Atmospheric carbon dioxide, a major contributor to climate change, can now be converted into a valuable fuel source thanks to a groundbreaking solar-powered reactor developed by University of Cambridge researchers. This innovative technology mimics photosynthesis and offers a potentially scalable solution for producing sustainable fuels, powering off-grid locations, and even contributing to pharmaceutical manufacturing.
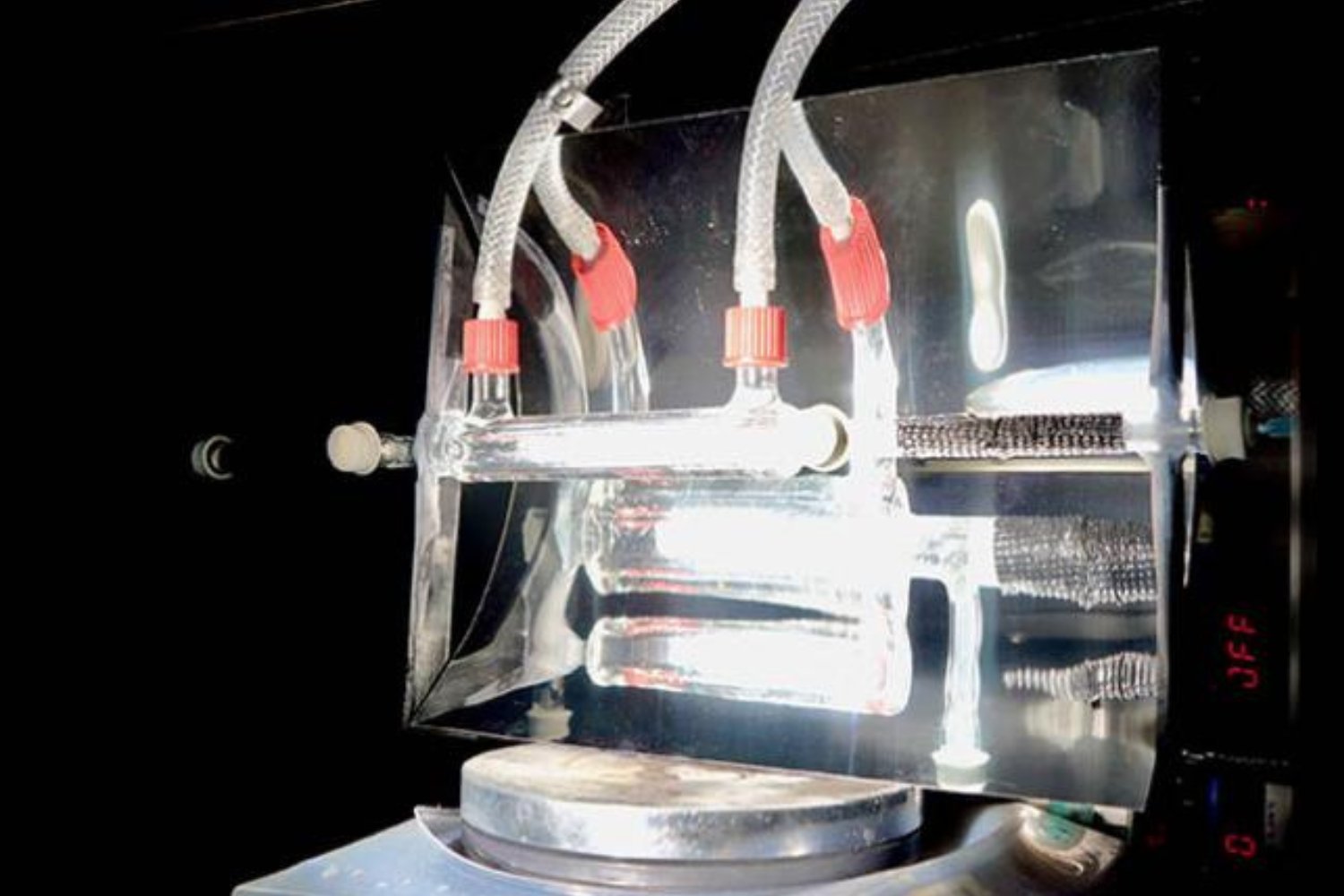
This new development in carbon capture technology addresses a critical challenge: conventional methods often rely on fossil fuels, perpetuating the very problem they aim to solve. The Cambridge team’s research, published in Nature Energy, details a novel approach that bypasses this limitation. Their reactor is entirely solar-powered, eliminating the need for external power sources and offering a truly sustainable solution.
