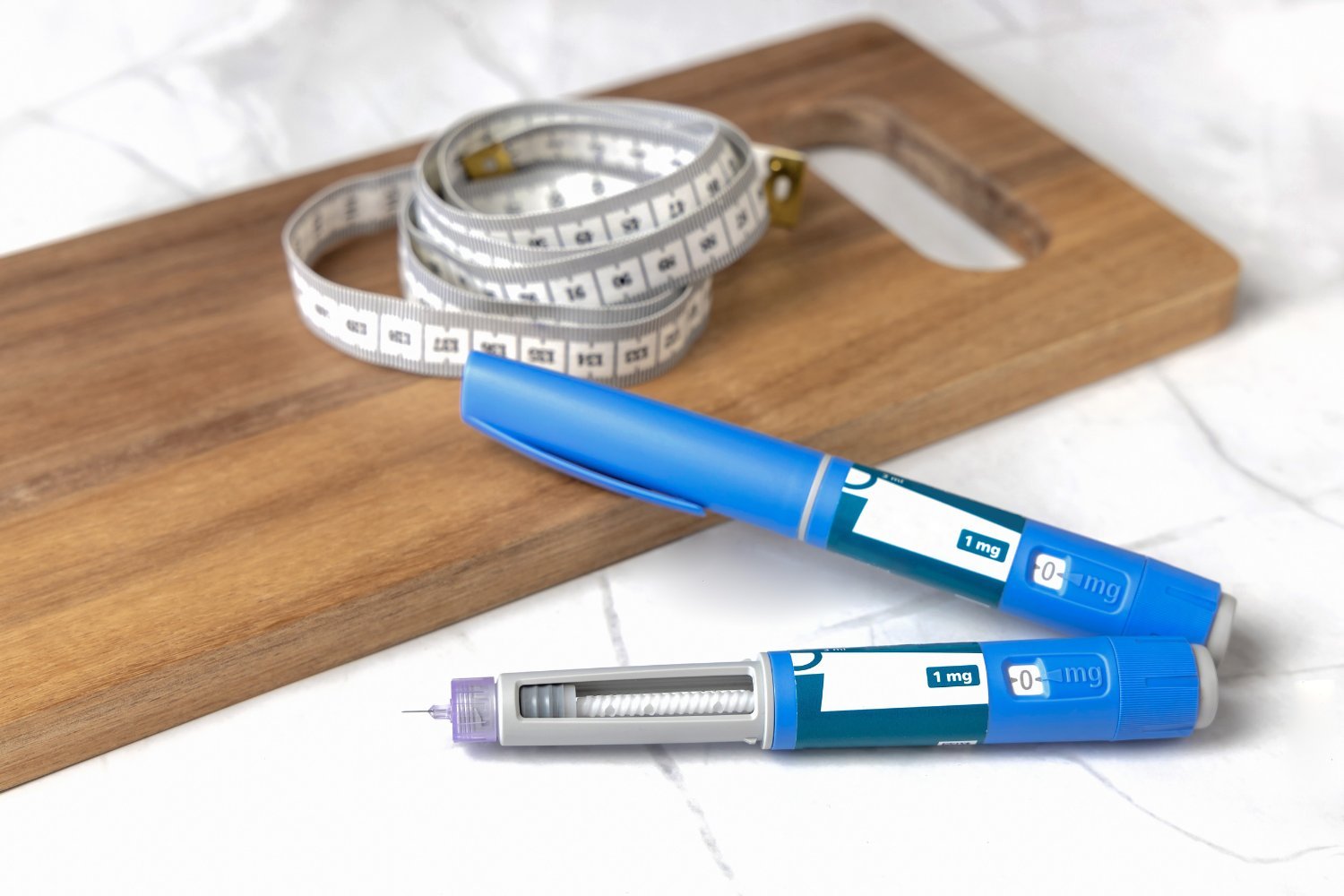
GLP-1 medications, like Ozempic and Wegovy, are revolutionizing weight management. A recent study sheds light on how these drugs impact dietary choices, revealing which foods people tend to avoid or reduce after starting treatment. This research offers valuable insights for individuals considering GLP-1 therapy and for the food industry adapting to evolving consumer preferences.
The study, conducted by scientists at the Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station, surveyed approximately 2,000 individuals across four distinct groups: current GLP-1 users for weight loss, past users, prospective users, and individuals with no plans to use these medications. Participants were asked about their daily caloric intake over the past week and their desire for specific food groups. Current and former GLP-1 users also reported on any changes in their food consumption while on the medication.
The results showed a significant reduction in overall caloric intake among GLP-1 users, estimated between 720 and 990 fewer calories daily compared to pre-treatment. Specifically, consumption of processed foods, sugary drinks, refined grains, and beef decreased. Conversely, participants reported increased intake of fruits, leafy greens, and water while using GLP-1 drugs. These findings, published in the journal Food Quality and Preference, suggest that GLP-1 medications support weight loss by reducing calorie intake and influencing food choices toward healthier options.
Interestingly, despite consuming less of certain foods, participants on GLP-1 therapy still reported a desire for them. This suggests that these medications may alter taste sensitivity or the pleasure response to food, although further research is needed to understand the underlying mechanisms.
The study highlights the potential impact of GLP-1 drugs on the food landscape. Some companies are already anticipating these shifts by developing products with less sugar and higher protein content, catering to the changing preferences of GLP-1 users.
This research provides valuable information for individuals considering GLP-1 therapy, offering insights into potential dietary changes. It also underscores the importance of continued research to fully understand the complex interplay between GLP-1 drugs, metabolism, and eating behavior.
This new understanding of how GLP-1 medications affect food preferences will likely shape future dietary recommendations and product development in the food industry. The ongoing research will continue to refine our knowledge and contribute to more effective weight management strategies.