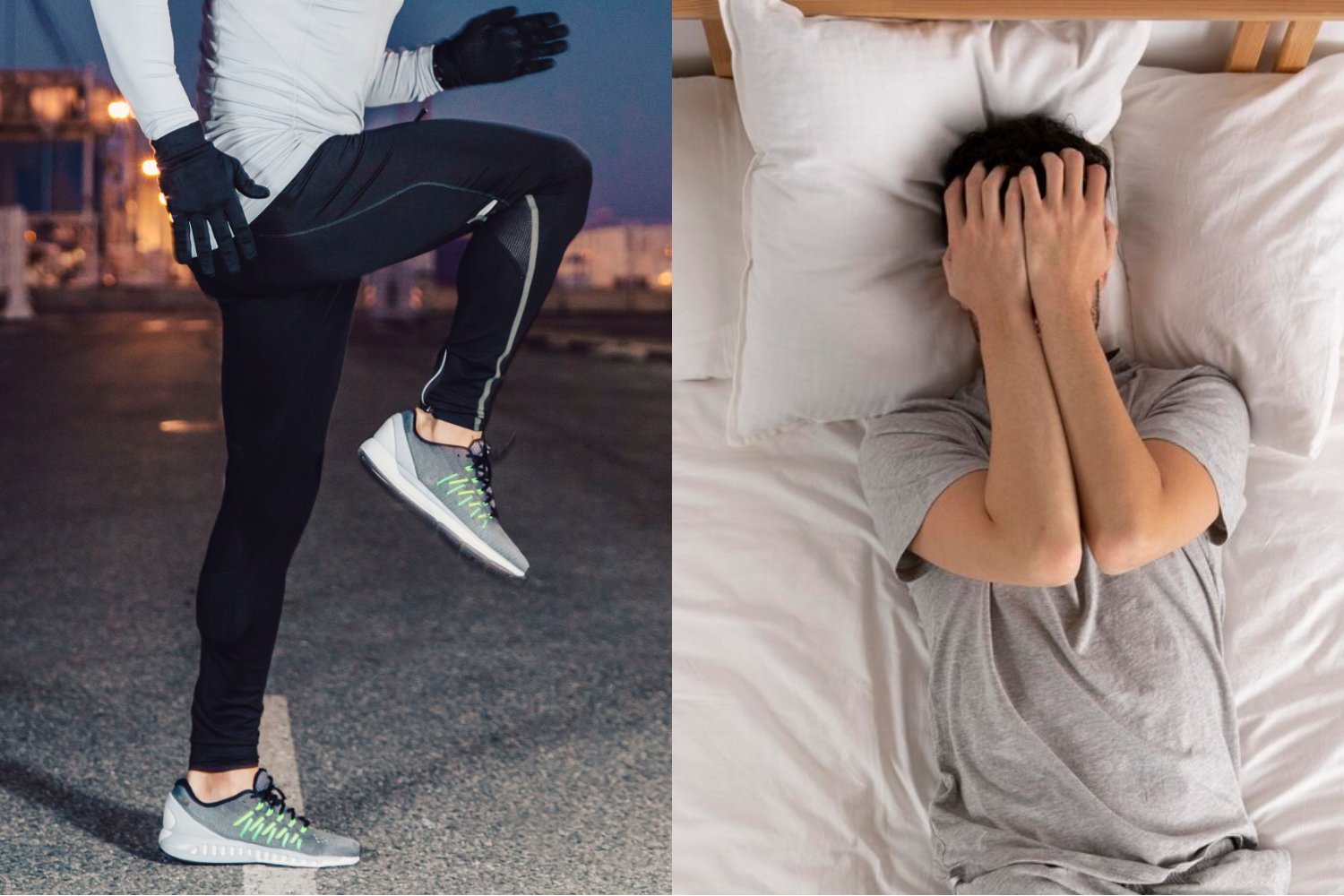
Late-night workouts are often seen as a necessary evil when busy schedules leave little room for exercise. But is squeezing in a quick, intense session before bed really beneficial? A recent study suggests that intense workouts close to bedtime might actually hinder your sleep quality.
This large-scale study, involving nearly 15,000 participants and tracking over four million nights of sleep, revealed a correlation between late-night exercise and sleep disruption. Researchers found that vigorous exercise within four hours of sleep was associated with increased time to fall asleep, reduced total sleep time, and poorer overall sleep quality. Furthermore, the study linked late workouts to a higher nocturnal resting heart rate and lower nocturnal heart rate variability, both potential indicators of health risks.
Previous studies on this topic have yielded mixed results, with some suggesting minimal impact from late workouts. However, researchers argue that these studies often had smaller sample sizes, controlled laboratory settings, and didn’t always involve workouts that significantly challenged the cardiovascular system. This new research, published in Nature Communications, aimed to address these limitations with a more comprehensive approach using biometric data and a larger, more representative sample.
The study meticulously controlled for factors like age, gender, season, weekday, fitness levels, and prior sleep patterns to isolate the effects of late-night exercise. The findings highlight that strenuous exercises, characterized by sustained increases in breathing rate, heart rate, body temperature, and mental alertness, can interfere with subsequent sleep. High-intensity interval training (HIIT), long-distance running, and competitive sports are examples of such activities.
While the study emphasizes the potential drawbacks of intense evening workouts, it also offers practical advice. For those who prefer exercising closer to bedtime, opting for shorter, low-intensity activities like gentle jogging or swimming may minimize sleep disruption and allow the body to wind down.
This research contributes valuable insights into the relationship between exercise timing and sleep health. By understanding how late-night workouts can affect sleep quality, individuals can make informed decisions about their exercise routines to prioritize both physical activity and restful sleep.
Ultimately, finding the right balance between exercise and sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being.