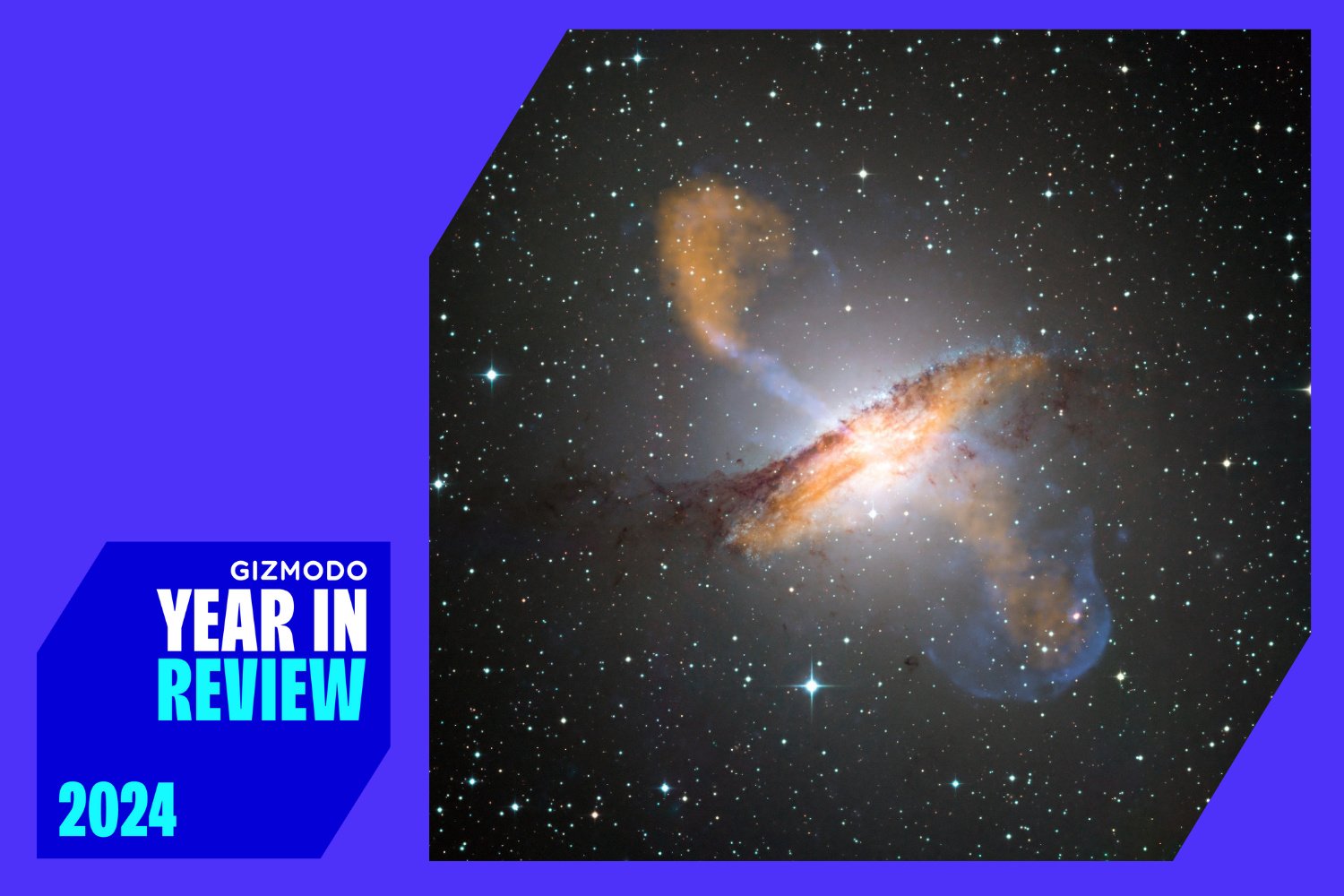
The universe is a vast and mysterious place, constantly revealing new wonders. In 2024, scientists made remarkable strides in understanding the cosmos, from imaging the oldest black hole to modeling the universe’s expansion on supercomputers. This year’s astrophysical discoveries and advances have redefined our understanding of everything from black holes and neutron stars to distant galaxies and the very fabric of spacetime.
The Oldest Black Hole Discovered
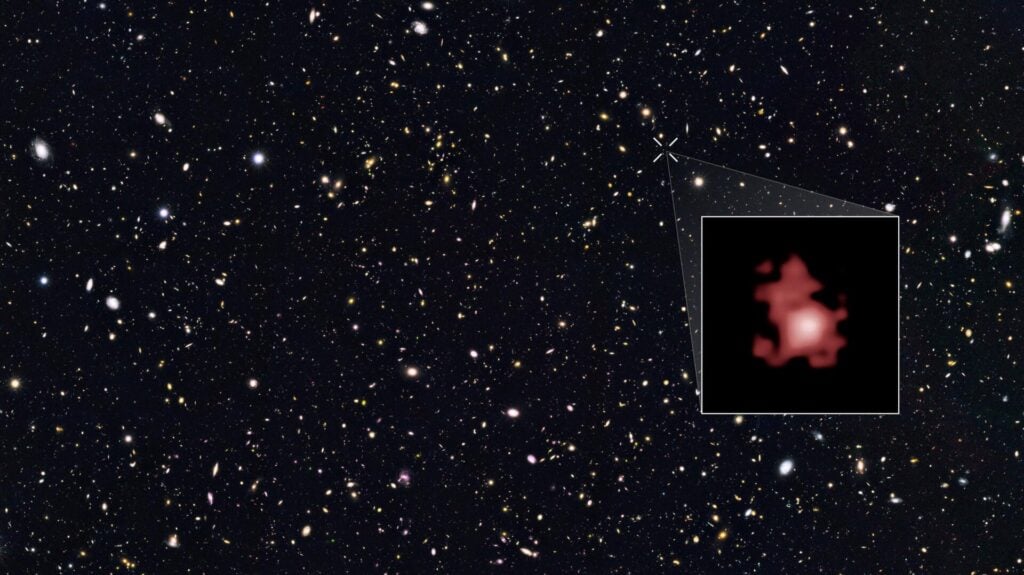 An image of the distant galaxy GN-z11 captured by the Hubble Space Telescope.
An image of the distant galaxy GN-z11 captured by the Hubble Space Telescope.
In January, researchers identified a black hole dating back to just 400 million years after the Big Bang, making it over 13 billion years old. This discovery pushes the boundaries of our understanding of early universe formation, given the relatively short timeframe between the Big Bang and the emergence of this ancient celestial giant.
First Detailed Image of a Star Outside the Milky Way
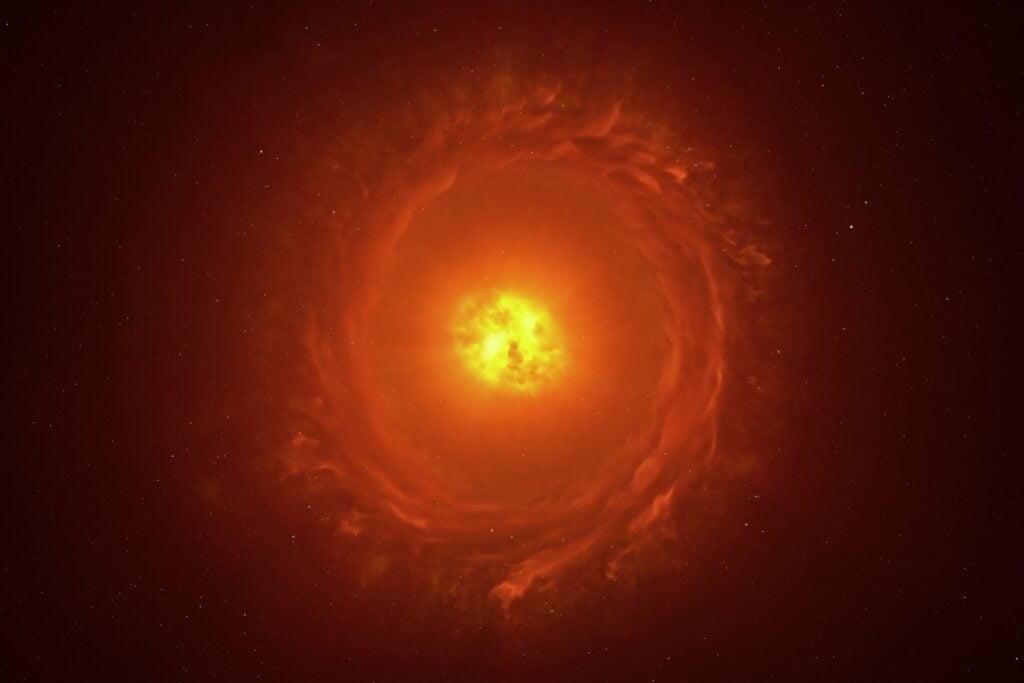 An artist's rendering of a red supergiant star.
