Nvidia, a leading GPU manufacturer in the AI industry, has announced the release of NVLM 1.0, an open-source large language model (LLM) designed to compete with proprietary models like OpenAI’s GPT-4, Anthropic’s Claude, Meta’s Llama 2, and Google’s Gemini. This new family of LLMs, spearheaded by the 72 billion-parameter NVLM-D-72B model, boasts state-of-the-art performance in vision-language tasks, as detailed in a recently published white paper.
 Nvidia CEO Jensen in front of a background.
Nvidia CEO Jensen in front of a background.
The researchers claim NVLM 1.0 achieves results comparable to leading proprietary and open-access models. This “production-grade multimodality” enables exceptional performance across various vision and language tasks, exceeding the capabilities of the base LLM it’s built upon. The team achieved this by incorporating a high-quality text-only dataset into multimodal training, along with substantial multimodal math and reasoning data, resulting in enhanced math and coding capabilities across modalities.
The NVLM models can perform diverse tasks, from explaining the humor in a meme to solving complex mathematical equations step-by-step. Furthermore, Nvidia’s multimodal training approach has boosted the model’s text-only accuracy by an average of 4.3 points across standard industry benchmarks.
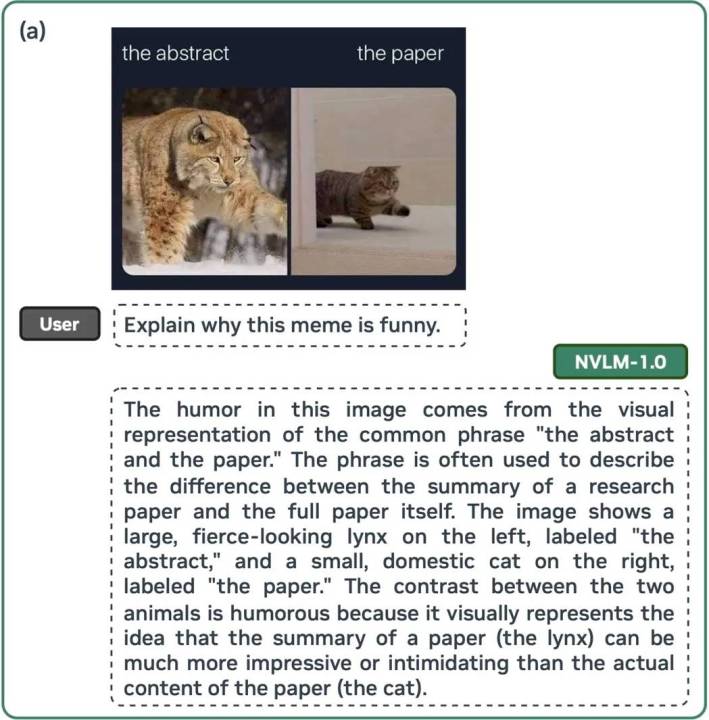 screenshot of the NVLM white paper explaining the process of explaining why a meme is funny
screenshot of the NVLM white paper explaining the process of explaining why a meme is funny
Nvidia’s commitment to open-source principles is evident in their decision to make the NVLM training weights publicly available and their promise to release the source code soon. This contrasts sharply with the closed-source approach of competitors like OpenAI and Google, who restrict access to their LLM weights and code. Instead of directly competing with established models like GPT-4 and Gemini 1.5 Pro, Nvidia aims to empower third-party developers to leverage NVLM as a foundation for building their own chatbots and AI applications. This open-source strategy positions NVLM as a potential catalyst for innovation in the LLM ecosystem.