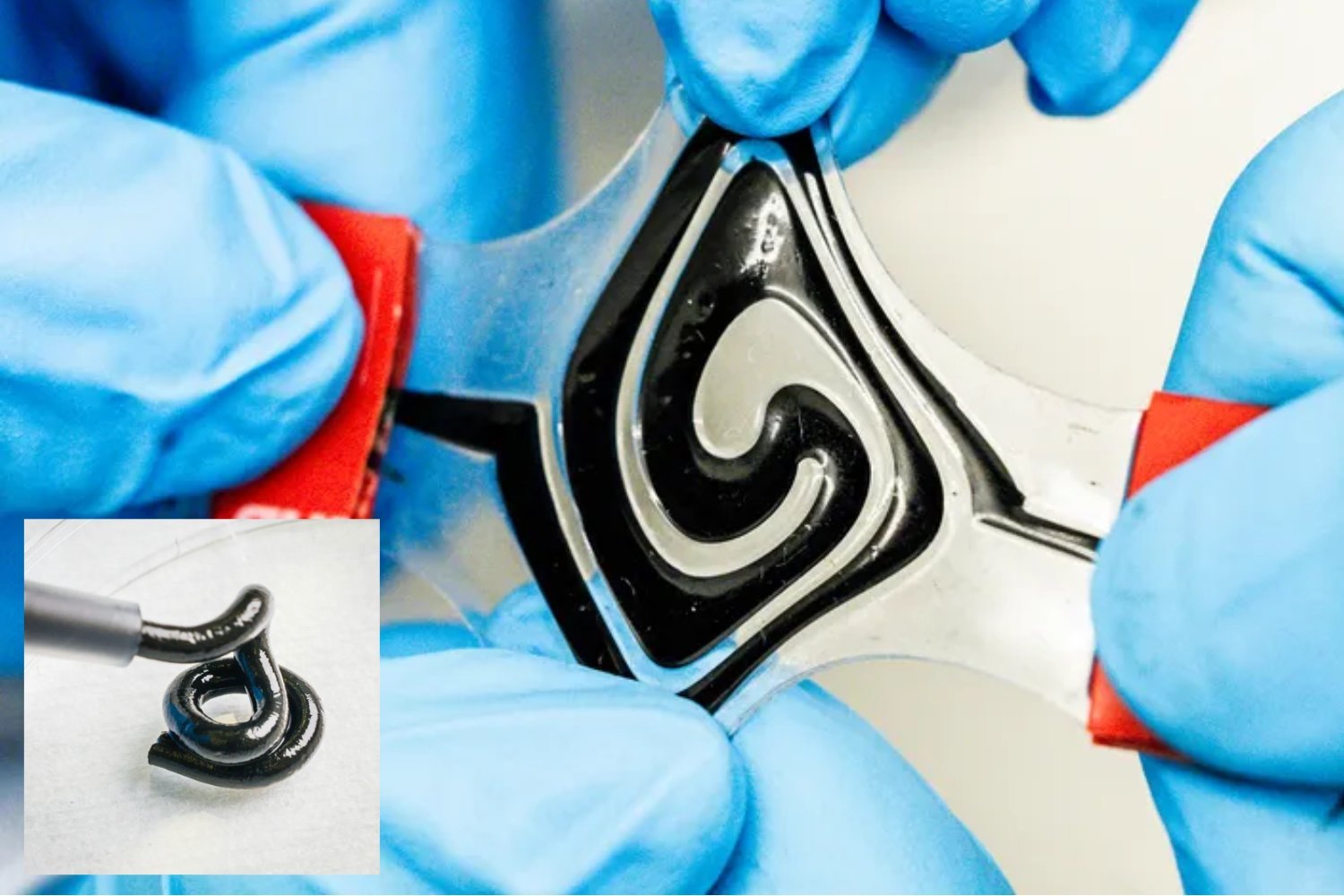
From smartphones and smartwatches to laptops and electric vehicles, batteries power our modern world. These power sources are typically rigid and bulky, often dictating the design and functionality of our devices. But imagine a future where batteries are malleable, flexible, and even printable. Researchers in Sweden are turning this vision into reality with the development of a groundbreaking fluid battery.
A recent study published in Science details the creation of this innovative battery, which utilizes fluid electrodes – the key conductive components within any battery. This novel soft structure has the potential to revolutionize the design of future battery-powered technology, offering unprecedented flexibility and adaptability.
“Batteries are often the largest component in electronics, and their rigid form factor imposes design limitations,” explains Aiman Rahmanudin, co-author of the study and research leader at Linköping University’s Soft Electronics Group. “With a soft, conformable battery, these limitations disappear. Integration becomes seamless, adapting to the user and device.” The material, he adds, has a toothpaste-like consistency and could be 3D printed into virtually any shape.
 Toothpaste Consistency
Toothpaste Consistency
Previous attempts to create flexible batteries often relied on complex mechanical designs or rare, environmentally harmful materials. This new approach bypasses these challenges by transforming the electrodes themselves into a liquid form.
How Fluid Electrodes Work
To grasp the significance of this innovation, it’s crucial to understand the basic principles of battery operation. An electrochemical battery consists of two electrodes: an anode and a cathode. A chemical reaction within the battery causes electrons to flow from the anode to the cathode, creating an electrical current that powers our devices. Traditional batteries with higher capacity require thicker, more rigid electrodes, limiting their flexibility.
“Our research demonstrates that capacity doesn’t have to be tied to rigidity,” states Rahmanudin. Previous attempts at fluid electrodes often employed liquid metals that were prone to solidification, hindering their effectiveness. The Swedish team overcame this hurdle by utilizing conjugated polymers – plastics capable of conducting electricity – and lignin, a readily available byproduct of paper production. This innovative combination allows the battery to be recharged over 500 times, even when stretched to double its original length.
Sustainability and Future Potential
“The use of conjugated polymers and lignin makes this a sustainable alternative,” says Mohsen Mohammadi, lead author of the study and postdoctoral fellow at Linköping University. “We’re repurposing a waste product into a high-value commodity.”
While the current prototype generates 0.9 volts – lower than standard AA batteries (1.2-1.5 volts) or smartphones (3.7-4.2 volts) – the team is optimistic about future improvements. “We’ve proven the concept,” Rahmanudin explains. “Our next focus is exploring different chemical compounds to increase the voltage.”
A New Era of Battery Technology
This groundbreaking research has the potential to reshape the landscape of battery-powered devices. Imagine clothing integrated with flexible batteries, powering wearable sensors or displays. Medical implants could be powered by biocompatible, conformable batteries. The possibilities are vast and exciting, paving the way for a future where energy storage is seamlessly integrated into our lives. The development of fluid batteries represents a significant step towards a more flexible, adaptable, and sustainable energy future.