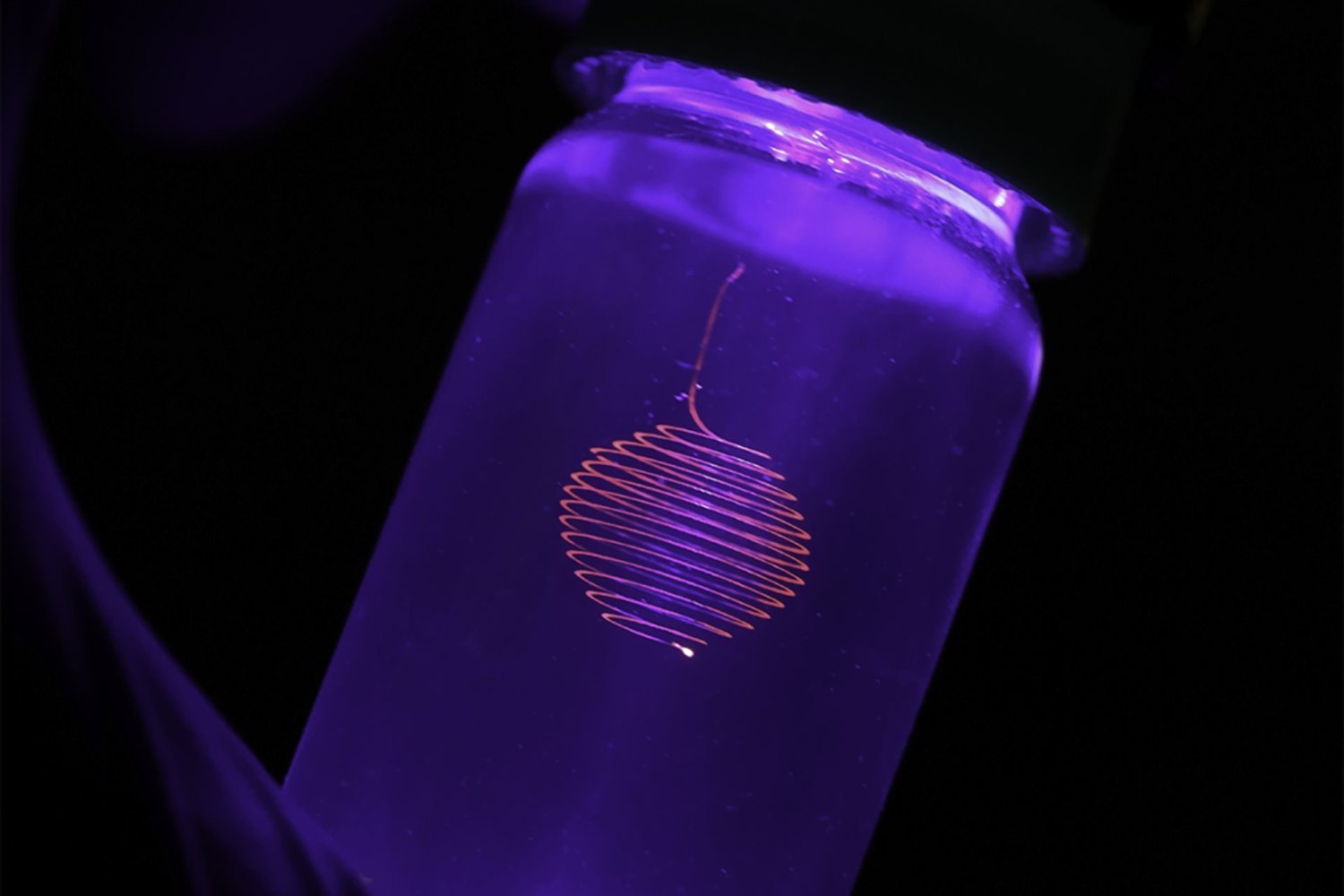
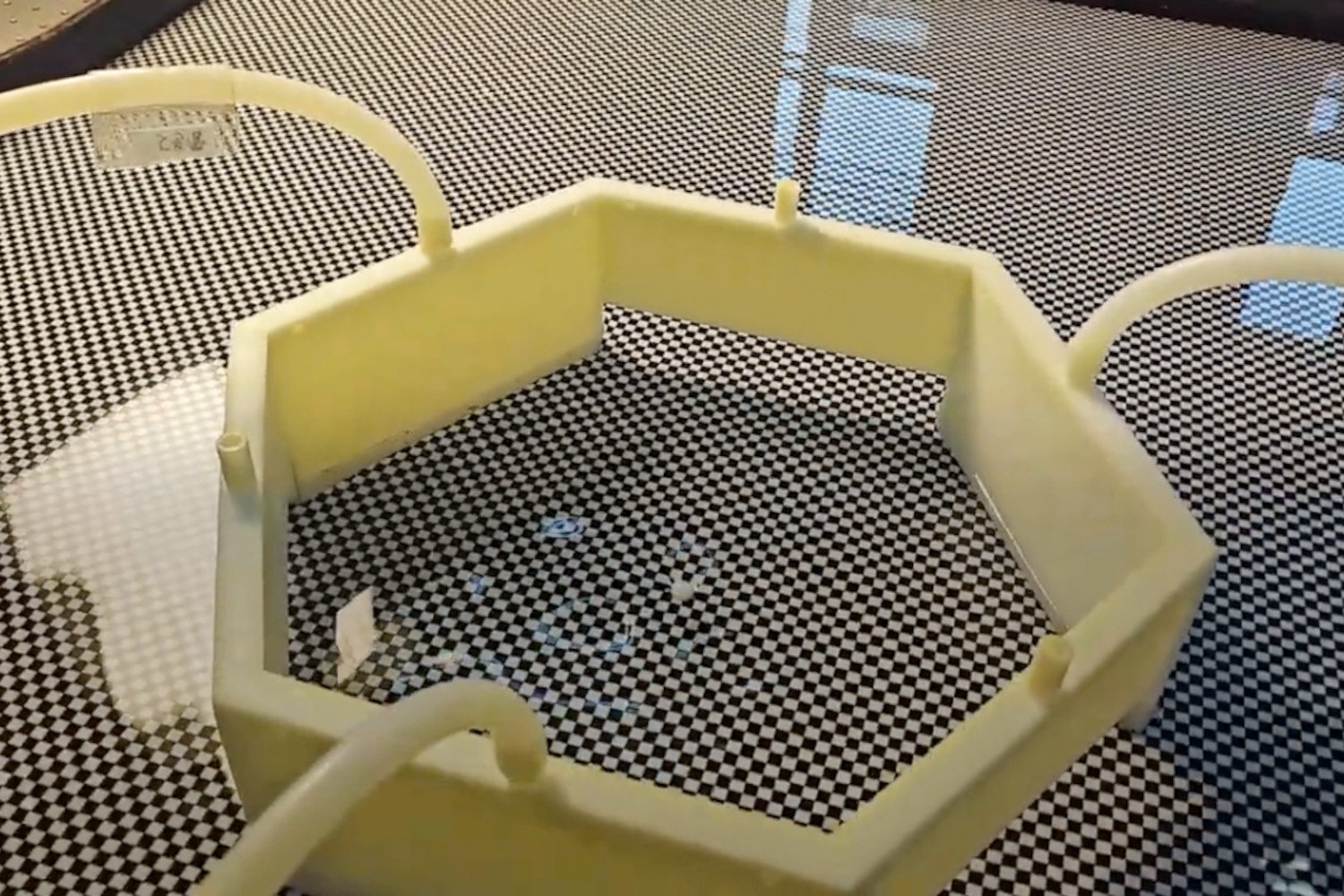
The reactor operates in two phases. During the night, it absorbs CO2 from the air, much like a sponge absorbs water. When sunlight hits the reactor, a mirror concentrates the light onto a semiconductor powder and the collected CO2. The semiconductor absorbs ultraviolet radiation, while the CO2 absorbs infrared radiation. This process triggers a chemical reaction, transforming the CO2 into syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. Syngas is a key component in the production of various fuels and chemicals.
The research team is currently exploring methods to convert this solar-generated syngas into liquid fuels suitable for powering vehicles like cars and airplanes. This advancement could revolutionize the transportation sector by providing a clean, sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Beyond transportation, the potential applications of this technology are vast. Individual solar reactors could provide power for remote areas, offering a sustainable energy solution for off-grid communities. Moreover, syngas plays a crucial role in the chemical industry. Utilizing solar syngas could significantly reduce the carbon footprint of chemical production.
This innovation represents a significant step towards a circular economy. Instead of relying on fossil fuels, we can harness atmospheric CO2 and transform it into valuable resources. This sustainable approach addresses both the challenge of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and the need for clean energy alternatives. The widespread adoption of this technology could pave the way for a more sustainable future, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
The researchers envision a future where carbon dioxide is viewed not as waste, but as a valuable resource. This shift in perspective, coupled with continued advancements in solar technology, holds immense promise for a cleaner, more sustainable world.