James Webb Space Telescope to closely monitor asteroid 2024 YR4, a recently discovered space rock with a slight chance of impacting Earth in 2032. While the probability is currently low, NASA is taking proactive steps to refine impact predictions and gather crucial data.
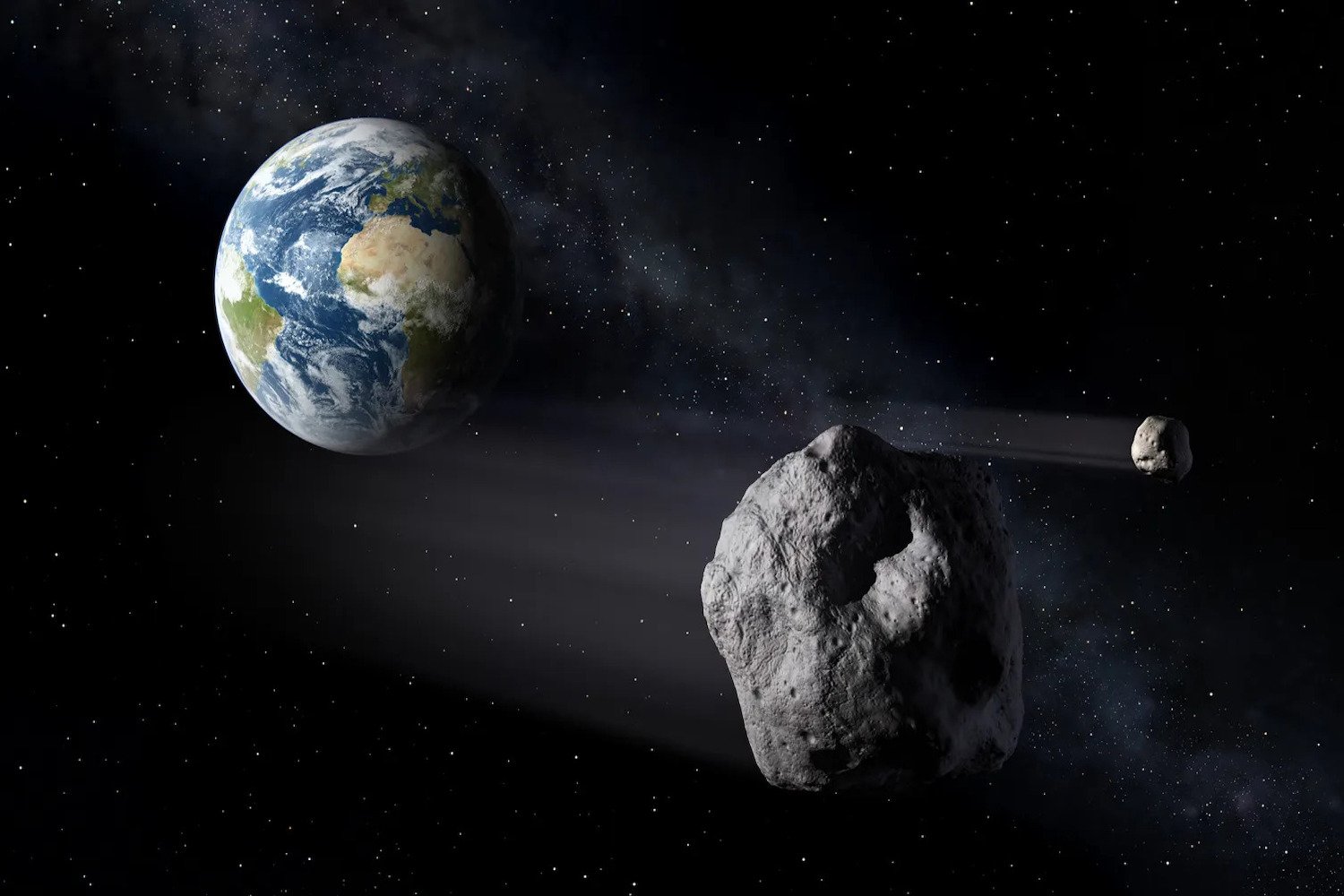
NASA’s Planetary Defense Coordination Office considers asteroid 2024 YR4 a potential threat, warranting close observation. Discovered on December 27, 2024, by the Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) in Chile, the asteroid initially had a 1.3% impact probability. Subsequent observations adjusted this figure, peaking at 2.3% before settling at 2.1% as of February 2025. These fluctuating probabilities underscore the need for more precise data. Notably, among currently tracked large asteroids, 2024 YR4 stands out with the highest impact probability exceeding 1%, according to NASA.
The asteroid’s next close approach to Earth isn’t until December 2028. Ground-based telescopes within the International Asteroid Warning Network are tracking 2024 YR4, but its increasing faintness will limit observations beyond April. This is where the Webb telescope comes in, offering a unique vantage point from space to continue observations in March and gather vital information.
The Webb telescope’s observations are crucial for refining estimates of the asteroid’s size and other characteristics. Current projections, based on reflected light, place the asteroid’s width between 130 and 300 feet (40 and 90 meters). While not large enough to cause global devastation, an impact would release substantial energy, estimated at around 8 megatons—over 500 times the energy of the Hiroshima atomic bomb and comparable to the 1908 Tunguska event.
NASA classifies asteroids as potentially hazardous if they are between 100 and 165 feet (30 and 50 meters) in diameter and their orbits come within 5 million miles (8 million kilometers) of Earth’s orbit. 2024 YR4 sits atop NASA’s Sentry risk list, a catalog of near-Earth asteroids with a non-zero probability of impacting Earth. It’s currently the only asteroid ranked a 3 on the Torino Impact Hazard Scale, a classification meaning “Meriting Attention by Astronomers.”
Historically, many objects have appeared on the risk list, only to be removed as new data emerges. NASA anticipates that further observations of 2024 YR4 could lead to its reclassification to a lower risk level. The agency remains vigilant in monitoring the asteroid’s trajectory and refining impact predictions.