QR codes are everywhere, from sharing contact information to making payments. However, this convenience has a dark side: QR code scams. These scams, ranging from petty theft to stealing sensitive financial data, are a growing problem. Even banking giants are now on high alert, urging users to change passwords immediately if entered after scanning a suspicious QR code. Government agencies like the US Federal Trade Commission and the Swiss national security agency have issued warnings about “quishing,” or QR phishing, where malicious QR codes are used to steal passwords and other sensitive information.
 Sample of an SDMQR code appearing on an iPhone screen.
Sample of an SDMQR code appearing on an iPhone screen.
Self-Authenticating QR Codes: A Promising Solution
A potential solution to this growing problem is the self-authenticating dual-modulated QR (SDMQR) code, developed by researchers at the University of Rochester. This technology flags potential scams before users are even directed to a fraudulent website. Here are some key advantages of SDMQR codes:
- Self-Authentication: Each code contains the verified digital signature of the entity behind it, verified upon every scan.
- Versatile Use: Beyond website navigation, SDMQR codes can be used for payments and secure data encoding.
- Offline Verification: No internet connection is required to verify the code’s legitimacy.
- Seamless Integration: No special app or software update is needed for existing QR code scanners.
- No Latency: The verification process adds no noticeable delay.
- Customizable Design: SDMQR codes can be customized to fit branding requirements without compromising security.
- Universal Compatibility: Works with any standard smartphone camera.
- Color Integration: Supports color customization for brand recognition.
- Backward Compatibility: Existing QR code readers can scan SDMQR codes, with a built-in warning system for potentially fraudulent traditional QR codes.
For businesses, implementing SDMQR codes is straightforward, requiring only the registration of their official website URL and embedding their signature in the code. Visually, SDMQR codes differ from traditional QR codes by using ellipses instead of square pixels.
How SDMQR Codes Work
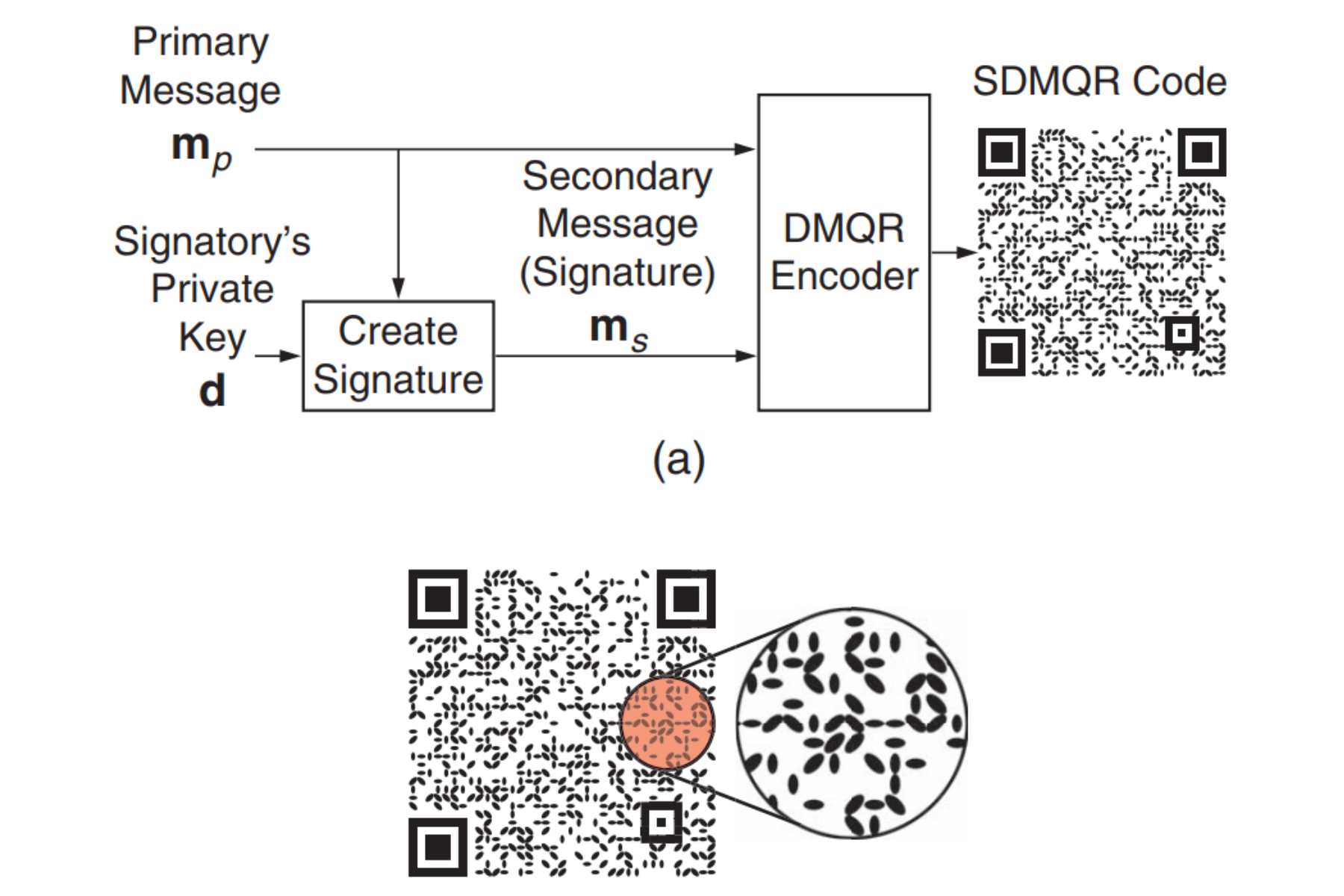 The process of creating an SDMQR code.
