The CPU market is in a peculiar state. AMD’s delayed Zen 5 launch and Intel’s ongoing stability issues make direct comparisons challenging. AMD’s new Ryzen 5 9600X and Ryzen 7 9700X are among the best processors available, yet their arrival coincides with this uncertain landscape. These CPUs aren’t specifically designed for gaming, as AMD’s 3D V-Cache CPUs reign supreme in that arena. Their performance improvements vary, from substantial to modest. While these latest chips are undoubtedly fast and easily recommendable, the current CPU market volatility suggests waiting a few weeks to assess the overall situation before making a purchase.
AMD Ryzen 5 9600X and Ryzen 7 9700X Specifications
 CPU pads on the AMD Ryzen 7 9700XImage: Close-up of the AMD Ryzen 7 9700X CPU pads.
CPU pads on the AMD Ryzen 7 9700XImage: Close-up of the AMD Ryzen 7 9700X CPU pads.
The Ryzen 5 9600X and Ryzen 7 9700X prioritize architectural advancements, evident in their specifications. Compared to the last-gen Ryzen 7000 series, these retain similar core counts, clock speeds, and cache sizes. The key improvements lie within the new Zen 5 architecture.
Zen 5 boasts numerous technical enhancements over Zen 4, such as an 8-wide dispatch unit (up from 6-wide) and six Arithmetic Logic Units (ALUs), increased from four. However, the overarching architectural goals are more significant. AMD focused on single-threaded performance and implemented a true 512-bit data path for AVX-512 instructions, laying the groundwork for future CPU generations.
| Feature | Ryzen 7 9700X | Ryzen 7 7700X | Ryzen 5 9600X | Ryzen 5 7600X |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cores/Threads | 8/16 | 8/16 | 6/12 | 6/12 |
| L3/L2 Cache | 32MB / 8MB | 32MB / 8MB | 32MB / 6MB | 32MB / 6MB |
| Max Turbo | 5.5GHz | 5.4GHz | 5.4GHz | 5.3GHz |
| TDP | 65W | 105W | 65W | 65W |
| MSRP | $360 | $400 | $280 | $300 |
The performance results demonstrate AMD’s success in achieving these design objectives. While this architecture represents a new starting point, it’s not the culmination of AMD’s vision. Performance appears uneven, with some workloads showing moderate gains while others exhibit dramatic improvements.
Beyond architecture, the Ryzen 7 9700X boasts a significant TDP reduction to 65W, down from the 105W of the Ryzen 7 7700X. Though the chip often exceeds 65W in practice, this shift towards efficiency is commendable, echoing the success of the Ryzen 5 7600 (non-X).
Test Setup
 A PC test bench with DDR5 RAM installed.Image: A PC test bench showcasing installed DDR5 RAM modules.
A PC test bench with DDR5 RAM installed.Image: A PC test bench showcasing installed DDR5 RAM modules.
Two comparable test configurations were used, one for AMD and one for Intel. Both included high-end motherboards, 360mm AIO liquid coolers, 32GB of DDR5-6000 memory, a 1200W PSU (AMD) / 850W PSU (Intel), and an RTX 4080 Founders Edition GPU. All BIOS settings were default, with XMP/EXPO and Resizable BAR enabled on both platforms.
| Component | AMD | Intel |
|---|---|---|
| GPU | RTX 4080 Founders Edition | RTX 4080 Founders Edition |
| RAM | 32GB Gigabyte Aorus DDR5-6000 | 32GB Corsair Vengeance DDR5-6000 |
| Motherboard | Gigabyte X670E Aorus Master | MSI MPG Z790 MAG Tomahawk |
| CPU Cooler | Corsair H150i Elite Capellix | Corsair H150i Elite Capellix |
| Power Supply | Gigabyte Aorus P1200W | MSI MPG A850GF |
| Storage | Corsair MP400 1TB | MSI M450 1TB |
Current discussions around BIOS settings and Intel CPU instability are acknowledged. These issues are still being addressed, and performance may shift once stability is achieved. The presented performance data reflects out-of-the-box expectations for each CPU.
Productivity Performance
Cinebench R23 highlights AMD’s single-core advancements. The new chips surpass all but the Core i9-13900K and Core i9-14900K, demonstrating a significant leap, especially considering these are the lower-tier Zen 5 offerings. The Ryzen 7 9700X achieves near Core i9-14900K performance despite a lower clock speed.
