The electric vehicle (EV) revolution is upon us, but the terminology surrounding this innovative technology can be overwhelming. From charging levels to battery components, understanding the language of EVs is crucial for navigating this new landscape. This comprehensive EV glossary decodes the essential jargon, empowering you to confidently embrace the electric future.
Understanding EV Classifications
The term “electric vehicle” encompasses a broad spectrum of vehicle types. Here’s a breakdown of the key classifications:
- Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV): Powered solely by a battery, BEVs represent the purest form of electric vehicle.
- Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV): Combining an electric motor with a traditional internal combustion engine (ICE), HEVs offer improved efficiency but still rely on gasoline.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV): Similar to HEVs, PHEVs also include a plug for charging the battery, enabling longer electric-only driving ranges.
- Extended Range Electric Vehicle (EREV): Primarily electric-powered, EREVs utilize a combustion engine as a backup generator when the battery depletes, extending their range. Unlike hybrids, the engine never directly powers the wheels.
- Mild Hybrid Electric Vehicle (MHEV): Relying mainly on an ICE, MHEVs receive support from a small electric motor for improved efficiency but cannot operate on electric power alone.
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle (FCEV): Employing hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity for the vehicle’s battery, FCEVs represent another alternative fuel pathway.
- Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV): Encompassing BEVs and FCEVs, ZEVs produce no tailpipe emissions during operation.
Key EV Components
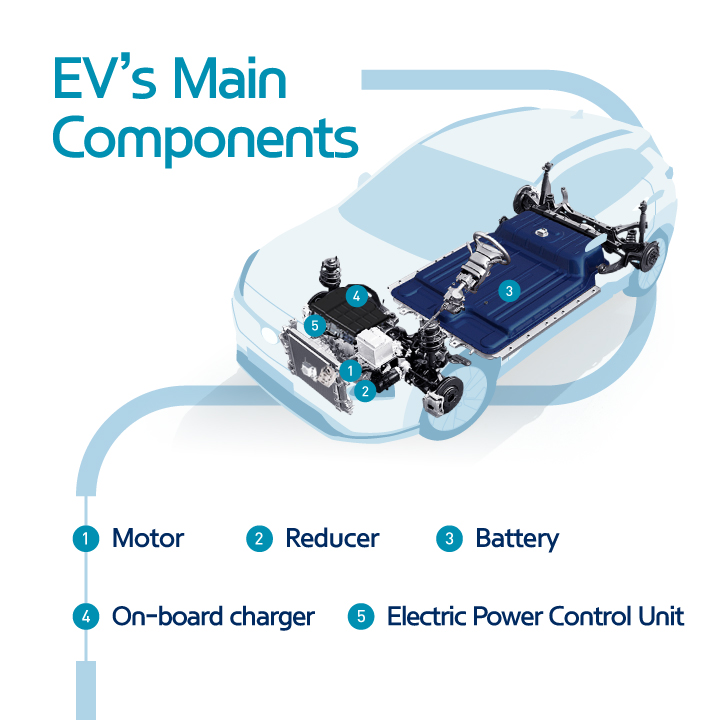 A diagram showing the main components of an electric vehicle.Diagram of an EV’s main components. Credit: Hyundai
A diagram showing the main components of an electric vehicle.Diagram of an EV’s main components. Credit: Hyundai
Understanding the core components of an EV is essential for grasping its functionality:
- Motor: The electric heart of an EV, converting electrical energy into mechanical power to propel the vehicle.
