Jump-starting a car is a simple process that can save you time and money, especially if you have the right tools. This guide provides a step-by-step walkthrough to get your car back on the road in minutes.
Why Do Car Batteries Die?
Regularly driven cars rarely experience a dead battery. Dead batteries are more common when vehicles are left unused for extended periods. Older batteries also struggle to hold a charge, leading to unexpected failures. Leaving power-consuming accessories like the radio on with the engine off can quickly drain your battery.
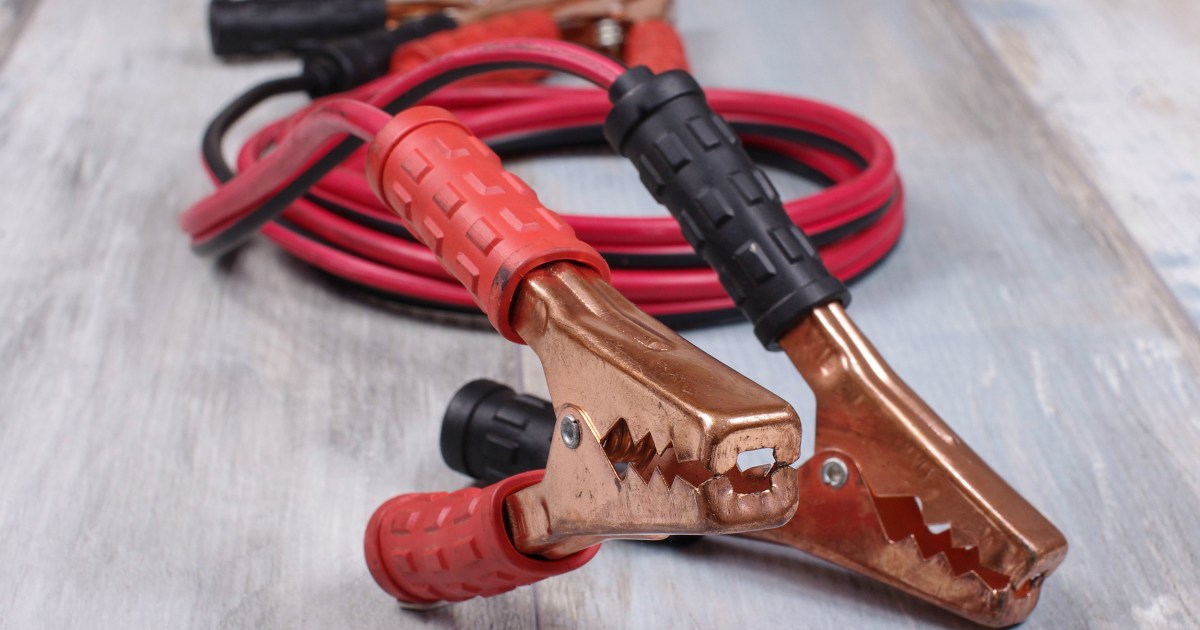
Step 1: Equip Yourself with Jumper Cables
Keeping a set of jumper cables in your car is essential. While any set will work, we recommend 4 to 6 gauge cables, 10 to 20 feet long. This size offers reliable performance and flexibility for various parking situations. Excessively long cables can reduce the charge strength, so avoid those. Portable jump-starters are an alternative, but remember to keep their internal batteries charged.
Step 2: Locate a Power Source
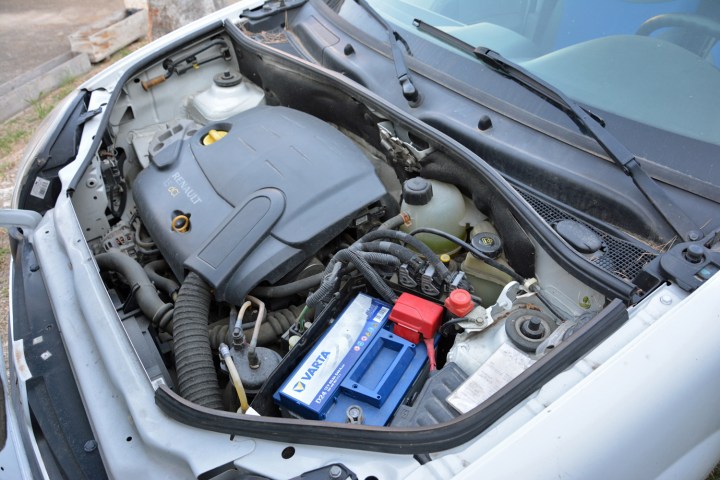 altConnecting jumper cables requires access to both batteries.
altConnecting jumper cables requires access to both batteries.
