Hybrid cars, once considered niche “science projects,” have become mainstream, powering everything from everyday sedans to high-performance supercars. With increasing environmental concerns and stricter emissions regulations, hybrids are poised to become even more prevalent in the coming years. This article explores what hybrid cars are, how they function, the various types available, and the advantages they offer.
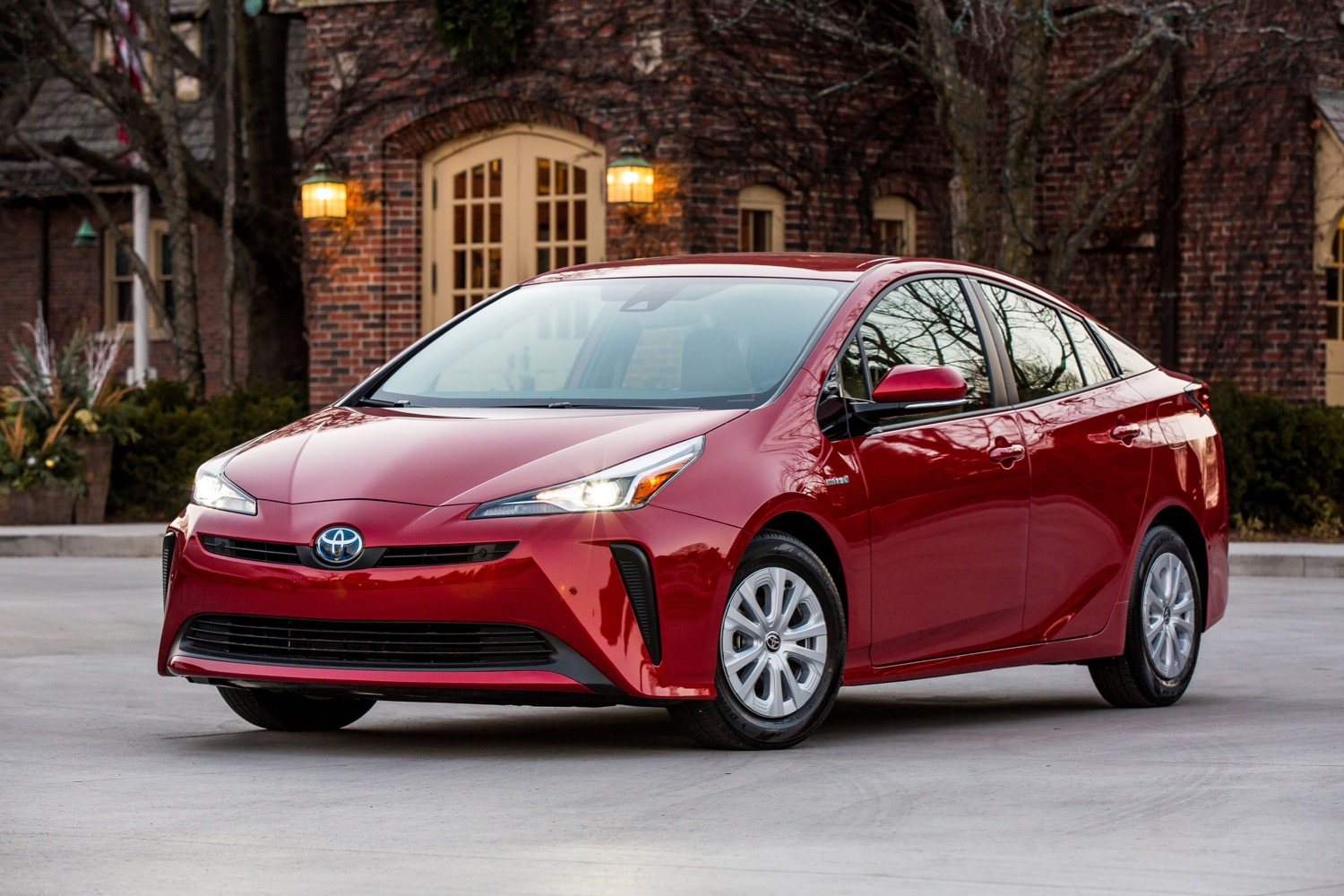 2020 Toyota Prius Pricing and SpecsThe Toyota Prius, a pioneer in hybrid technology.
