The discovery of Homo floresiensis, nicknamed the “Hobbit,” on the Indonesian island of Flores in 2004 revolutionized our understanding of human evolution. Now, new fossil evidence pushes the story back even further, revealing an even smaller ancestor. These findings shed light on the evolutionary journey of these diminutive hominins.
Tiny Fossils Reveal an Even Smaller Ancestor
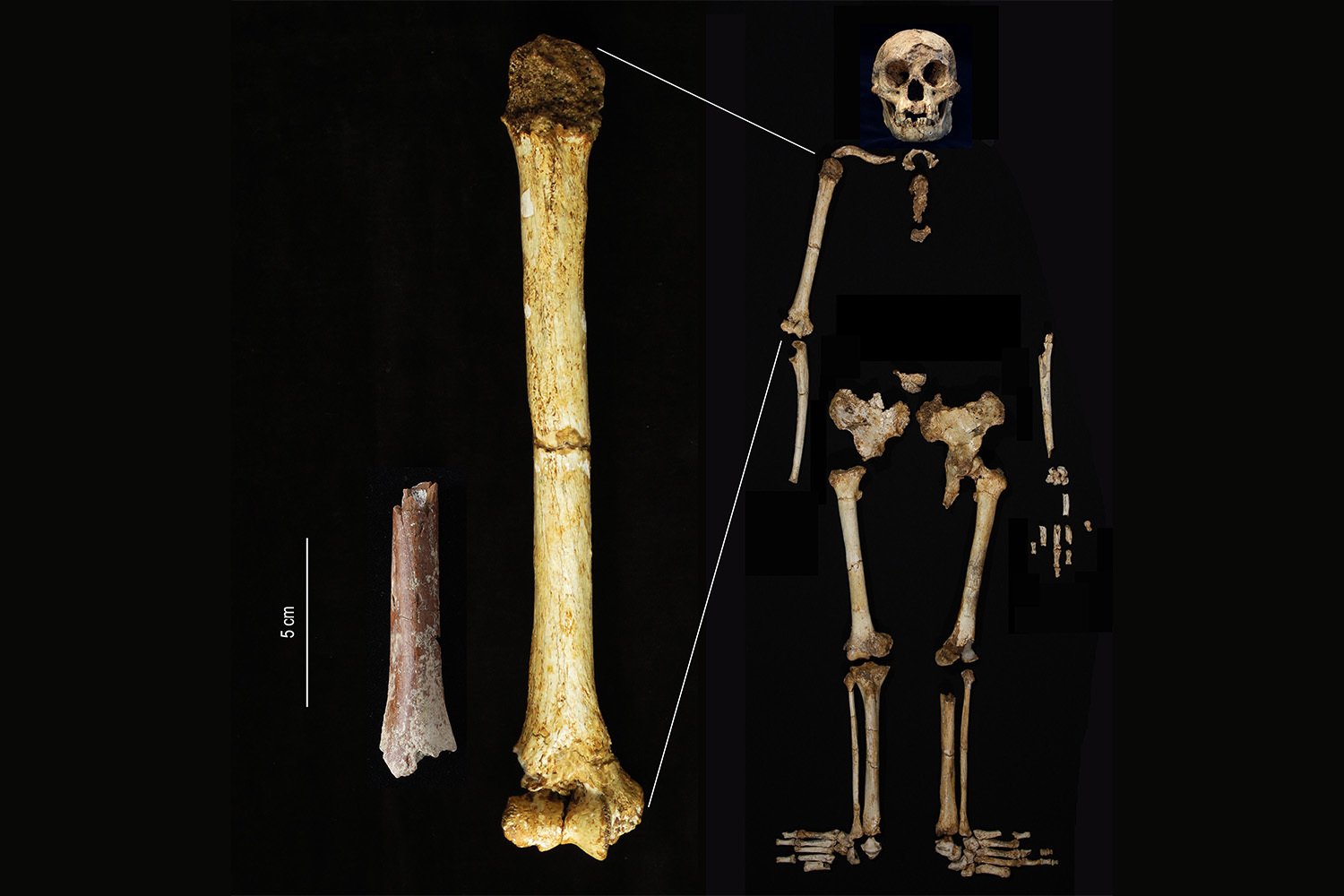
The original H. floresiensis remains, dating back approximately 60,000 years, revealed adults standing at just 3 feet 7 inches (109 centimeters) tall. The new research, published in Nature Communications, describes teeth, jaw fragments, and a piece of a humerus (upper arm bone) from at least four H. floresiensis individuals. These fossils are significantly older, approximately 700,000 years old, and notably smaller than the later Liang Bua finds.
