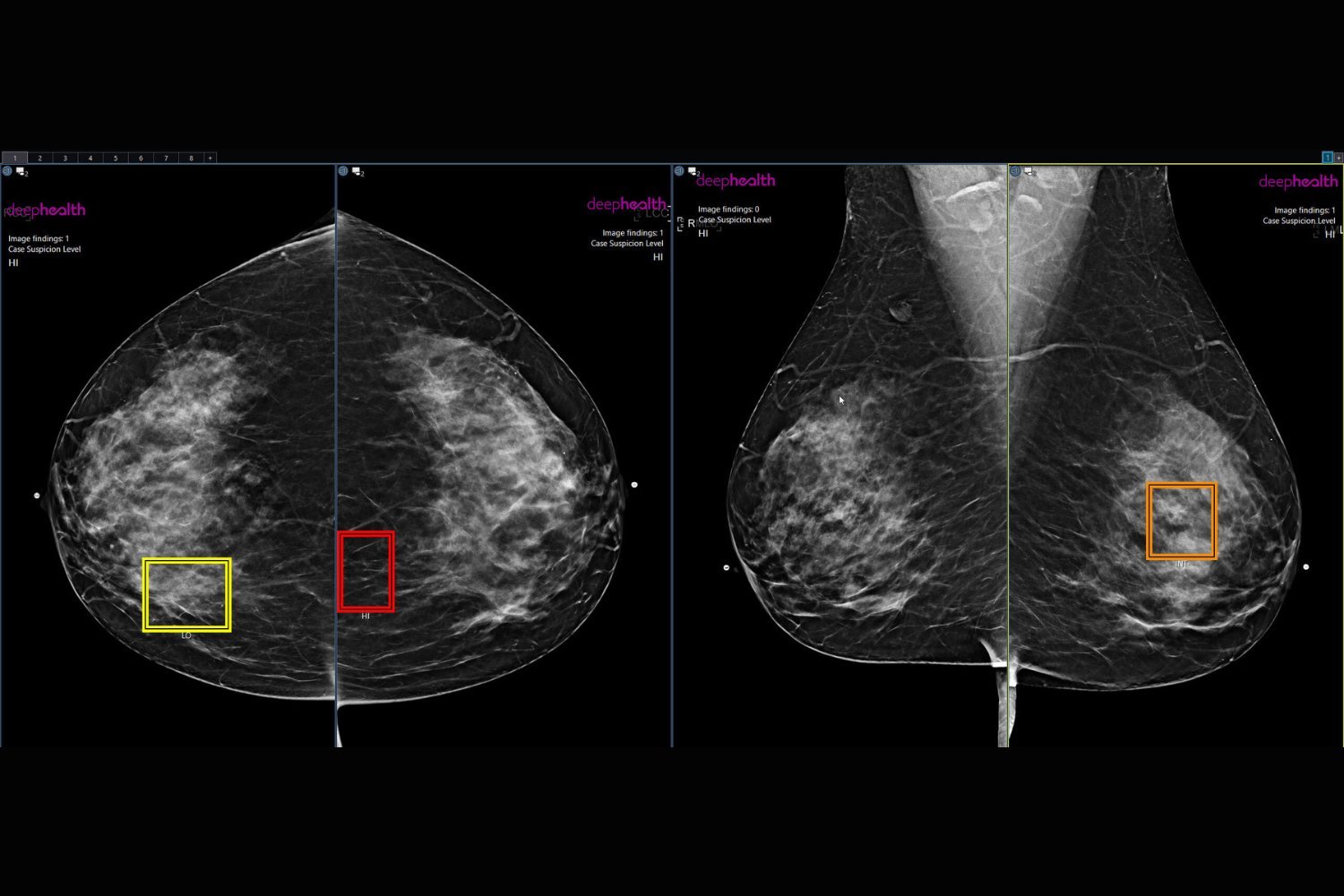
AI is transforming medical diagnostics. A recent study presented at the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) annual meeting revealed a significant increase in breast cancer detection rates when artificial intelligence is incorporated into mammography screenings. Over 30% of women opted for the AI-enhanced program, demonstrating a growing interest in this advanced technology.
This groundbreaking study, conducted across 10 clinical practices, offered patients a self-pay, FDA-compliant AI-powered screening mammography program. The process involved a breast radiologist reviewing the mammograms, followed by a review by the AI software. Discrepancies between the two triggered a third review by a second radiologist. This multi-layered approach ensured a comprehensive and accurate assessment.
AI as a “Second Set of Eyes”
Bryan Haslam, chief product officer at DeepHealth and leader of the study, emphasized the innovative nature of this program. It represents the first reported results using AI in this specific workflow, providing patients with an optional enhanced review. Haslam highlighted the program’s growing popularity, with enrollment now at 36% and rising, correlating with consistently higher cancer detection rates.
Significant Increase in Detection Rates
The study analyzed data from 747,604 women who underwent mammograms over a year. Results showed a remarkable 43% higher cancer detection rate for women enrolled in the AI-enhanced program compared to those who weren’t. This increase was observed across all participating practices.
While 22% of this increase can be attributed to higher-risk women opting for the enhanced program, the remaining 21% is directly attributed to the AI’s contribution. This suggests that AI acts as a highly effective “second set of eyes,” identifying potential cancers that might otherwise be missed.
Improved Accuracy of Recalls
The study also revealed a 21% higher recall rate for enrolled women. Importantly, the positive predictive value for cancer (the probability that a positive test result truly indicates cancer) was 15% higher in this group. This indicates that AI-triggered recalls were more likely to result in accurate cancer diagnoses, reducing unnecessary anxiety and further investigations for women with false positives.
Gregory Sorensen, senior writer on the study and also from DeepHealth, emphasized the significance of these findings. They demonstrate not only women’s willingness to embrace AI in their healthcare but also the tangible benefits of improved cancer detection rates when AI is coupled with expert review. Future research aims to address potential biases from self-selection through randomized controlled trials.
The Future of AI in Radiology
These results underscore the transformative potential of AI in radiology. While cost remains a barrier, with many insurance companies currently not covering AI-enhanced screenings, the increasing patient demand and proven efficacy may drive wider adoption. Further research will be crucial in solidifying the role of AI in diagnostics and potentially revolutionizing cancer detection. The hope is that this promising technology will become more accessible, contributing to earlier diagnosis and improved outcomes for patients.
The potential impact of AI in radiology is immense, promising earlier and more accurate diagnoses. As research progresses and insurance coverage evolves, AI-enhanced screenings could become the standard of care, significantly improving the fight against breast cancer.