You’ll need a running vehicle parked close enough to your dead car for the jumper cables to reach both batteries. Locate the battery in both vehicles. Batteries are typically in the engine compartment towards the front, but not always. They might be under plastic covers, in the trunk, or even under the rear seat. Knowing your car’s battery location beforehand saves valuable time during a jump-start. Some vehicles have specific jump points; consult your owner’s manual for these.
Step 3: Connecting the Jumper Cables
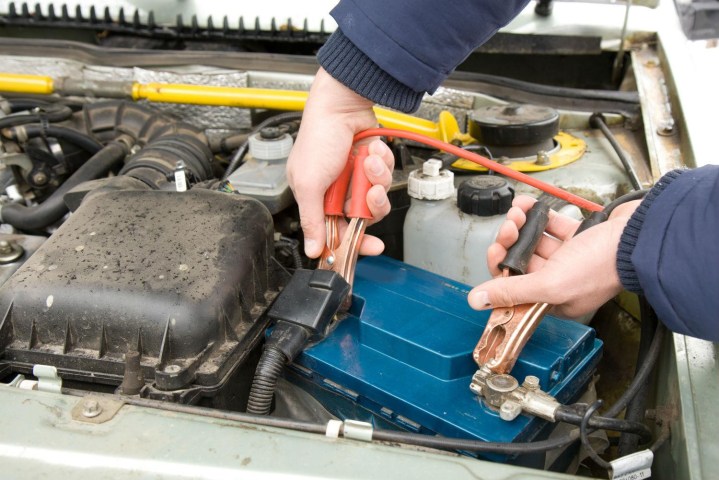 altProperly connecting jumper cables is crucial for a successful jump-start.
altProperly connecting jumper cables is crucial for a successful jump-start.
Once the running vehicle is positioned, turn it off and open both hoods. When handling jumper cables, prevent the red (positive) and black (negative) clamps from touching each other. Contact between the clamps while current is flowing can cause sparks and potentially short-circuit one or both vehicles. Having a person at each end of the cables simplifies the process.
The clamps connect to the battery terminals, which are exposed metal nodes with wires attached. Clean any dirt or grime from the terminals before connecting the cables to ensure a good connection. Identify the positive (+) and negative (–) terminals, usually marked on the battery. The positive terminal might be under a red cover. If unsure, seek assistance to avoid potential damage.
Connect one red clamp to the positive terminal of the dead battery. Connect the other red clamp to the positive terminal of the live battery. Next, connect one black clamp to the negative terminal of the live battery. For the final connection, attach the other black clamp to an unpainted metal surface on the dead car’s chassis, away from the battery. This grounding method enhances safety.
Step 4: Starting the Car
 altStarting the car after connecting the jumper cables.
altStarting the car after connecting the jumper cables.
After connecting the cables, try starting the dead car. If it starts immediately, the process is complete. If not, let the running car run for a few minutes to provide additional charge. If the car still doesn’t start after a second attempt, the battery might be faulty or other issues may be present.
If the car starts, keep it running and disconnect the cables in reverse order: remove the black clamp from the grounded metal surface, then the black clamp from the live battery, followed by the red clamps from both batteries. Avoid letting the clamps touch each other during removal.
Keep the revived car running and drive for at least 15 minutes to recharge its battery. Store the jumper cables in your car for future use. If you frequently need to jump-start your car despite a good battery, your alternator might be the problem.
Conclusion
Jump-starting a car is a straightforward process with these steps. Remember to prioritize safety and double-check connections to avoid potential issues. Keeping jumper cables handy and understanding the process can save you from a frustrating situation. For further car maintenance tips, explore our guide on understanding check engine lights.