2020 Toyota Prius Pricing and SpecsThe Toyota Prius, a pioneer in hybrid technology.
What Defines a Hybrid Car?
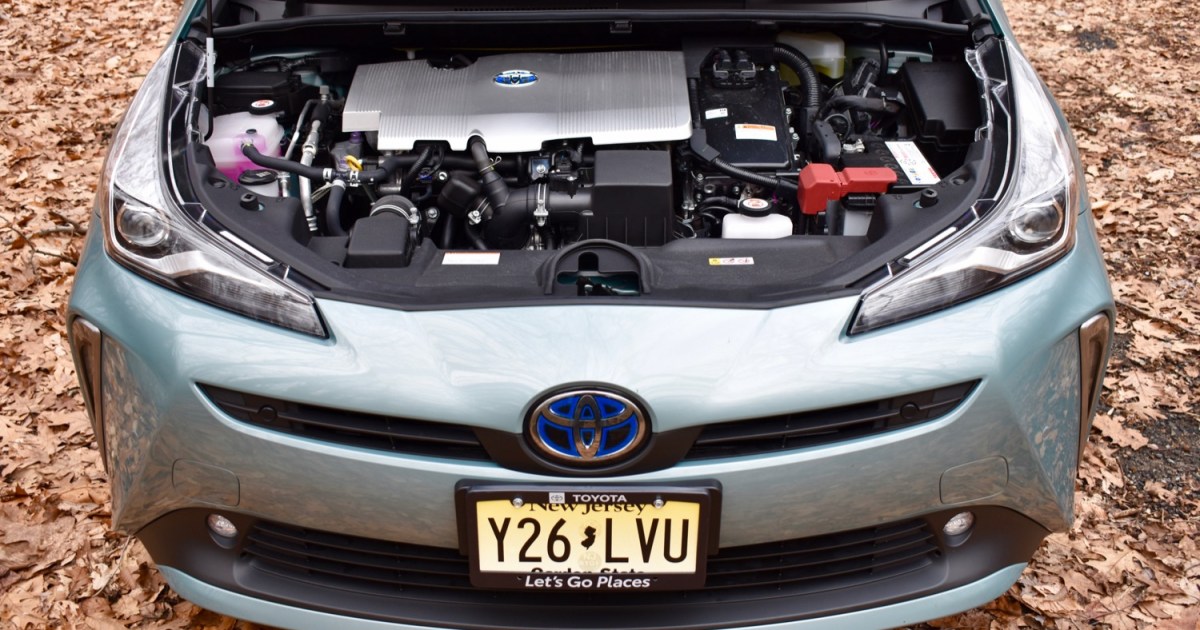
A hybrid car combines two distinct power sources: an internal combustion engine (ICE) and an electric motor. These systems work in concert to propel the vehicle, offering improved fuel efficiency and, in some cases, enhanced performance. The Toyota Prius, introduced in 1997, became the first mass-produced modern hybrid, paving the way for the hybrid vehicles we see today.