An artist's rendering of a red supergiant star.
November brought the first detailed image of a star outside our galaxy. The European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope Interferometer captured a red supergiant in the Large Magellanic Cloud, 2,000 times larger than our Sun. The image reveals a surrounding cocoon of material, likely shed as the star approaches its eventual supernova fate.
Jupiter’s Magnetosheath Jets Revealed
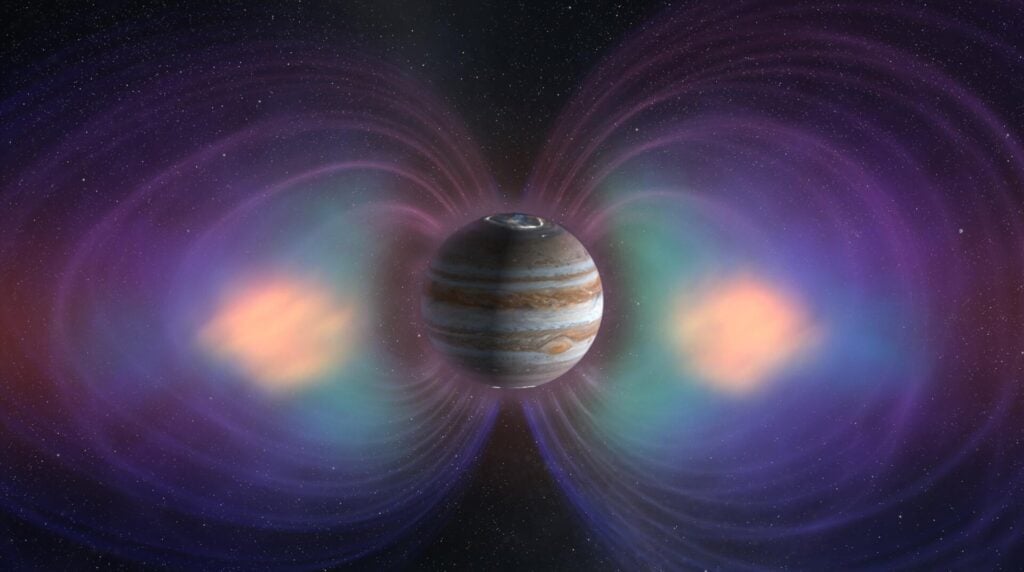 An illustration of Jupiter's magnetosphere.
An illustration of Jupiter's magnetosphere.
Analysis of 45-year-old Voyager 2 data unveiled jets within Jupiter’s magnetosheath. This discovery provides further insight into the dynamics of Jupiter’s magnetosphere, the largest structure in our solar system, dwarfing even the Sun.
Ingenuity Helicopter’s Final Flight on Mars
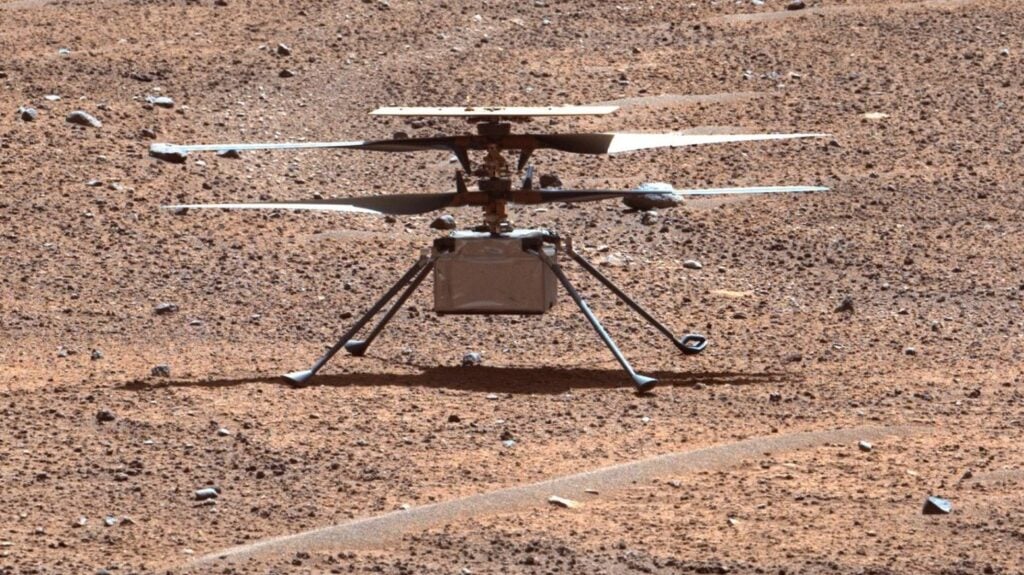 The Ingenuity helicopter on Mars.
The Ingenuity helicopter on Mars.
Ingenuity, the Mars helicopter, concluded its mission in January after a rotor blade broke during its 72nd flight. Despite its unfortunate end, Ingenuity achieved a historic milestone – the first controlled, powered flight on another planet, paving the way for future aerial exploration beyond Earth.
Asteroid Bennu Sample Arrives on Earth
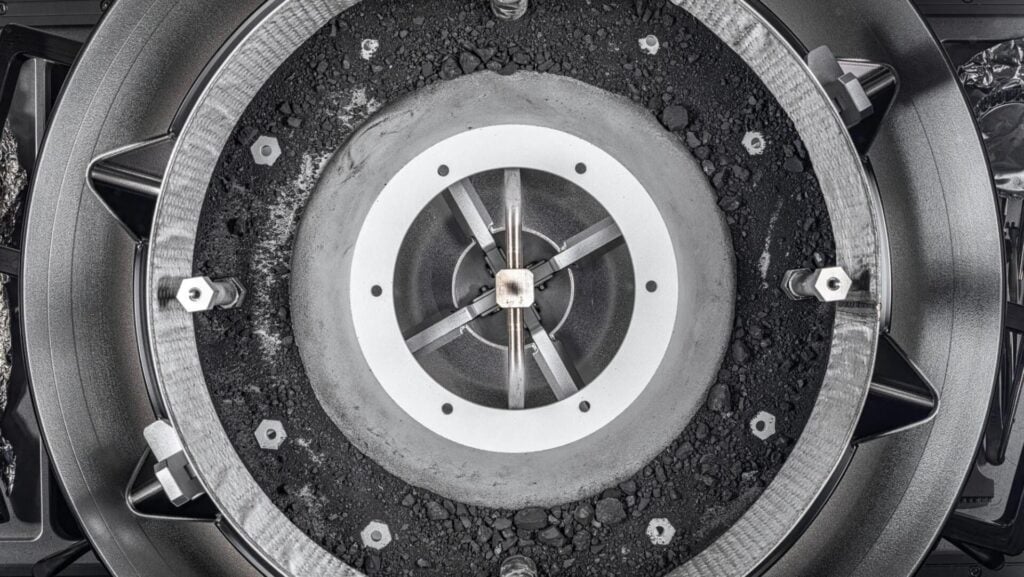 The OSIRIS-REx sample return capsule containing material from asteroid Bennu.
The OSIRIS-REx sample return capsule containing material from asteroid Bennu.
The OSIRIS-REx mission delivered a substantial sample from asteroid Bennu to Earth in January. This precious cargo offers scientists an unprecedented opportunity to study the asteroid’s composition and gain insights into the early solar system’s history.
