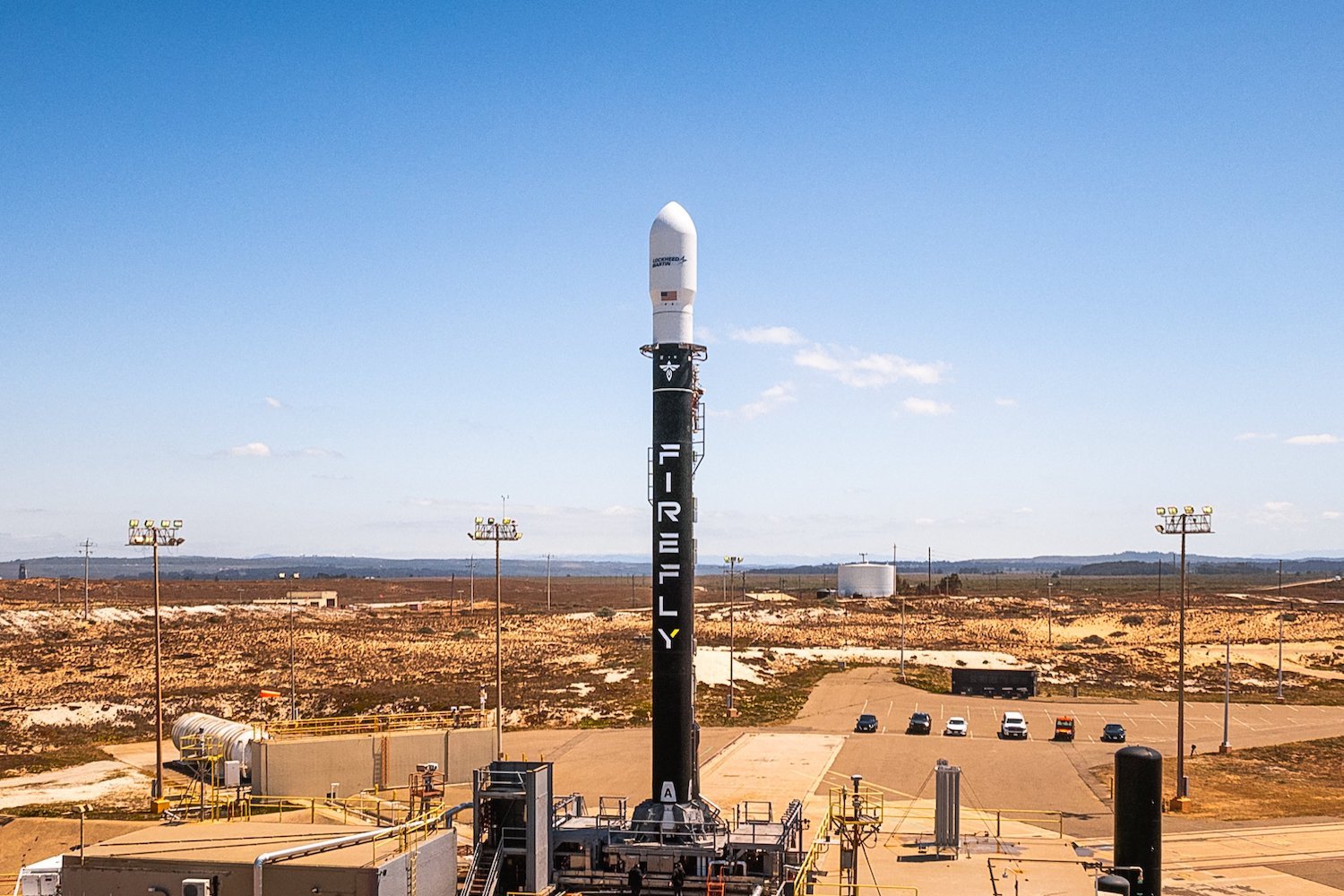
Firefly Aerospace’s Alpha rocket experienced a critical failure during its most recent launch attempt on April 29, 2024, scattering debris and ultimately falling back to Earth. The mission, intended to deliver a Lockheed Martin technology demonstration satellite to orbit, marked another setback for the company’s Alpha launch vehicle.
The launch, initially scheduled for April 28, 2024, was delayed by a day due to complications with ground support equipment. Shortly after liftoff at 9:37 a.m. ET on April 29th, a catastrophic event occurred during the first stage separation. According to a statement released by Firefly, damage to an engine nozzle significantly diminished the rocket’s thrust, preventing the upper stage from achieving orbital velocity and deploying its payload. The rocket reached an altitude of approximately 198 miles (320 kilometers) before plummeting into a designated safety zone in the Pacific Ocean, north of Antarctica.
The payload, a Lockheed Martin technology demonstration satellite equipped with SmartSat software, was designed to test orbital capabilities. This mission had previously faced delays, initially slated for mid-March but postponed due to range availability issues at Vandenberg Space Force Base, as reported by SpaceNews. A subsequent attempt on April 28th was scrubbed due to problems with ground support equipment.
Firefly’s Alpha, a 95-foot-tall (29-meter) expendable rocket, aims to provide cost-effective launch solutions for mid-sized satellites, boasting a payload capacity of up to 2,866 pounds (1,300 kilograms) at a price point of $15 million per launch. However, the Alpha rocket has encountered repeated challenges. Its maiden flight in September 2021 ended in a fiery explosion after an engine shutdown triggered the flight termination system. A subsequent launch in October 2022 saw the rocket deliver its payload to a lower-than-intended orbit. A December 2023 mission also experienced a second-stage anomaly, resulting in an incorrect satellite deployment.
While Firefly’s Alpha rocket hasn’t established a flawless track record, it represents a significant step in providing more affordable access to space. The company remains one of the few private enterprises to have successfully reached orbit. As the commercial space sector continues to evolve, such setbacks are inevitable. Firefly is currently investigating the root cause of this latest failure.
Firefly’s continued efforts, despite these challenges, underscore the dynamic and competitive nature of the burgeoning space launch industry. The pursuit of more accessible and cost-effective orbital launch solutions is fraught with complexities, but the lessons learned from each failure pave the way for future advancements.