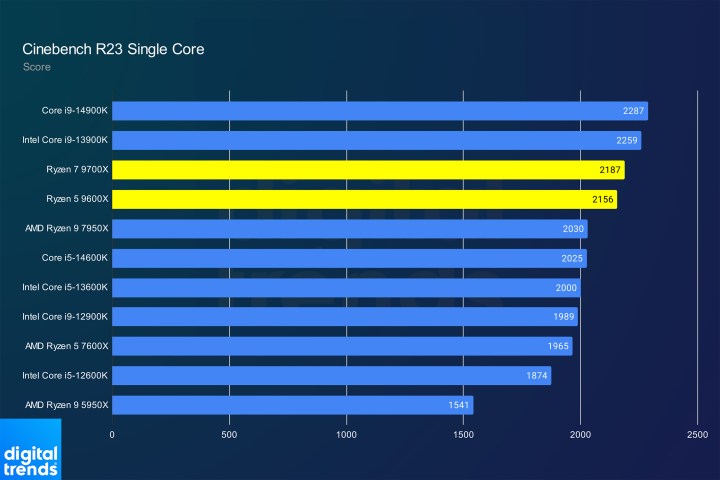 Single core performanceImage: Single-core performance comparison in Cinebench R23.
Single core performanceImage: Single-core performance comparison in Cinebench R23.
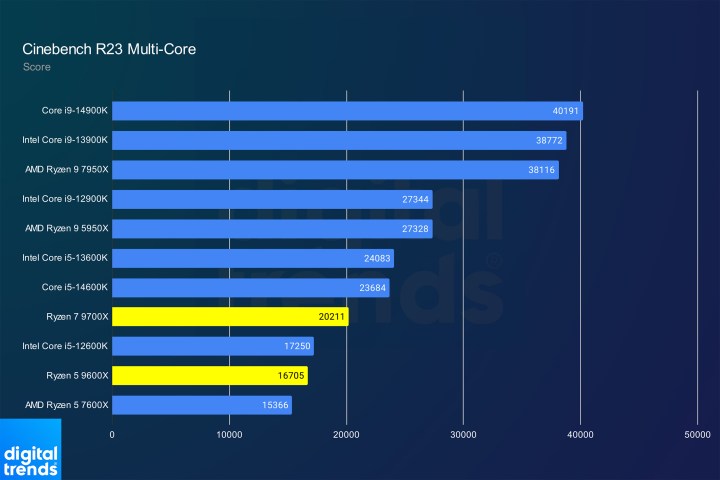 Multi-core performanceImage: Multi-core performance comparison in Cinebench R23.
Multi-core performanceImage: Multi-core performance comparison in Cinebench R23.
As expected, multi-core performance is less striking. Intel’s hybrid architecture allows for higher core counts, which benefit multi-threaded tests like Cinebench. However, improvements are still evident. The Ryzen 5 9600X matches the Core i5-12600K despite having four fewer cores.
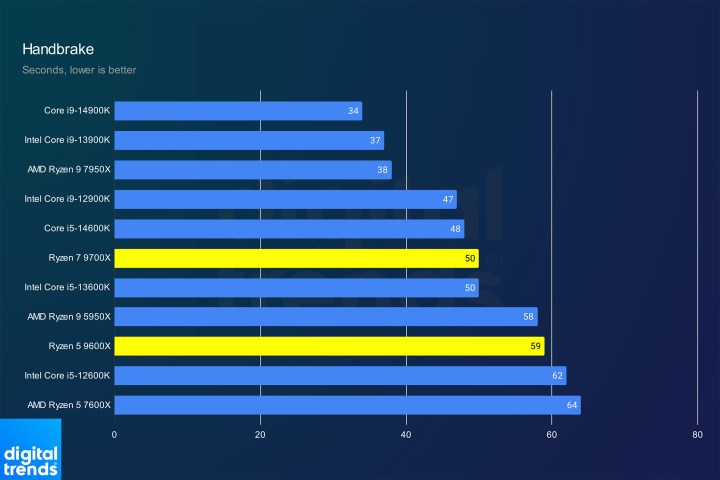 Handbrake performanceImage: Handbrake transcoding performance comparison.