Webb Telescope Captures Stunning Spiral Galaxies
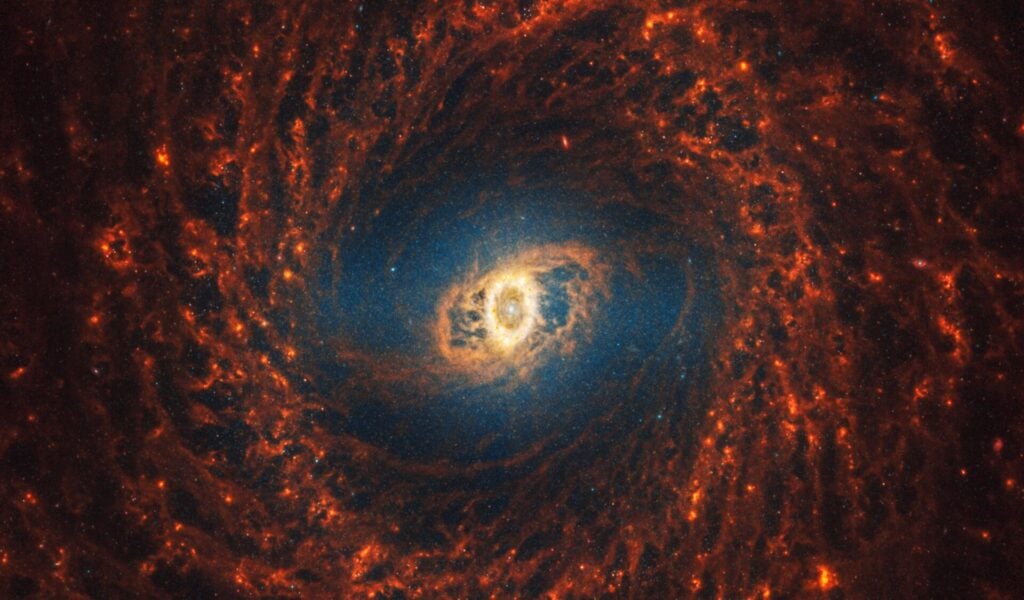 A composite image of 19 spiral galaxies captured by the James Webb Space Telescope.
A composite image of 19 spiral galaxies captured by the James Webb Space Telescope.
The James Webb Space Telescope continues to amaze with breathtaking images. The PHANGS project released 19 images of face-on spiral galaxies, showcasing the vastness and beauty of these cosmic structures while highlighting the relative smallness of our own planet.
New Moons Discovered Orbiting Uranus and Neptune
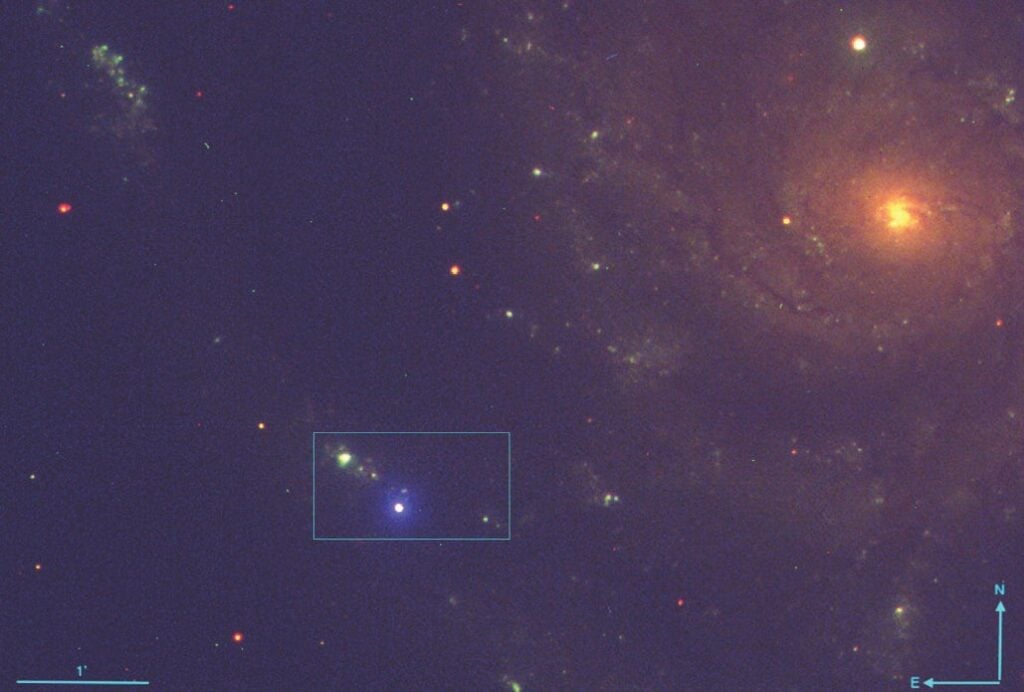
 Three newly discovered moons of Uranus and Neptune.
Three newly discovered moons of Uranus and Neptune.
Astronomers discovered new moons orbiting Uranus and Neptune in February, demonstrating that our solar system still holds undiscovered secrets. These moons, ranging in size and orbital period, offer further opportunities for planetary science research.
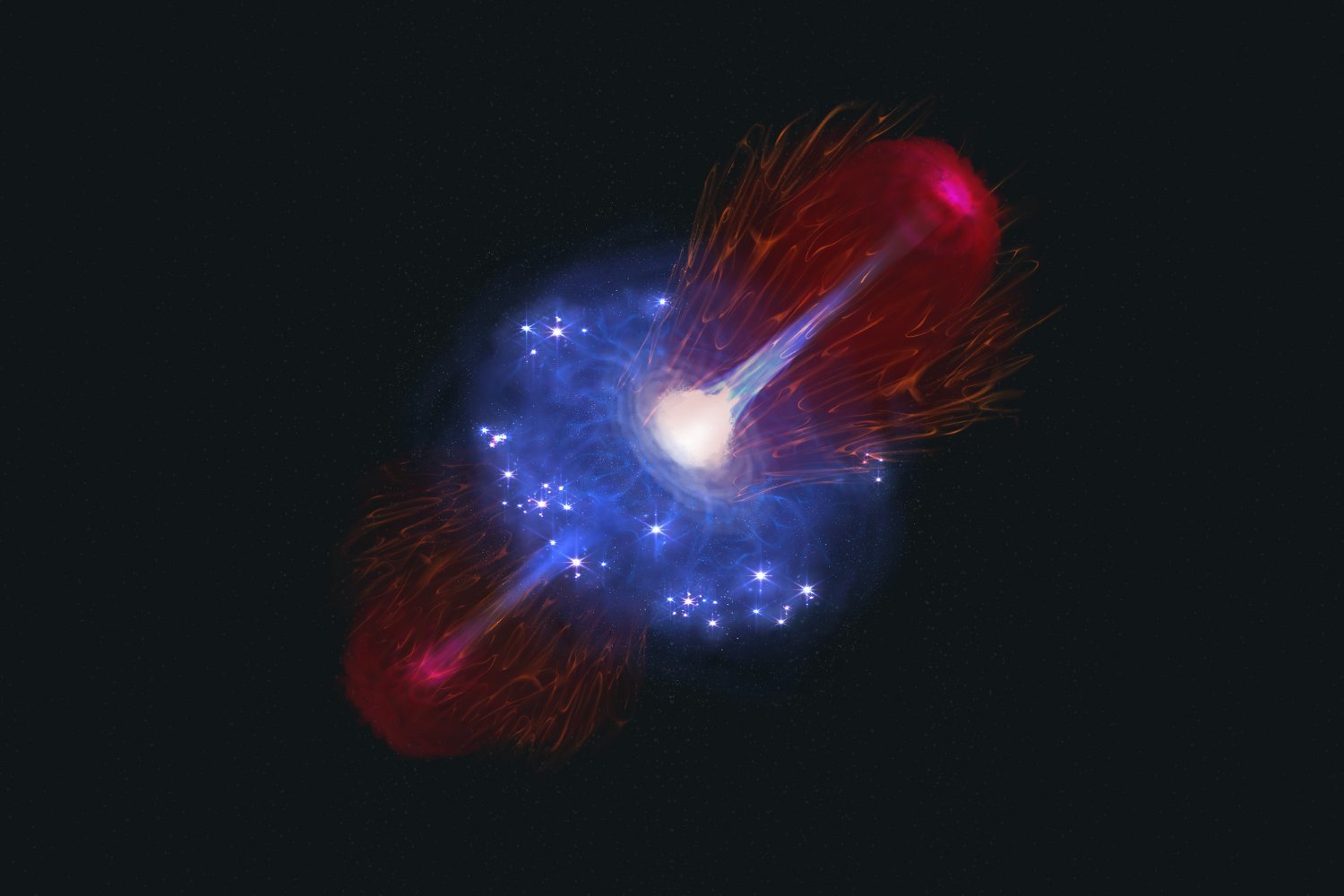
Supernova Captured Birthing a Black Hole
 An image of a supernova.
An image of a supernova.
Astronomers witnessed the dramatic moment a star went supernova, capturing the formation of a black hole. This observation provides crucial data for understanding the life cycle of stars and the creation of these enigmatic spacetime regions.