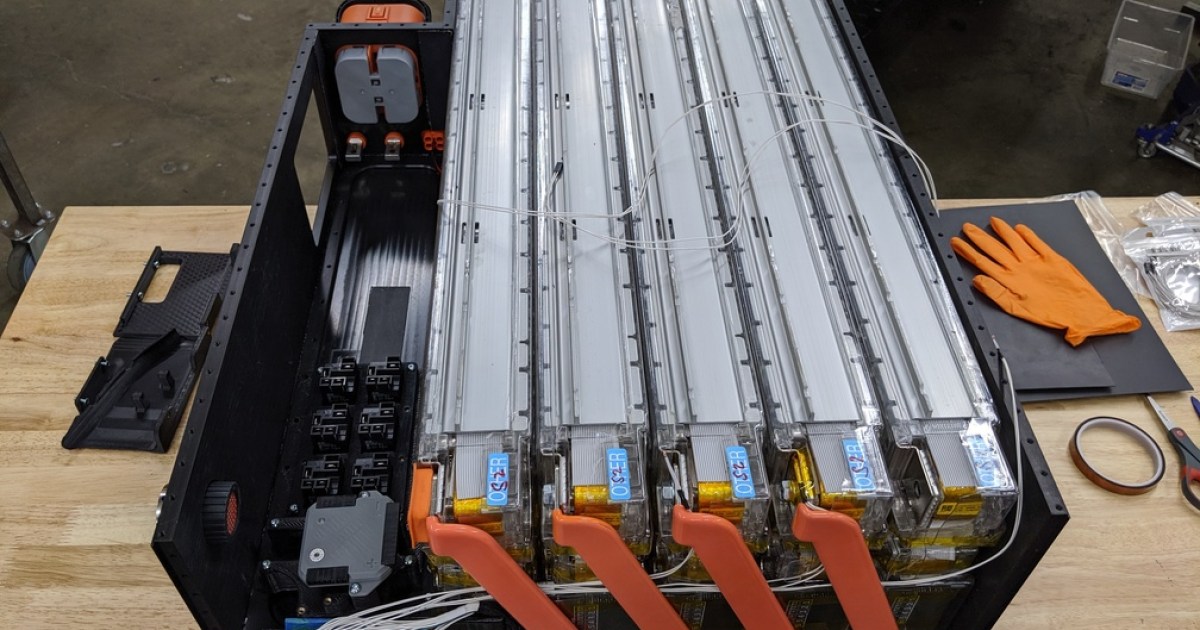
- Battery: The EV’s energy storage unit, analogous to a fuel tank in a gasoline car. Different battery chemistries and architectures exist, including the prevalent lithium-ion and the emerging solid-state batteries.
- Battery Pack: The complete battery system, comprising individual cells, modules, and the protective enclosure.
- Battery Management System (BMS): A crucial system that monitors and regulates the battery’s performance, ensuring optimal charging, discharging, and overall health.
- On-Board Charger (OBC): Converts AC power from the grid to DC power for charging the battery.
- Inverter: Converts DC power from the battery to AC power for the motor.
- Drive Unit: Combines the motor and transmission to efficiently deliver power to the wheels.
Electrical Terminology Explained
Navigating the electrical aspects of EVs requires understanding these key terms:
- Kilowatt-hour (kWh): The standard unit for measuring EV battery capacity, representing the amount of energy stored.
- Miles per Kilowatt-hour (mpkWh): Indicates an EV’s efficiency, expressing how far it can travel on one kWh of energy.
- Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC): Different forms of electrical current, with AC being the standard for household electricity and DC being used by EV batteries.
- Level 1, 2, and 3 Charging: Different charging speeds, with Level 1 being the slowest (using a standard outlet) and Level 3 being the fastest (DC fast charging).
Mechanical and Performance Metrics
Understanding EV performance involves these terms:
- Torque: Rotational force, a key indicator of an EV’s acceleration capability.
- Horsepower (hp): A traditional unit of power, often used alongside kW in EV specifications.
- Range: The distance an EV can travel on a single charge.
- Regenerative Braking: A system that captures energy during braking and uses it to recharge the battery, increasing efficiency.
EV Charging Infrastructure
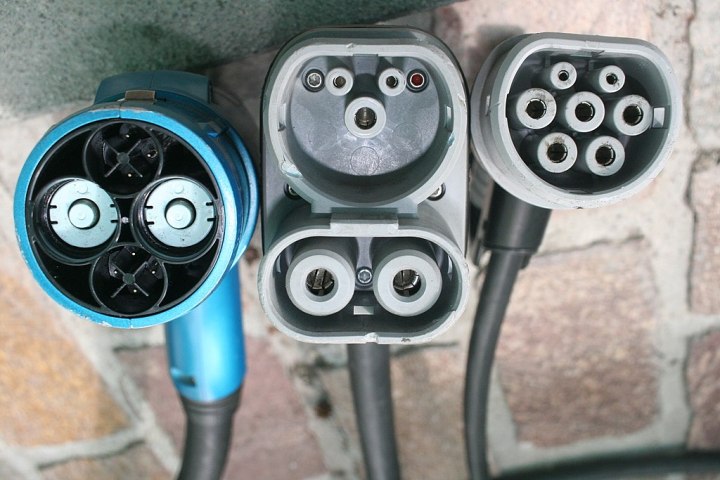 CHAdeMO, Combo2, aand Type 2 EV plugs side by side.Various EV plugs. Credit: Paul Sladen
CHAdeMO, Combo2, aand Type 2 EV plugs side by side.Various EV plugs. Credit: Paul Sladen
The expanding network of EV charging infrastructure introduces its own set of terminology:
- Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE): Encompasses all the hardware and software involved in charging an EV.
- Connector: The physical plug that connects the EV to the charging station. Different connector types exist, including CCS, CHAdeMO, and Type 1/Type 2.
- Charge Point Operator (CPO): Companies that own and operate charging networks.
Conclusion
This glossary provides a foundation for understanding the key terminology surrounding electric vehicles. As the EV landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about these terms will be crucial for embracing the electric future.