Handbrake performanceImage: Handbrake transcoding performance comparison.
In Handbrake, the six-core Ryzen 5 9600X rivals the 16-core Ryzen 9 5950X, while the Ryzen 7 9700X closely trails the Core i5-14600K.
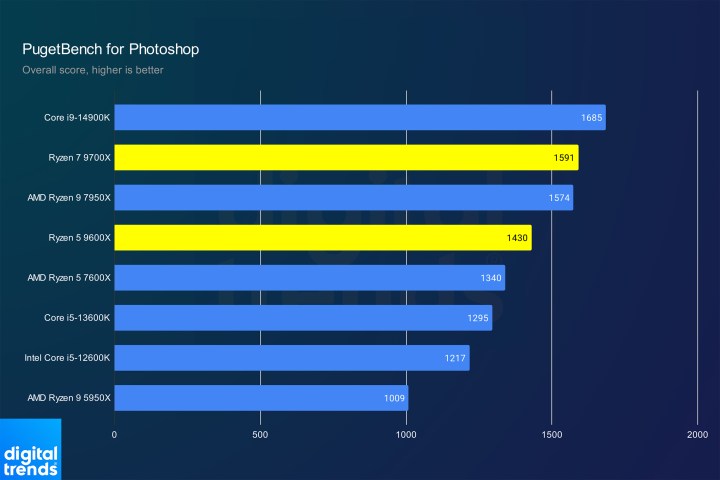 Photoshop performanceImage: Photoshop performance comparison.
Photoshop performanceImage: Photoshop performance comparison.
Photoshop performance is even more remarkable. The Ryzen 7 9700X matches the Ryzen 9 7950X, with the Ryzen 5 9600X not far behind. While Photoshop isn’t the most demanding application, it showcases the performance gains.
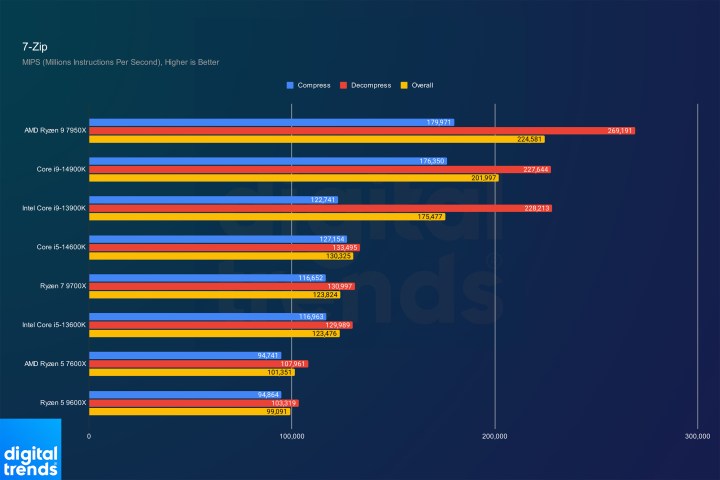 7-Zip PerformanceImage: 7-Zip benchmark results.
7-Zip PerformanceImage: 7-Zip benchmark results.
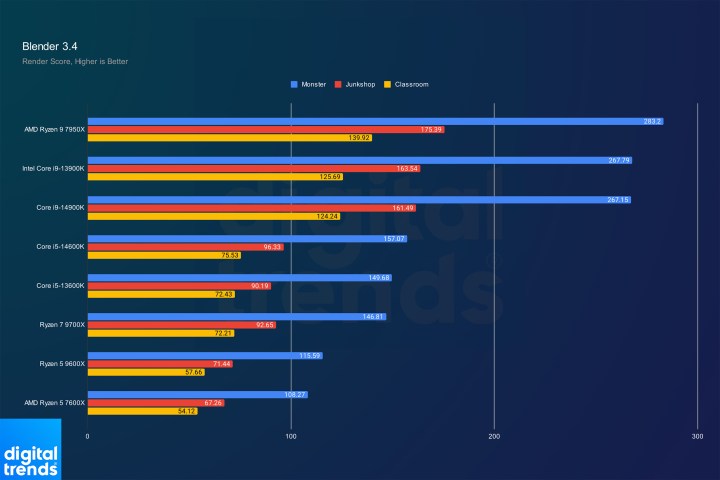 Blender PerformanceImage: Blender benchmark results.