North American Total Solar Eclipse
 A photograph of the 2024 total solar eclipse.
A photograph of the 2024 total solar eclipse.
A total solar eclipse graced North America in April, offering a spectacular celestial event for millions. The Moon momentarily obscured the Sun, creating a stunning ring of light and plunging the sky into temporary darkness.
Lava Lake Discovered on Jupiter’s Moon Io
 A GIF showing a lava lake on Io.
A GIF showing a lava lake on Io.
Juno flybys of Jupiter’s moon Io revealed a lava lake on its surface, highlighting the moon’s intense volcanic activity. This discovery underscores the diversity of moons in our solar system and their unique geological features.
Jupiter and its Diverse Moons
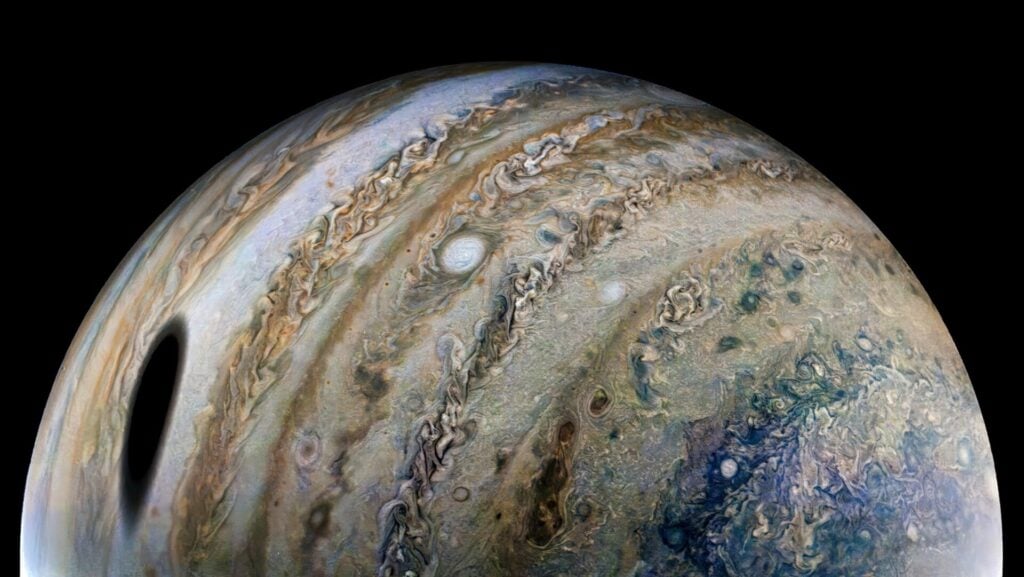 Jupiter with its moon, Io, casting a shadow.
Jupiter with its moon, Io, casting a shadow.
Jupiter’s 95 moons offer a fascinating array of characteristics, from the volcanic Io to the potentially life-harboring Europa. These moons provide ample opportunities for further planetary science and astrobiological investigation.
Increased Solar Activity and Auroras
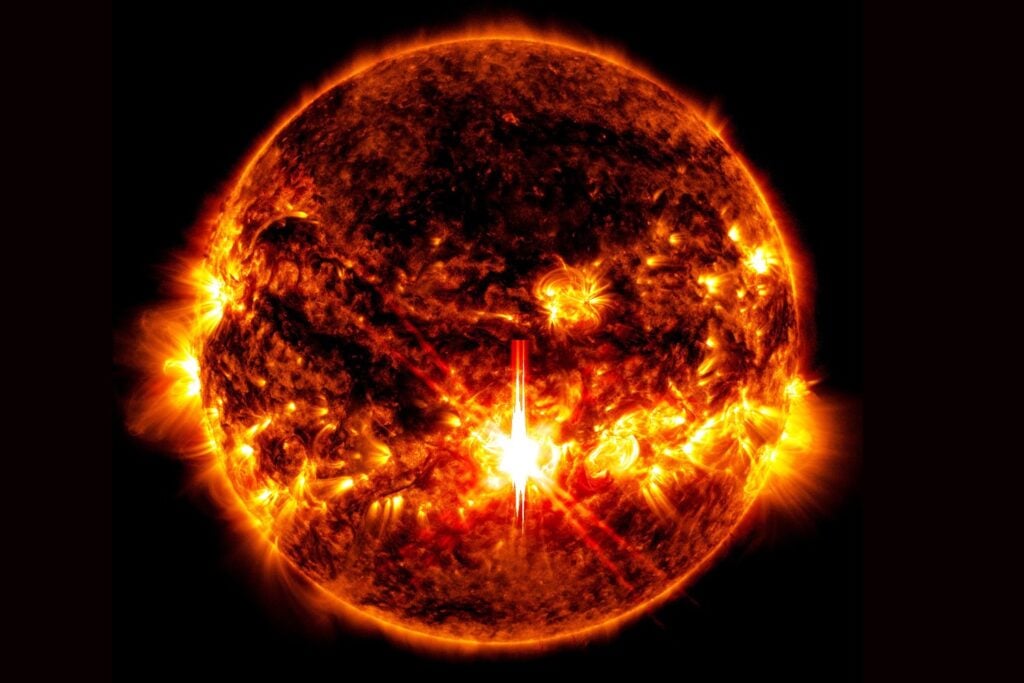 An X9.0 solar flare.
An X9.0 solar flare.
Intense solar activity, including sunspots and coronal mass ejections, led to vibrant auroras visible across Earth, even in lower latitudes. This heightened solar activity also impacted Mars, where Curiosity detected evidence of Martian auroras.
Webb Telescope Identifies Most Distant Galaxy
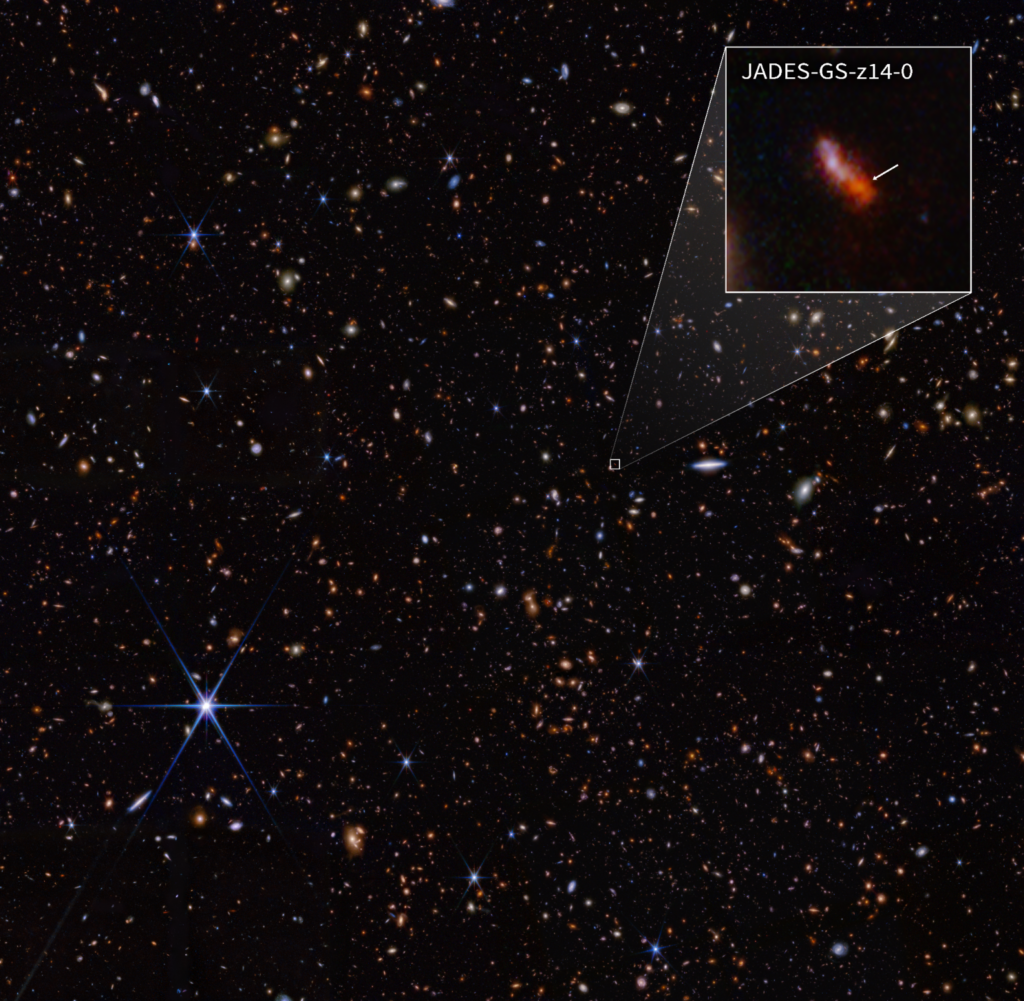 The most distant galaxy ever observed.