The process of creating an SDMQR code.
SDMQR codes offer proactive protection against quishing, as detailed in a research paper published in the IEEE Security & Privacy Journal. The system uses two key components: a primary message (e.g., a website URL) and a corresponding cryptographic signature. This signature, generated using the business’s private key, is embedded within the code.
The elliptical patterns in the code hide the primary message, while the orientation data carries the secondary message (the cryptographic signature). Upon scanning, the decoder separates these messages. The business’s public key then verifies if the cryptographic signature matches the primary message content.
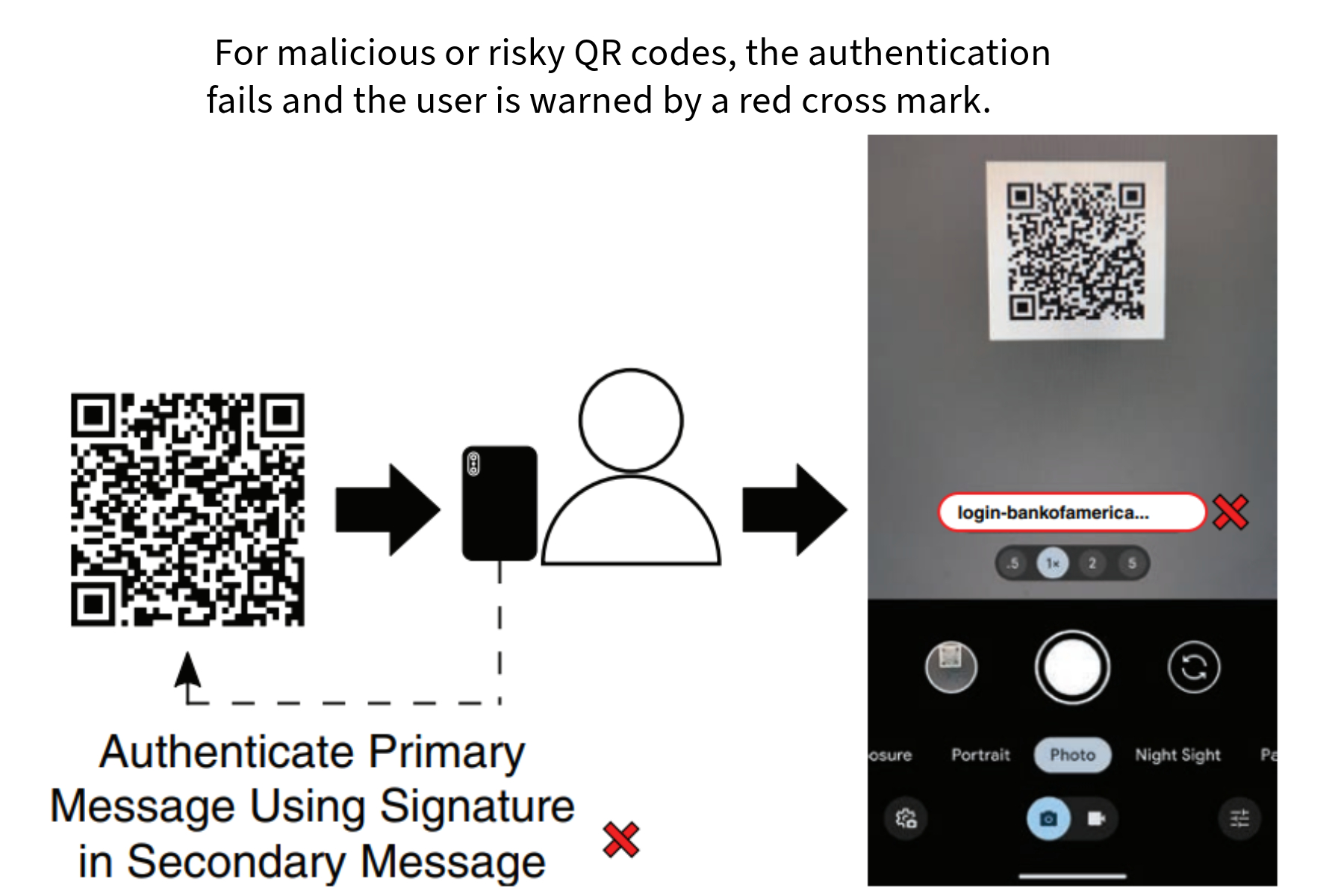 Authenticating an SDMQR code.