Blender PerformanceImage: Blender benchmark results.
However, some results are less impressive. In Blender and 7-Zip, the new CPUs offer minimal improvements, with the Ryzen 5 9600X even slightly underperforming the Ryzen 5 7600X in 7-Zip.
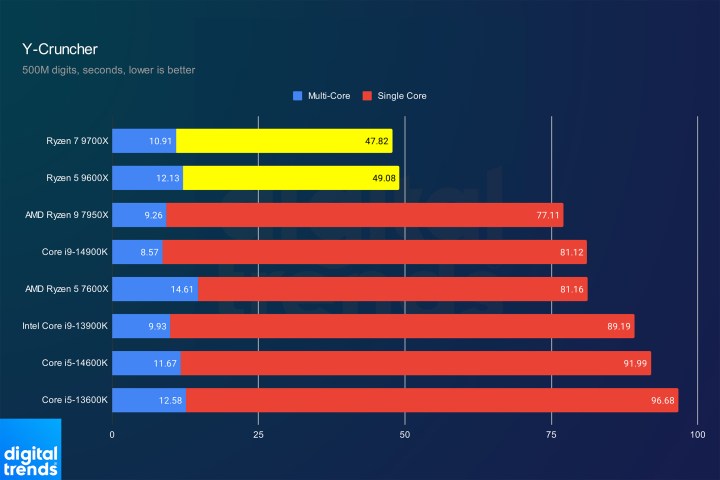 Y-Cruncher PerformanceImage: Y-Cruncher benchmark results.
Y-Cruncher PerformanceImage: Y-Cruncher benchmark results.
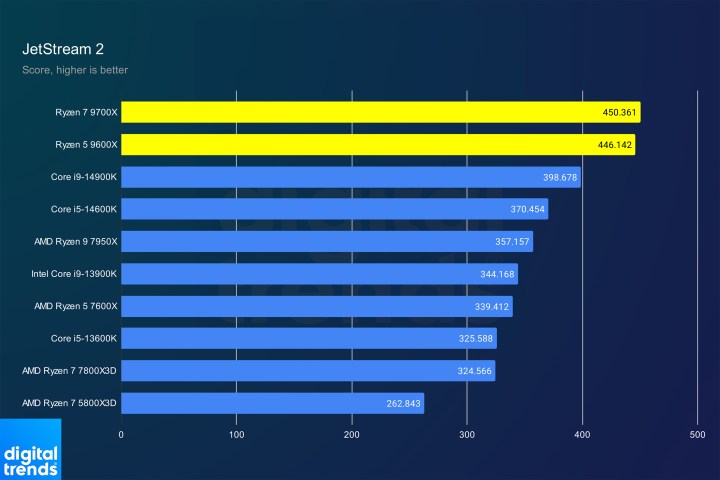 Jetstream 2 PerformanceImage: Jetstream 2 browser benchmark results.
Jetstream 2 PerformanceImage: Jetstream 2 browser benchmark results.
Conversely, JetStream 2 and Y-Cruncher showcase exceptional gains. The new CPUs deliver record-breaking JetStream 2 scores and dominate Y-Cruncher’s pi calculation, outperforming even flagship CPUs. While these are specific tests, they highlight Zen 5’s potential.
These CPUs excel in tasks like photo editing and video transcoding. However, performance gains vary depending on the workload. Zen 5 represents a new foundation, and further refinements are expected to address performance discrepancies in specific areas.
Gaming Performance
Evaluating gaming performance for the Ryzen 5 9600X and Ryzen 7 9700X is complex. While performance is decent, AMD’s 3D V-Cache technology remains crucial for achieving top frame rates. Gamers should prioritize 3D V-Cache variants over these standard models.