The most distant galaxy ever observed.
The James Webb Space Telescope identified the most distant galaxy ever observed, dating back to less than 300 million years after the Big Bang. This discovery demonstrates Webb’s remarkable ability to peer into the universe’s earliest epochs.
Most Distant Merging Quasars Discovered
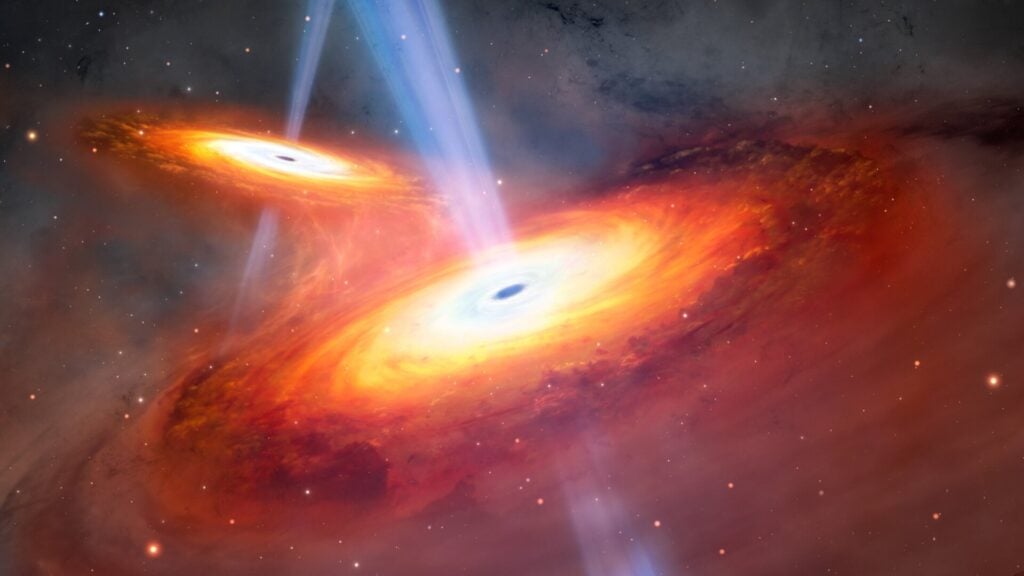 An artist's impression of merging quasars.
An artist's impression of merging quasars.
Astronomers identified the most distant merging quasars ever found, offering insights into the early universe’s structure and evolution. The massive black holes at the heart of these quasars provide valuable data for cosmological models.
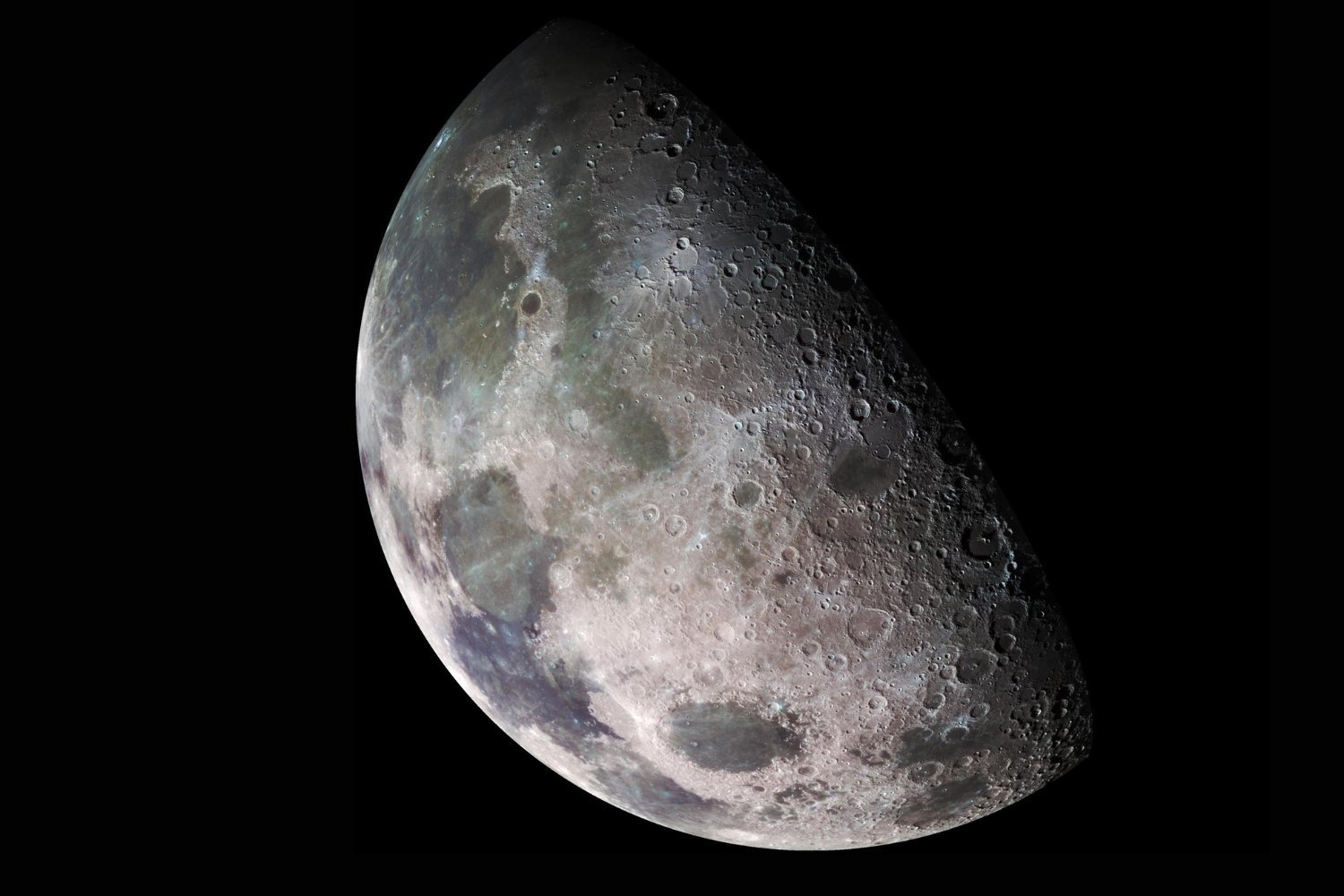
Lunar Tunnel Discovered in Sea of Tranquility
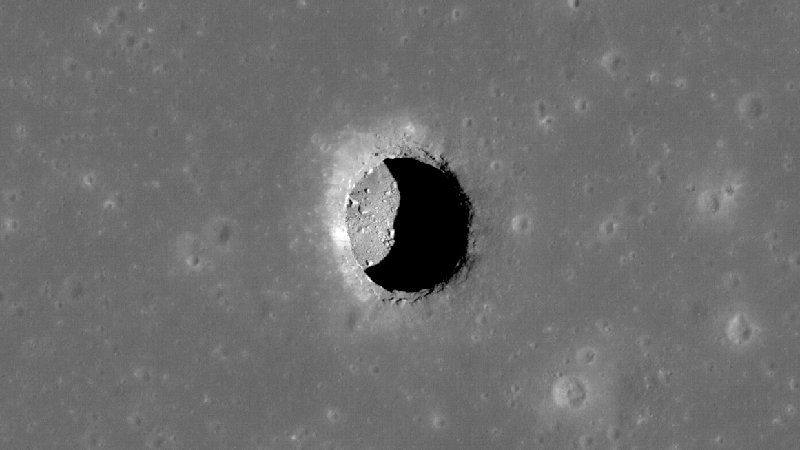 The Mare Tranquillitatis pit crater.
The Mare Tranquillitatis pit crater.
A pit crater in the Moon’s Sea of Tranquility, near the Apollo 11 landing site, is believed to contain a tunnel. This discovery could have significant implications for future lunar missions, offering potential shelter from radiation and temperature extremes.