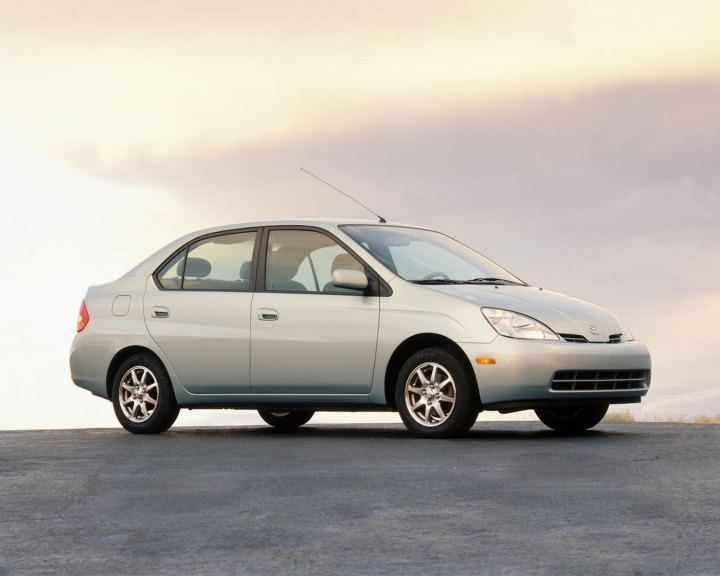 1997 Toyota PriusThe first-generation Prius marked a turning point in automotive history.
1997 Toyota PriusThe first-generation Prius marked a turning point in automotive history.
The electric motor draws power from a battery pack, typically located in the trunk or under the floor for optimal weight distribution. Under certain conditions, such as low speeds or idling, the car operates solely on electric power, resulting in zero gasoline consumption. When the battery depletes or more power is required, the ICE seamlessly engages to assist propulsion and recharge the battery.
Delving into Hybrid Functionality
While fuel efficiency remains a primary driver for hybrid adoption, the technology also offers performance benefits. Electric motors provide instant torque, complementing the ICE’s power delivery. Several types of hybrid systems exist, each with unique characteristics.
 2017 Toyota Prius PrimeThe Prius Prime’s hybrid system display provides real-time information.
2017 Toyota Prius PrimeThe Prius Prime’s hybrid system display provides real-time information.
In parallel hybrids, like the Prius, both the ICE and electric motor can power the wheels directly. Toyota’s Hybrid Synergy Drive utilizes two electric motors in place of a traditional gearbox. Other automakers, like Hyundai, integrate the electric motor within a conventional transmission.
 2018 Hyundai Sonata Hybrid Gauge ClusterThe Sonata Hybrid’s instrumentation provides insights into hybrid system operation.
2018 Hyundai Sonata Hybrid Gauge ClusterThe Sonata Hybrid’s instrumentation provides insights into hybrid system operation.
Series hybrids, less common, employ the ICE solely as a generator to charge the battery and power the electric motor. Nissan’s e-Power system exemplifies this approach.
High-performance hybrids, such as the Porsche 918, McLaren P1, and LaFerrari, leverage hybrid technology to achieve remarkable performance levels. These vehicles utilize sophisticated hybrid systems tailored for maximum power and efficiency.
Another emerging category is mild hybrids, which utilize a 48-volt electrical system alongside the standard 12-volt system. This powers a motor-generator unit connected to the engine’s crankshaft, providing electric assist and enabling smoother engine start/stop functionality.
 2018 Honda Accord Hybrid EngineThe Accord Hybrid’s engine bay showcases the integration of hybrid components.
2018 Honda Accord Hybrid EngineThe Accord Hybrid’s engine bay showcases the integration of hybrid components.
Advantages of Choosing a Hybrid
The most compelling reason to consider a hybrid is fuel savings. Hybrids significantly reduce fuel consumption, resulting in lower running costs. The increasing variety of hybrid models, from compact cars to SUVs, caters to a wide range of needs and budgets.
 2020 Hyundai Sonata HybridThe sleek design of the Sonata Hybrid demonstrates the increasing appeal of hybrid vehicles.
2020 Hyundai Sonata HybridThe sleek design of the Sonata Hybrid demonstrates the increasing appeal of hybrid vehicles.
Conclusion
Hybrid vehicles offer a compelling blend of fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and, in some cases, enhanced performance. As technology advances and charging infrastructure expands, hybrids are likely to play an increasingly important role in the automotive landscape. Careful consideration of individual needs and available options is crucial when choosing a hybrid vehicle.