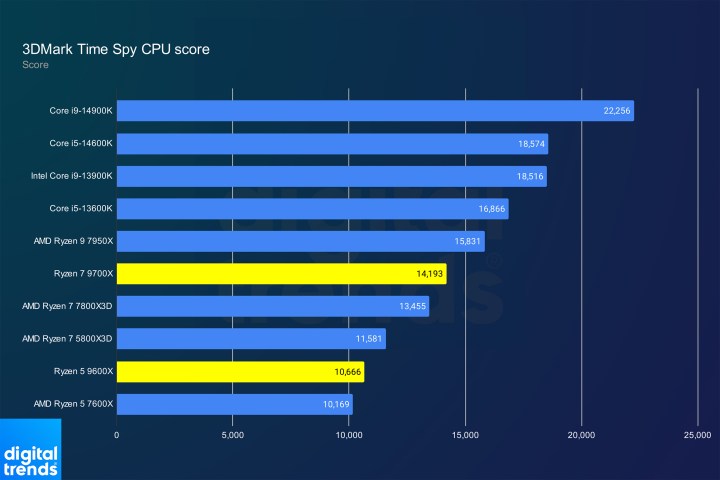 3DMark Time Spy PerformanceImage: 3DMark Time Spy CPU benchmark results.
3DMark Time Spy PerformanceImage: 3DMark Time Spy CPU benchmark results.
Broadly, Zen 5 offers improved gaming performance. The Ryzen 7 9700X surpasses the Ryzen 7 7800X3D in 3DMark Time Spy, and the Ryzen 5 9600X provides a modest uplift over its predecessor. However, real-world game performance presents a different picture.
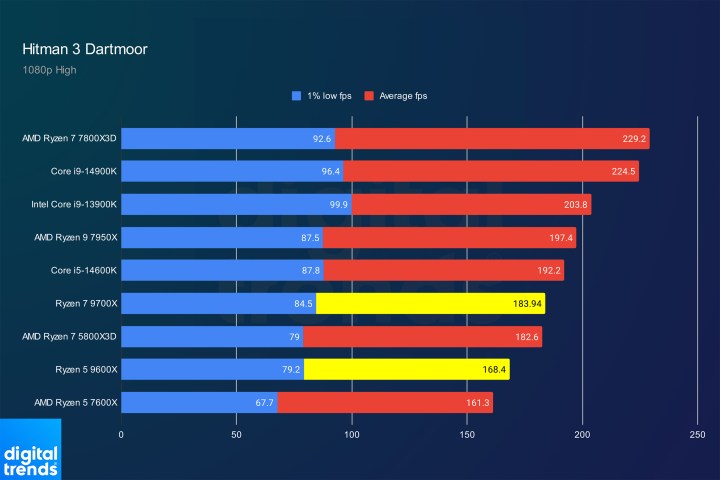 Hitman 3 PerformanceImage: Hitman 3 gaming benchmark results.
Hitman 3 PerformanceImage: Hitman 3 gaming benchmark results.
In Hitman 3, the Ryzen 7 9700X outperforms the Ryzen 7 5800X3D, but both lag significantly behind the Ryzen 7 7800X3D.
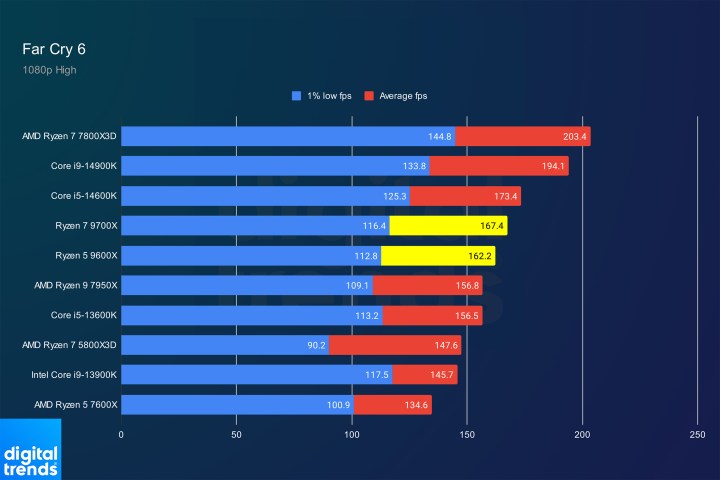 Far Cry 6 PerformanceImage: Far Cry 6 gaming benchmark results.
Far Cry 6 PerformanceImage: Far Cry 6 gaming benchmark results.
Far Cry 6 showcases a solid generational uplift, with the Ryzen 5 9600X even surpassing the Ryzen 9 7950X. However, the Ryzen 7 7800X3D remains significantly faster. PC gamers cannot ignore the advantages of 3D V-Cache. Waiting for the inevitable 3D V-Cache versions of these Zen 5 CPUs is advisable.