Astronomy Photographer of the Year Finalists
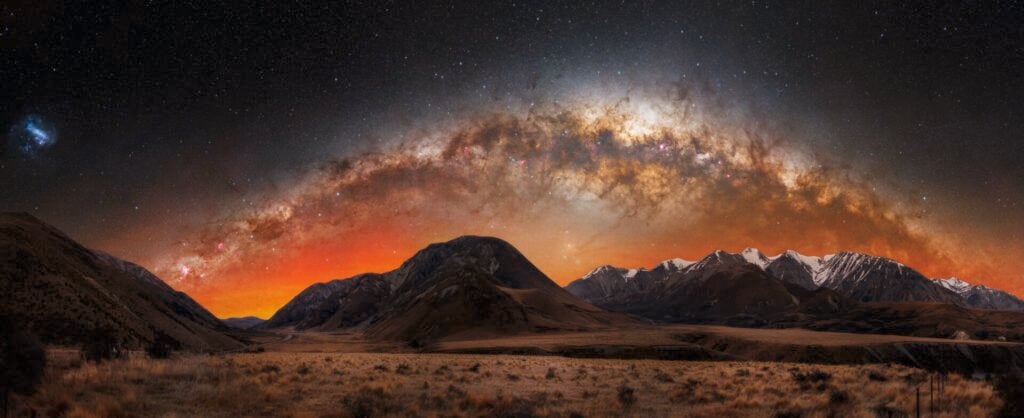 An image of the aurora borealis and the Milky Way.
An image of the aurora borealis and the Milky Way.
The Astronomy Photographer of the Year competition showcased stunning images of the cosmos, reminding us of the universe’s beauty and accessibility even from Earth.
The “Wow!” Signal Possibly Explained
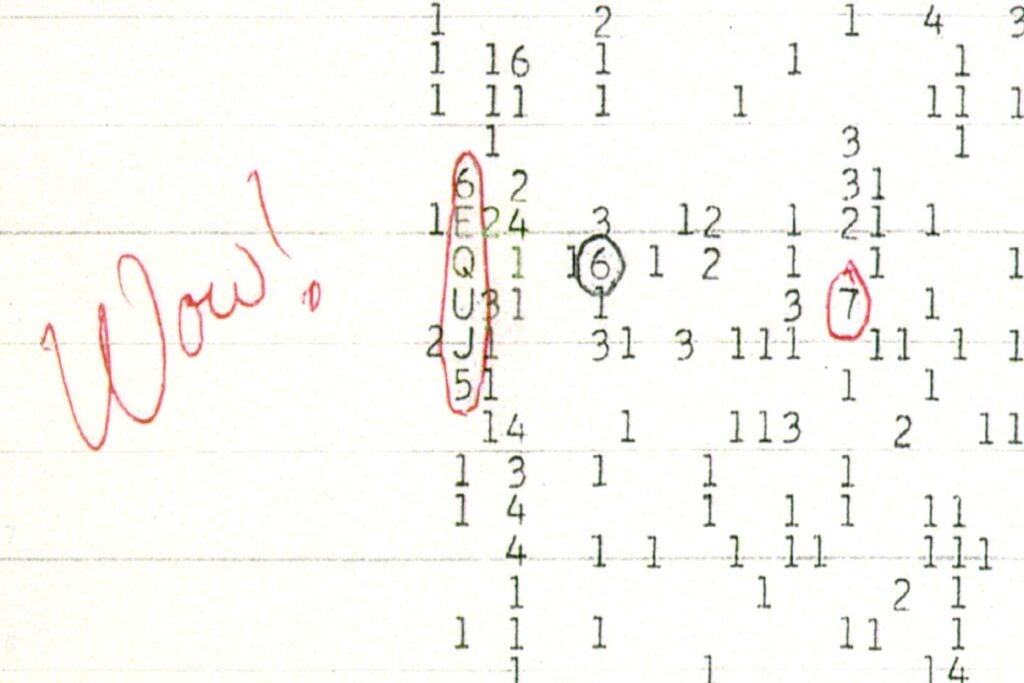 The "Wow!" signal printout.
The "Wow!" signal printout.
New data suggests that the mysterious “Wow!” signal, detected in 1977, might originate from a hydrogen cloud excited by a magnetar, a highly magnetized neutron star. This theory, while not extraterrestrial, offers a compelling explanation for this long-standing enigma.
Betelgeuse’s Dimming Pattern Potentially Explained
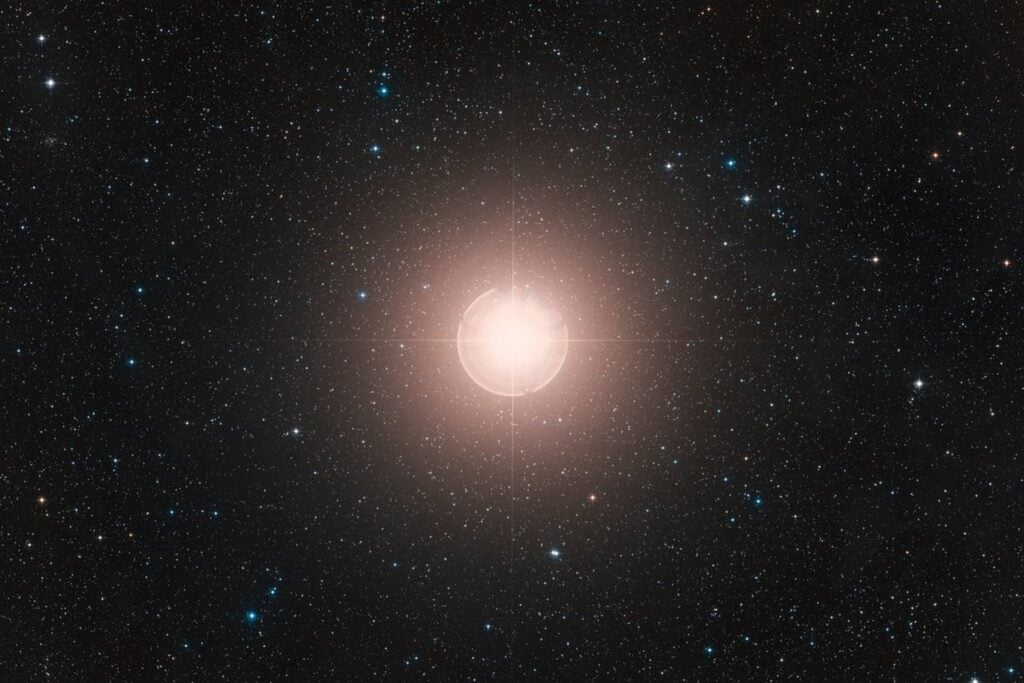 Betelgeuse as seen by the Hubble Space Telescope.
Betelgeuse as seen by the Hubble Space Telescope.
Astronomers propose that a smaller companion star, nicknamed “BetelBuddy,” might be responsible for Betelgeuse’s unusual dimming patterns. This theory sheds light on the behavior of this red supergiant, destined for a future supernova.
Gigantic Black Hole Jets and Star Explosions
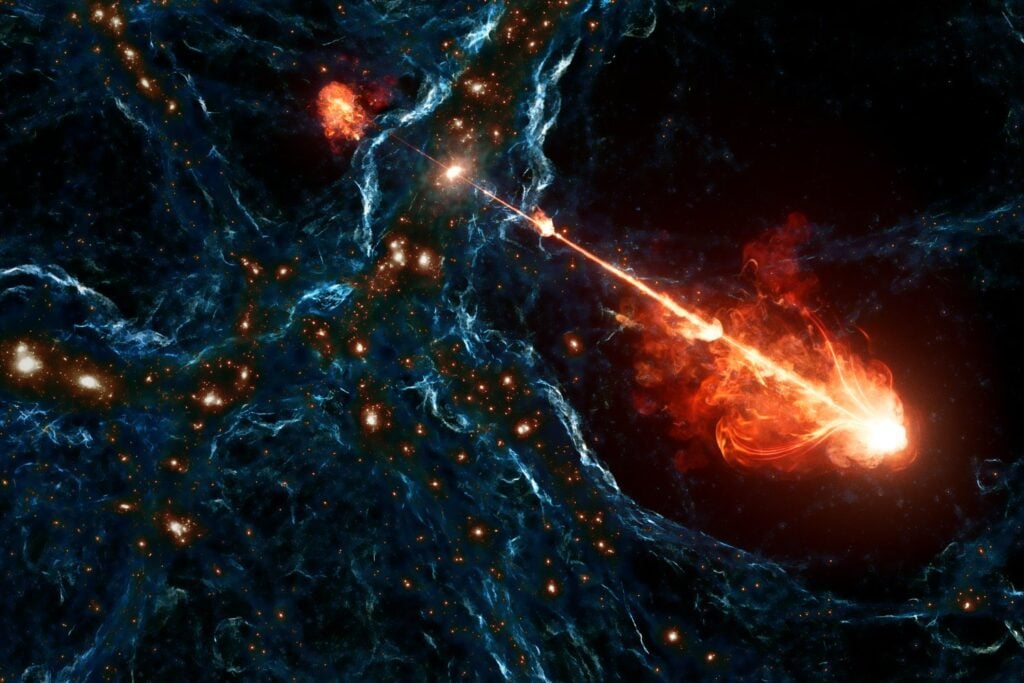 An artist's impression of gigantic black hole jets.