Authenticating an SDMQR code.
The main challenge lies in establishing a centralized registration system for businesses to create unique SDMQR codes and their associated public keys. This is where tech giants like Google and Apple can play a crucial role. Their participation as central signatories would simplify the verification process, requiring only their two public keys for authentication.
The Importance of SDMQR Adoption
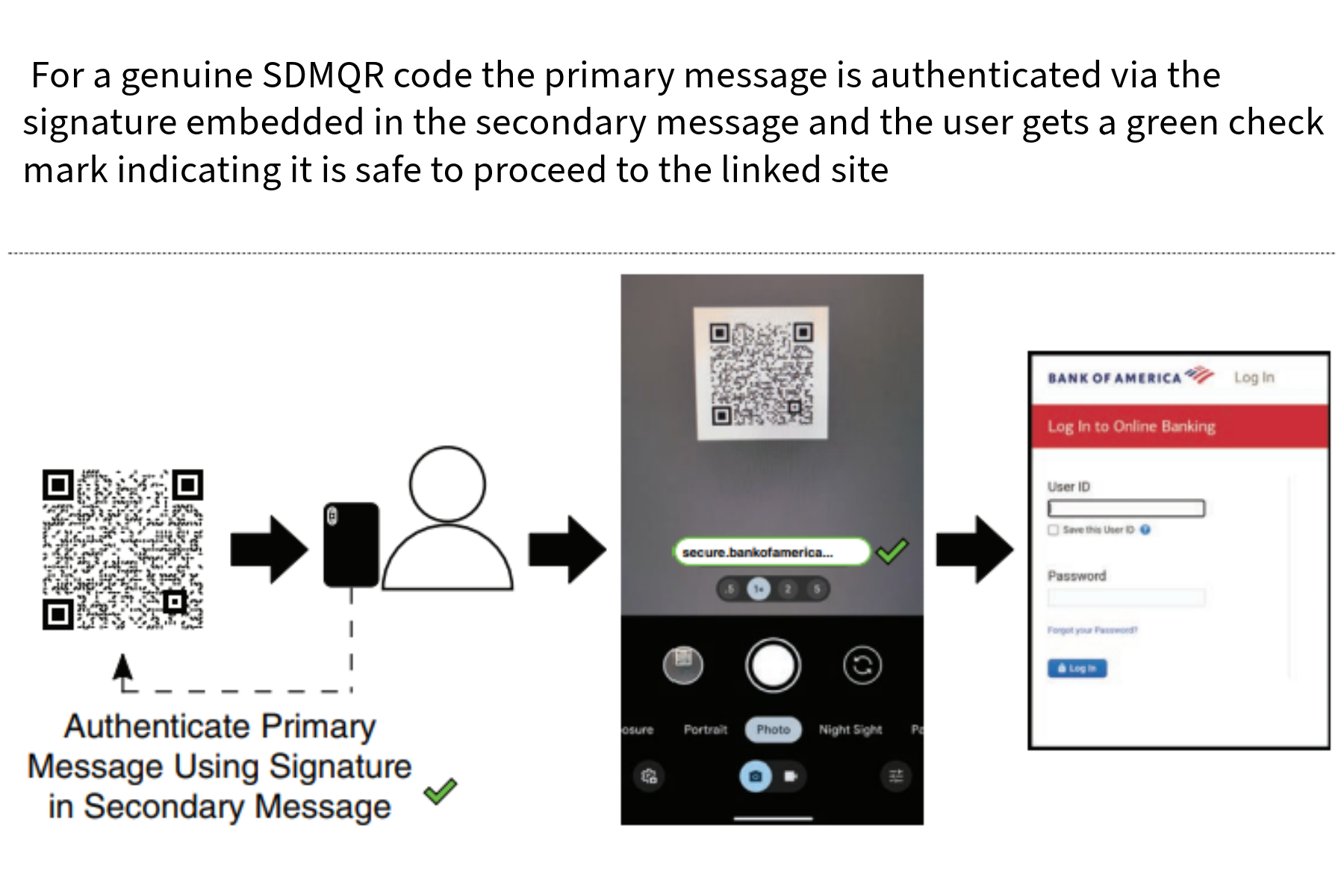 Verifying an SDMQR code.
Verifying an SDMQR code.
While other solutions to QR code scams have been proposed, SDMQR offers significant advantages. It provides transparent self-authentication without requiring software updates, simplifying adoption. The centralized signatory system further streamlines the process. Importantly, verification works offline, enhancing user convenience.
 A beautified SDMQR code on a phone.
A beautified SDMQR code on a phone.
SDMQR also offers potential benefits beyond website security. Its dual-modulating technology can be applied to barcodes, securing applications like airline boarding passes and package tracking. The technology could significantly enhance security in banking, parking payment systems, Wi-Fi access, and various other public applications of QR codes.
With built-in QR code scanning frameworks already in place within Android and iOS, the onus is on Google and Apple to implement support for the SDMQR framework. This adoption would significantly improve security for smartphone users worldwide.