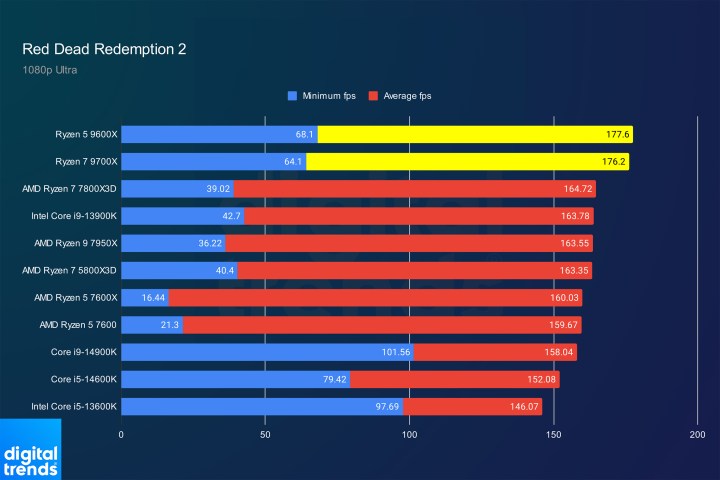 Red Dead Redemption 2 PerformanceImage: Red Dead Redemption 2 gaming benchmark results.
Red Dead Redemption 2 PerformanceImage: Red Dead Redemption 2 gaming benchmark results.
Red Dead Redemption 2 reveals interesting performance anomalies. The new Zen 5 CPUs break through a performance ceiling encountered by all other tested CPUs, including the Ryzen 7 7800X3D. This suggests significant potential for future 3D V-Cache versions.
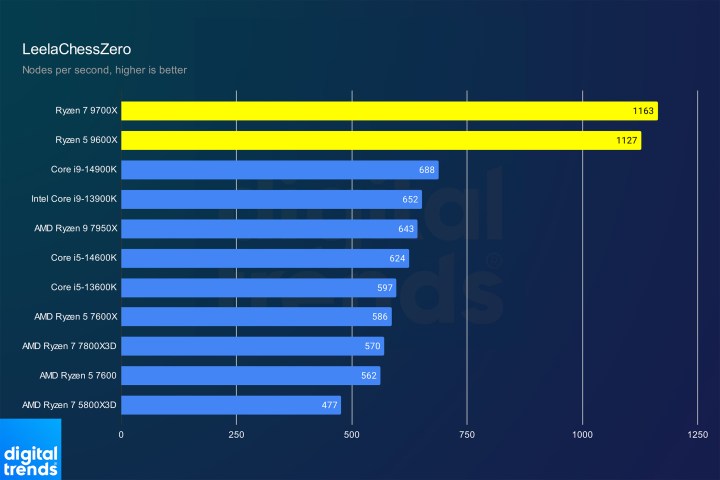 LeelaChessZero PerformanceImage: LeelaChessZero benchmark results.
LeelaChessZero PerformanceImage: LeelaChessZero benchmark results.
Finally, LeelaChessZero undeniably demonstrates the impact of the dedicated 512-bit AVX-512 data path. The massive performance improvement underscores the significance of this architectural advancement.
Should You Buy the Ryzen 5 9600X and Ryzen 7 9700X?
 AMD Ryzen 5 9600XImage: The AMD Ryzen 5 9600X held between two fingers.
AMD Ryzen 5 9600XImage: The AMD Ryzen 5 9600X held between two fingers.
Priced at $280 and $360 respectively, the Ryzen 5 9600X and Ryzen 7 9700X are attractive CPUs. AMD delivers a generational performance boost at a lower price. However, the unusual performance characteristics in various workloads should be considered.
Upgrading from Zen 4 isn’t justifiable unless specific workloads benefit significantly from AVX-512. Gamers should continue to prioritize the Ryzen 7 5800X3D or Ryzen 7 7800X3D, as 3D V-Cache remains crucial for optimal gaming performance.
For users yet to adopt the AM5 platform, these new CPUs are excellent choices, especially with decreasing DDR5 memory prices. However, current AM5 users can likely skip this generation, given AMD’s commitment to future generations on this socket.