An artist's impression of gigantic black hole jets.
Researchers discovered the largest known black hole jets, part of a megastructure called Porphyrion. These immense jets, spanning vast cosmic distances, play a significant role in shaping their surrounding environment. Separate research also revealed that black hole jets can trigger star explosions, making this a field ripe for further exploration.
Neutron Stars as Potential Dark Matter Breeding Grounds
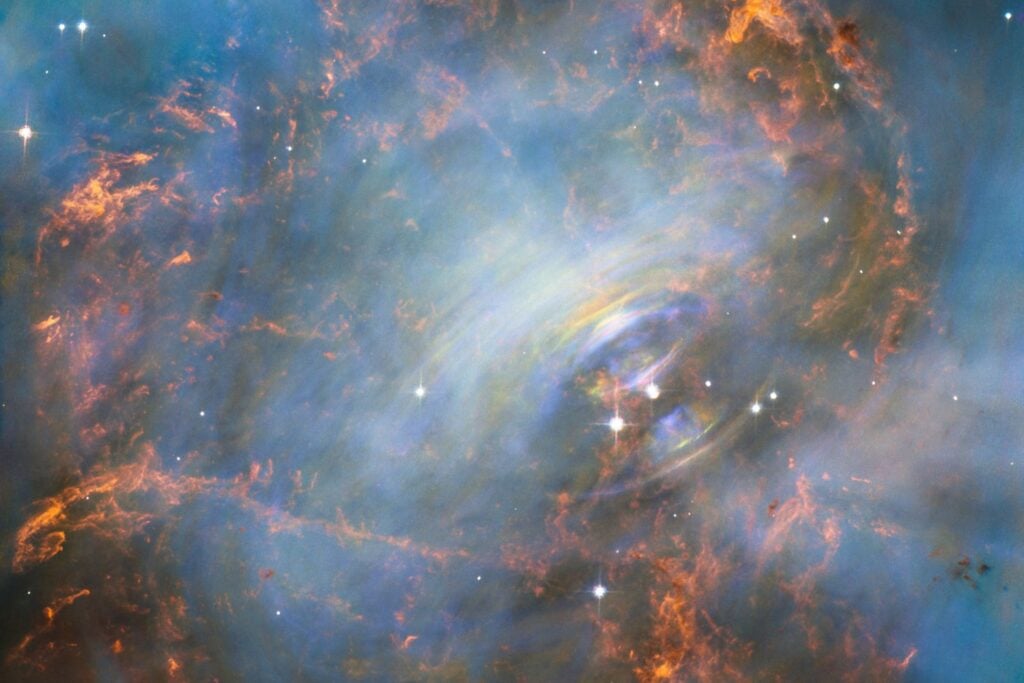 A neutron star in the Crab Nebula.
A neutron star in the Crab Nebula.
Scientists suggest that axions, a dark matter candidate, could form clouds around neutron stars. This theory proposes new avenues for dark matter detection, potentially using space-based radio telescopes.
Arecibo Observatory Collapse Report Released
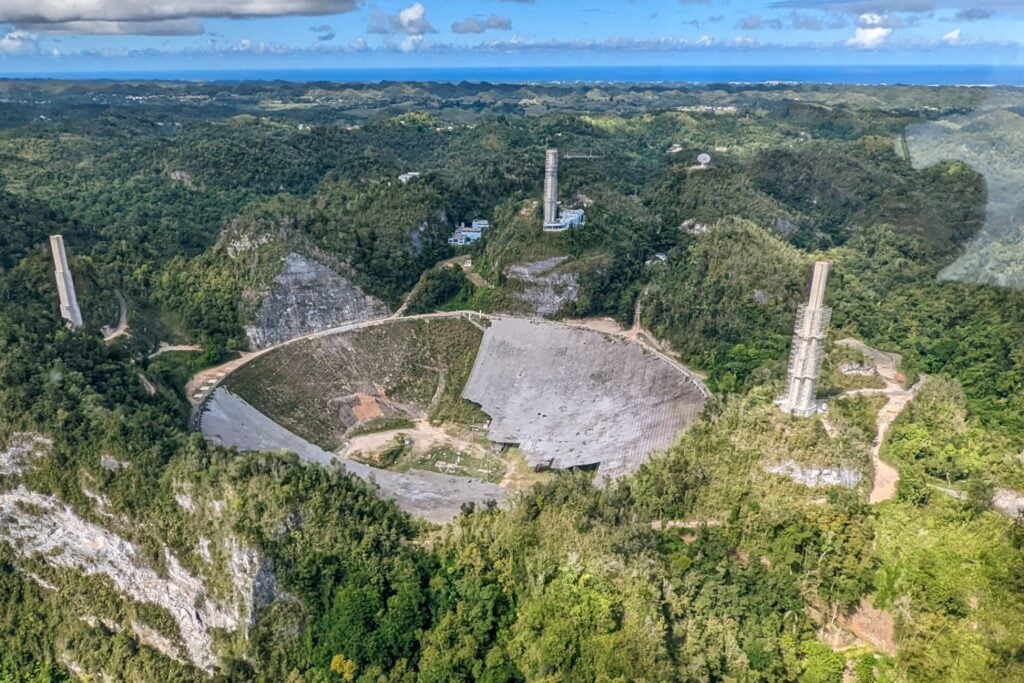 The collapsed Arecibo Telescope.
The collapsed Arecibo Telescope.
A report detailed the cause of the Arecibo Observatory collapse, citing Hurricane Maria damage and zinc decay in cable sockets as contributing factors. The collapse of this iconic observatory marks a significant loss for the scientific community.
Perseverance Rover Exits Jezero Crater
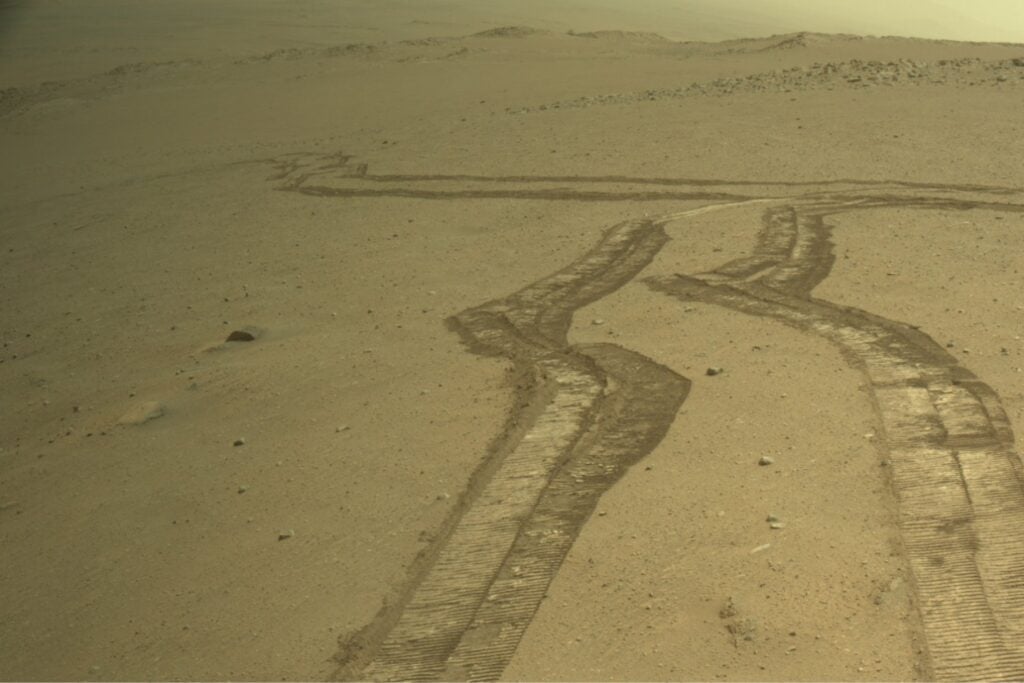 A view from the Perseverance rover.
