When you delete a file, it isn’t truly gone. Often, it can be recovered with readily available software. This is where SDelete, short for Secure Delete, becomes invaluable. SDelete permanently erases files by overwriting their data, sometimes multiple times, making recovery practically impossible. This powerful tool, part of the Sysinternals suite by Mark Russinovich, is now maintained by Microsoft and operates according to the U.S. Department of Defense’s Clearing and Sanitizing standard DOD 5220.22-M.
Using SDelete via the Command Line
SDelete is a command-line utility distributed within a zip archive. After extracting the files, you’ll need to place the sdelete.exe file in a directory included in your system’s PATH environment variable. The simplest approach is to copy it to the C:Windows folder.
To access the command prompt, press the Win+R keys, type cmd, and press Enter. You can now use the sdelete command to securely erase files and folders.
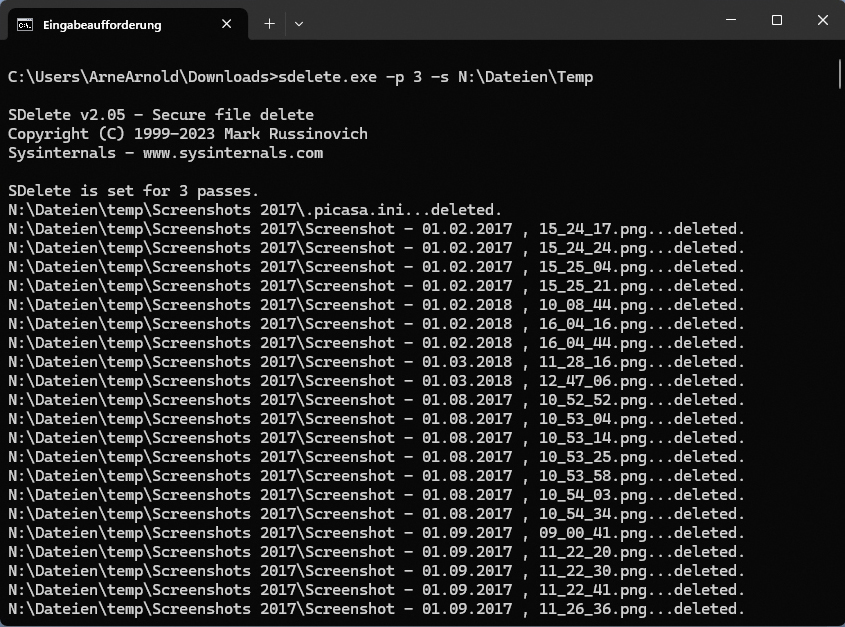 Sdelete
Sdelete
To delete a file named “Document1.docx” with three overwrites, use the following command:
sdelete -p 3 [path]Document1.docxReplace [path] with the file’s full path, including the drive letter (e.g., N:filesDocument1.docx). The -p 3 parameter specifies three overwrites.
To delete a folder, including all subfolders and files, such as the Temp folder, use the following command:
sdelete -p 3 -s [path]TempThe -s parameter includes subfolders in the deletion process. The -r parameter is useful for removing read-only attributes before deletion, preventing error messages for protected files.
Securely Wiping Free Drive Space
SDelete can also overwrite the free space on a drive, securely deleting any remaining file fragments. To do this, use the -z parameter. For example, to overwrite free space on the C: drive, use:
sdelete -z C:This process can take a considerable amount of time, depending on the drive’s size.
SDelete-GUI: A User-Friendly Interface
For those who prefer a graphical interface, SDelete-GUI provides a simpler way to utilize SDelete. Upon its first launch, SDelete-GUI will ask how many times you want to overwrite files, suggesting ten. While effective, three overwrites offer a strong balance between security and efficiency.
After setting the desired number of overwrites and enabling the feature, a “Secure Delete” option will appear in the Windows Explorer context menu. Right-click on the file(s) you wish to securely delete and choose this option. In Windows 11, you may need to select “Show more options” first.
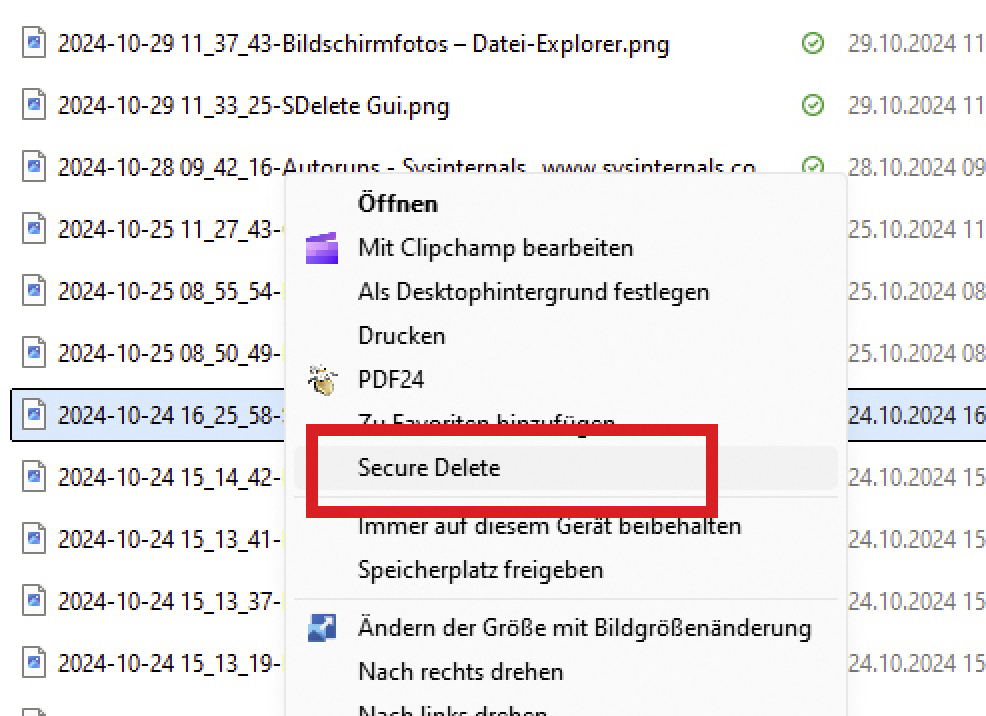 Sdelete-Gui
Sdelete-Gui
Important Considerations
Caution: SDelete deletes data immediately and irreversibly without confirmation. Exercise extreme caution when using this tool. Once data is deleted with SDelete, recovery is highly unlikely. Ensure you have backups of any important files before using this tool.
Conclusion
SDelete offers a powerful way to permanently remove sensitive data from your computer. Whether using the command line or the SDelete-GUI, understanding its functionality and exercising caution are crucial for safe and effective data destruction.