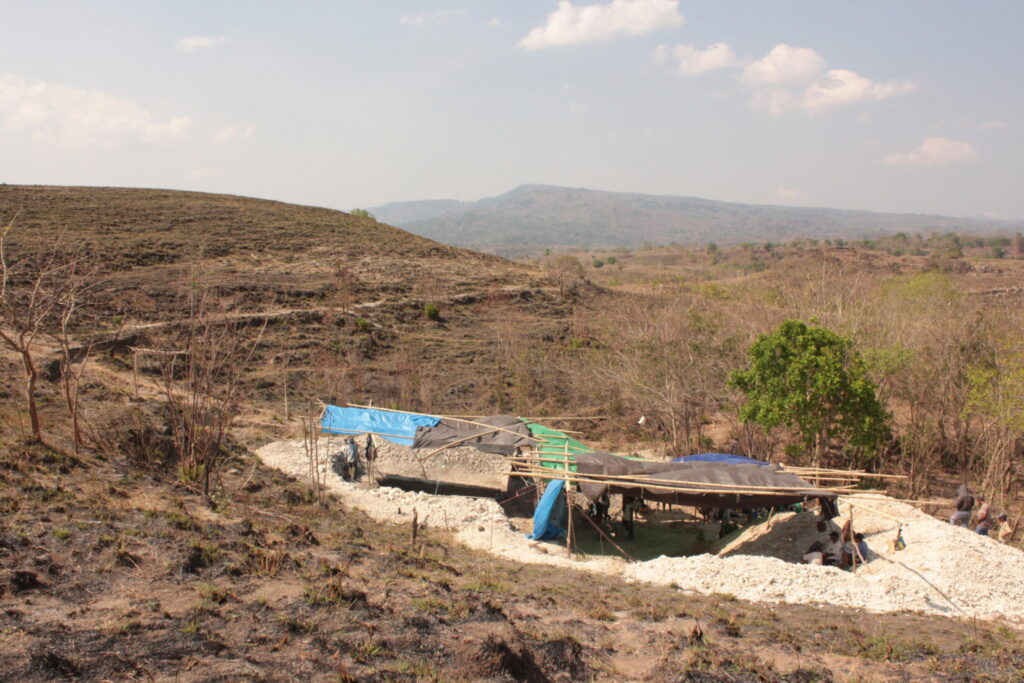 The Mata Menge excavation in 2014.The Mata Menge excavation site in 2014, where the new H. floresiensis fossils were discovered. Photo: Gerrit van den Bergh
The Mata Menge excavation in 2014.The Mata Menge excavation site in 2014, where the new H. floresiensis fossils were discovered. Photo: Gerrit van den Bergh
The Smallest Hominin Arm Bone Ever Found
The newly discovered humerus, measuring a mere 3.46 inches (8.79 centimeters) long, suggests an adult individual standing only 3.28 feet (100 cm) tall. This makes it the smallest hominin upper arm bone ever discovered, further emphasizing the diminutive stature of these early Hobbits. The findings reinforce the connection between the older Mata Menge remains and the younger Liang Bua specimens, highlighting the consistent small body size across a vast time span. This continuous lineage offers exciting prospects for future research into hominin evolution.
Island Dwarfism and the Hobbit Lineage
H. floresiensis coexisted on Flores with Stegodon, a now-extinct dwarf elephant, until their extinction roughly 50,000 years ago, around the time modern humans appeared in Southeast Asia. The small size of both the Hobbit and the Stegodon suggests insular dwarfism, an evolutionary process where limited resources on islands lead to a reduction in body size. The discovery of another small-statured hominin, Homo luzonensis, on the Philippine island of Luzon further supports this phenomenon.
Unraveling the Hobbit’s Ancestry
While previous theories suggested a link between H. floresiensis and Denisovans, another extinct hominin group, the age of the Mata Menge fossils predates the earliest Denisovan evidence. This makes a Denisovan ancestry less likely. The current research proposes a descent from Homo erectus in Java, citing similarities in teeth morphology and stone tools found in the So’a Basin. These tools suggest H. erectus may have been isolated on Flores about a million years ago, undergoing a gradual reduction in size over the subsequent 300,000 years.
Puzzles and Future Directions
However, the evolutionary path of the Hobbit isn’t entirely clear. The wrist bones of H. floresiensis resemble those of Australopithecus afarensis and chimpanzees, rather than humans, presenting a significant puzzle. This raises questions about whether early H. erectus possessed similar wrist bones, or if H. floresiensis re-evolved this primitive anatomy. Furthermore, while insular dwarfism likely occurred on Flores, it may have also impacted other nearby islands like Sumbawa or Sulawesi.
The Search Continues
The discovery of these smaller, older Hobbit ancestors adds a new chapter to the story of human evolution. While the 700,000-year-old arm bone sets a new record for the smallest ancient human, many questions remain. Further fossil discoveries and research are crucial to fully understanding the origins and ultimate fate of these fascinating small-statured hominins.