A view from the Perseverance rover.
The Perseverance rover successfully navigated out of Jezero Crater, opening a new chapter in its mission to explore ancient Martian rocks and search for signs of past microbial life.
The Hubble Constant and the Expanding Universe
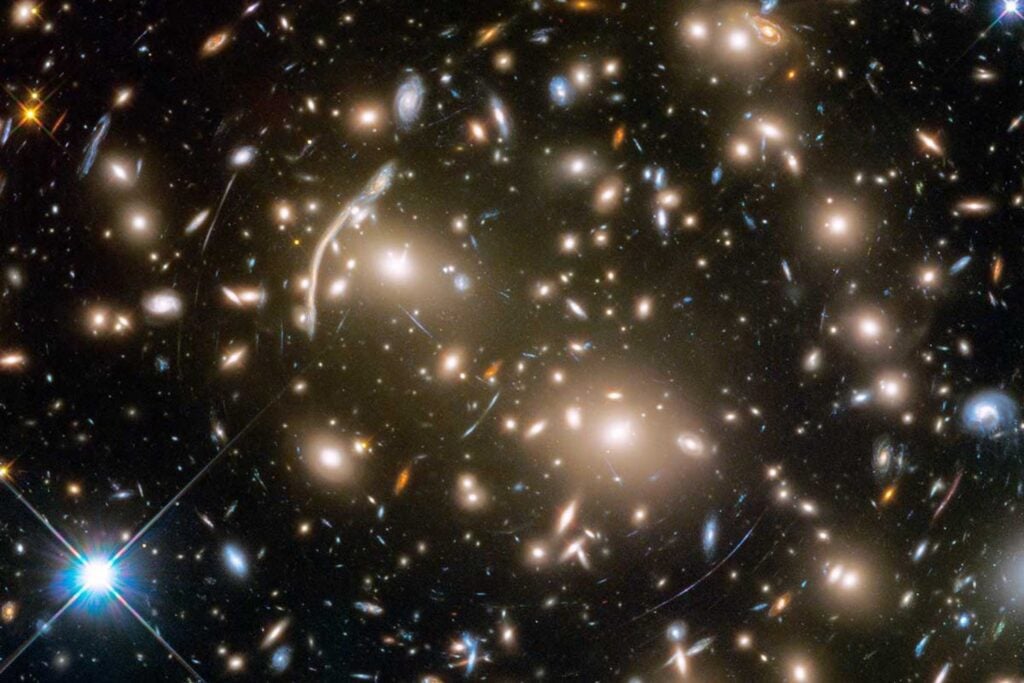 The galaxy cluster Abell 370.
The galaxy cluster Abell 370.
An “Einstein Zig-Zag” – a compound gravitational lens – offers a new method for measuring the Hubble constant, which describes the universe’s expansion rate. The discovery of a supernova appearing three times due to gravitational lensing provides further data for refining our understanding of this crucial cosmological parameter.
Potential Liquid Water Ocean on Uranus’ Moon Miranda
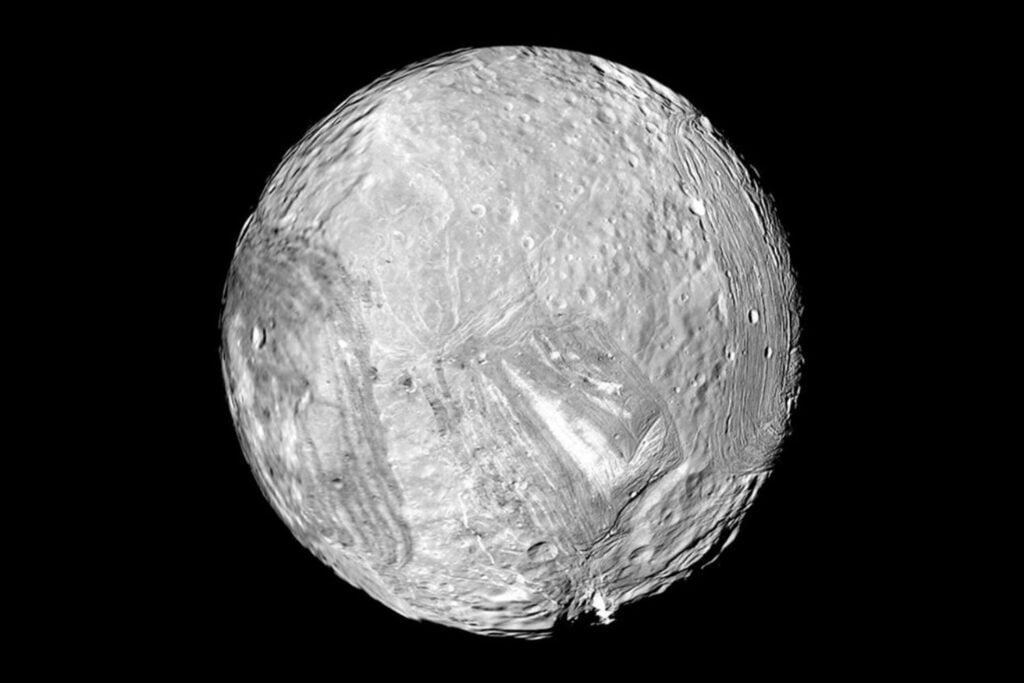 Uranus' moon Miranda.
Uranus' moon Miranda.
Scientists believe Uranus’ moon Miranda may harbor a liquid water ocean, or at least possessed one in the past. This finding adds Miranda to the growing list of celestial bodies potentially suitable for astrobiological research, the search for life beyond Earth.
Supercomputer Simulations of the Universe
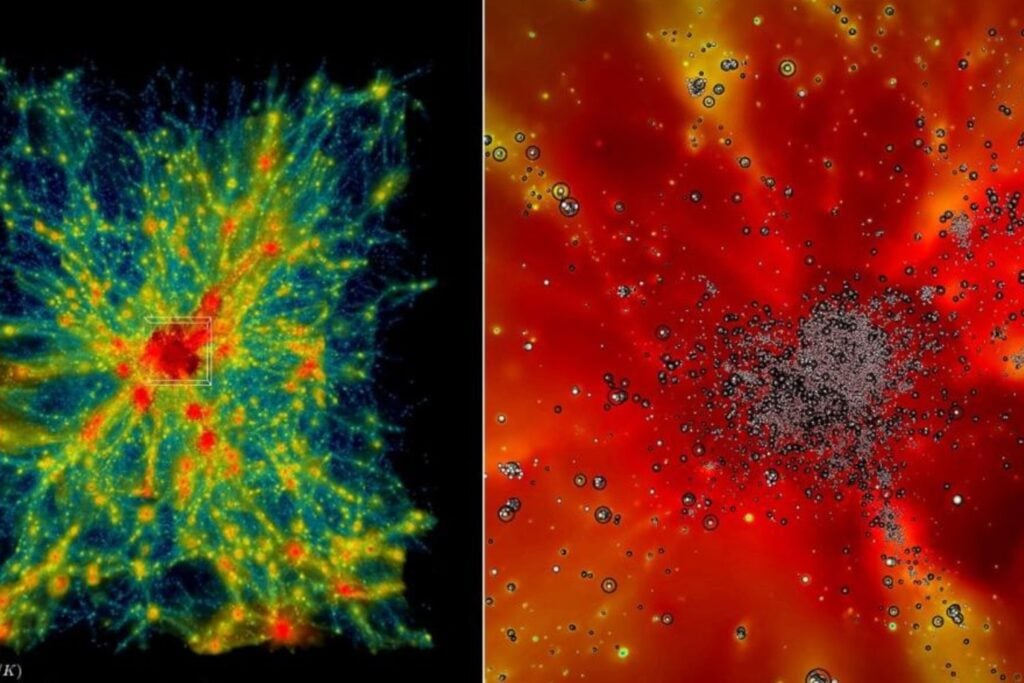 Supercomputer simulations of the universe.
Supercomputer simulations of the universe.
The Frontier supercomputer simulated the universe’s evolution, including the behavior of dark matter. These simulations provide valuable data for understanding galaxy formation and the universe’s expansion, furthering our comprehension of the cosmos.