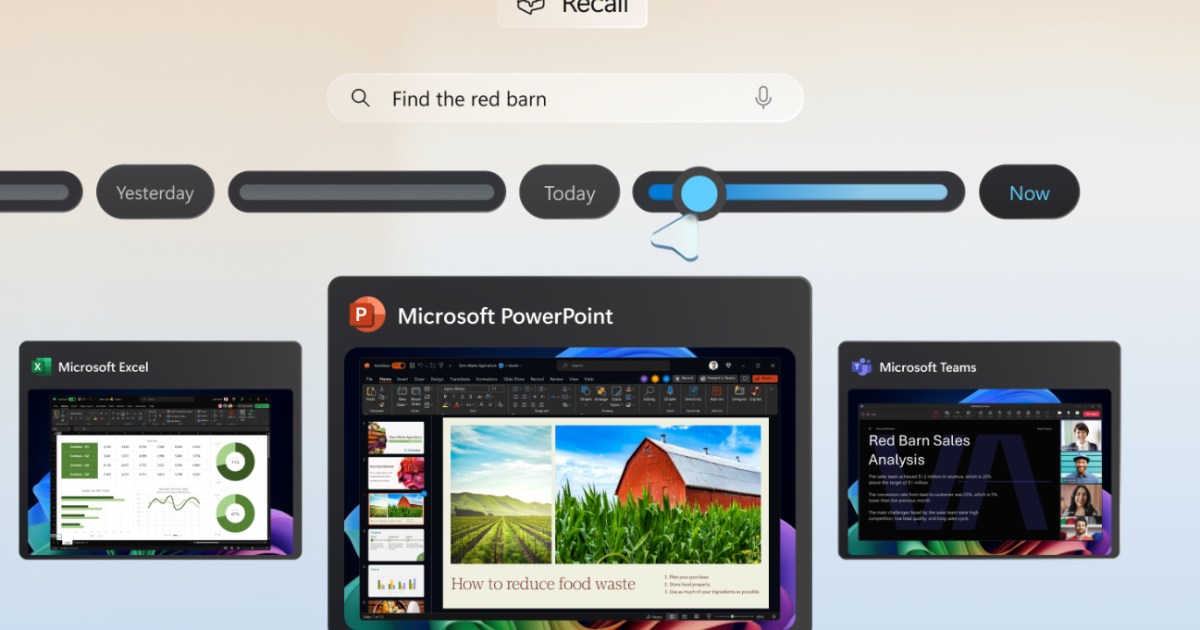
Microsoft has published an updated blog post detailing the security and privacy features of its Recall AI assistant. This post addresses concerns about data privacy and outlines the safeguards Microsoft has implemented, emphasizing user control and data protection.
User Control and Opt-in Features
A core principle of Recall is user control. Users can choose whether to enable Recall during the Copilot+ PC setup process. If opted out, Recall remains inactive. Microsoft clarifies that Recall can be removed in Windows settings, although the exact nature of this removal (complete uninstallation or disabling) remains unclear.
For those who opt in, granular control is provided. Users can specify which apps and websites are excluded from Recall’s data collection. Incognito browsing activity is never saved. Users also manage data retention duration and allocated disk space. Snapshots can be deleted based on time range or by specific app or website. Microsoft emphasizes the ability to delete any Recall data at any time.
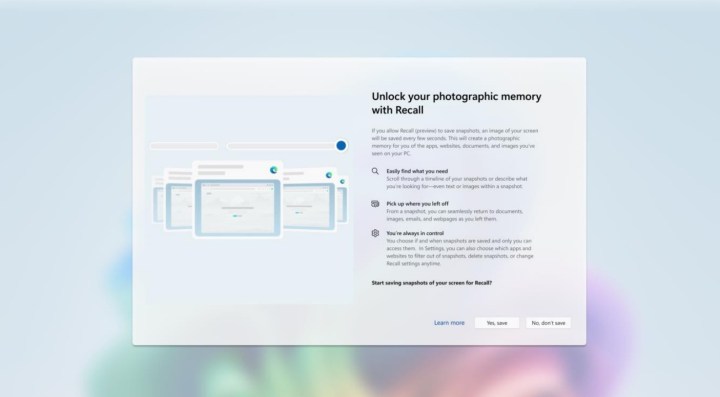 Setting up Microsoft Recall.
Setting up Microsoft Recall.
A system tray icon indicates when Recall is actively capturing snapshots, allowing users to pause the process. Accessing Recall content requires biometric authentication via Windows Hello.
Hardware and Software Security Measures
Recall operates exclusively on Copilot+-eligible PCs, which have stringent hardware requirements: TPM 2.0, System Guard Secure Launch, and Kernel DMA Protection. These features enhance the overall security of the system and contribute to Recall’s data protection.
 Recall promotional image.
Recall promotional image.
Sensitive data within Recall is encrypted, protected by the TPM, and linked to the user’s Windows Hello identity. Data resides within the Virtualization-based Security Enclave (VBS Enclave), isolating it from other users and processes. Only authorized data is released from the enclave upon request.
Microsoft explains the architecture further, stating that external processes never directly access snapshots or encryption keys. They receive only authorized data returned from the enclave. Sensitive content filtering prevents Recall from storing passwords, ID numbers, and credit card details.
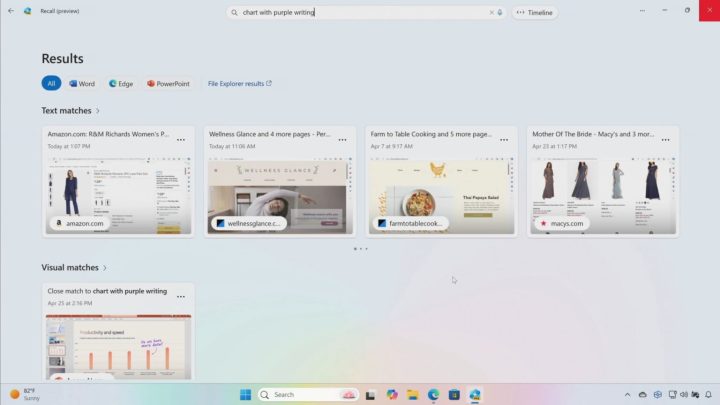 A screenshot of the Recall feature in Windows.
A screenshot of the Recall feature in Windows.
Third-Party Validation and Future Outlook
Microsoft has commissioned a penetration test by a third-party security vendor to independently verify Recall’s security.
Conclusion
Microsoft’s comprehensive approach to Recall’s security and privacy, including user controls, hardware and software safeguards, and third-party testing, demonstrates a commitment to addressing user concerns. While the long-term effectiveness of these measures remains to be seen, Microsoft’s proactive efforts to build trust are evident. Whether these measures will fully convince skeptics is uncertain, but the company is actively working to demonstrate the trustworthiness of its AI assistant.