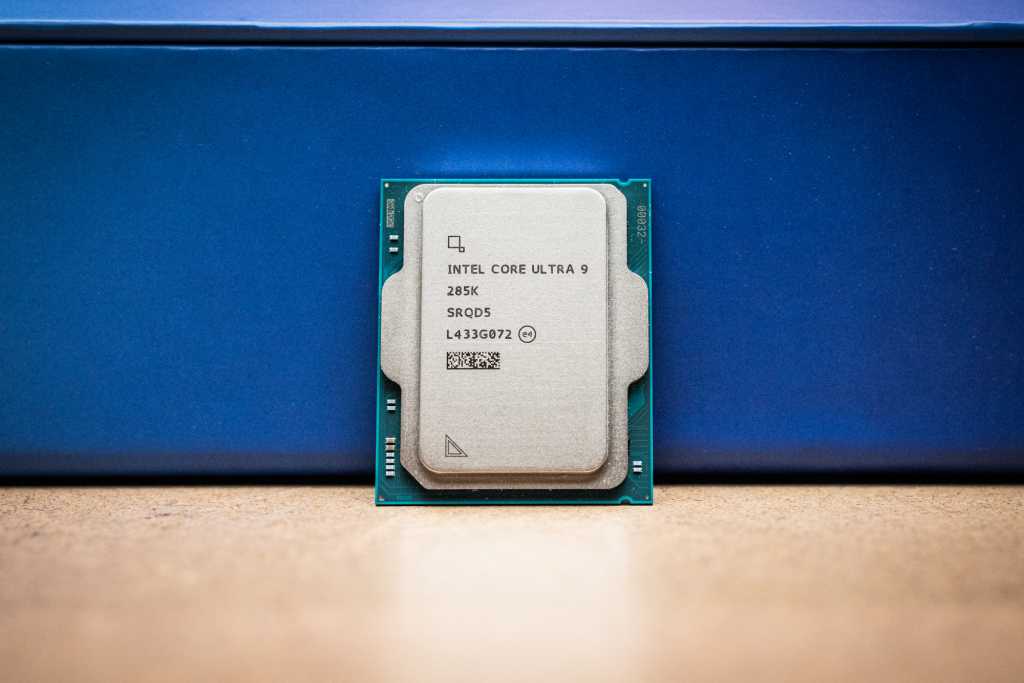
Intel’s new Core Ultra 200S series, codenamed Arrow Lake, marks a radical departure from previous Intel desktop CPUs. These processors boast improved speed and power efficiency compared to Raptor Lake, but their significance extends beyond performance. As the first desktop x86 processors shipped but not fabricated by Intel, Arrow Lake represents a significant shift in the company’s approach. Our extensive testing of the flagship Core Ultra 9 285K reveals key insights into this new generation.
 Intel Arrow Lake 245K and 285K side by side
Intel Arrow Lake 245K and 285K side by side
A New Naming Convention
Intel revamped its Core processor naming scheme last year, dropping the “i” prefix and generation reference. The “Ultra” designation now signifies CPUs with integrated Arc graphics and a Neural Processing Unit (NPU) for AI tasks. Arrow Lake’s numbering starts in the 200s, aligning with the laptop-based Lunar Lake processors.
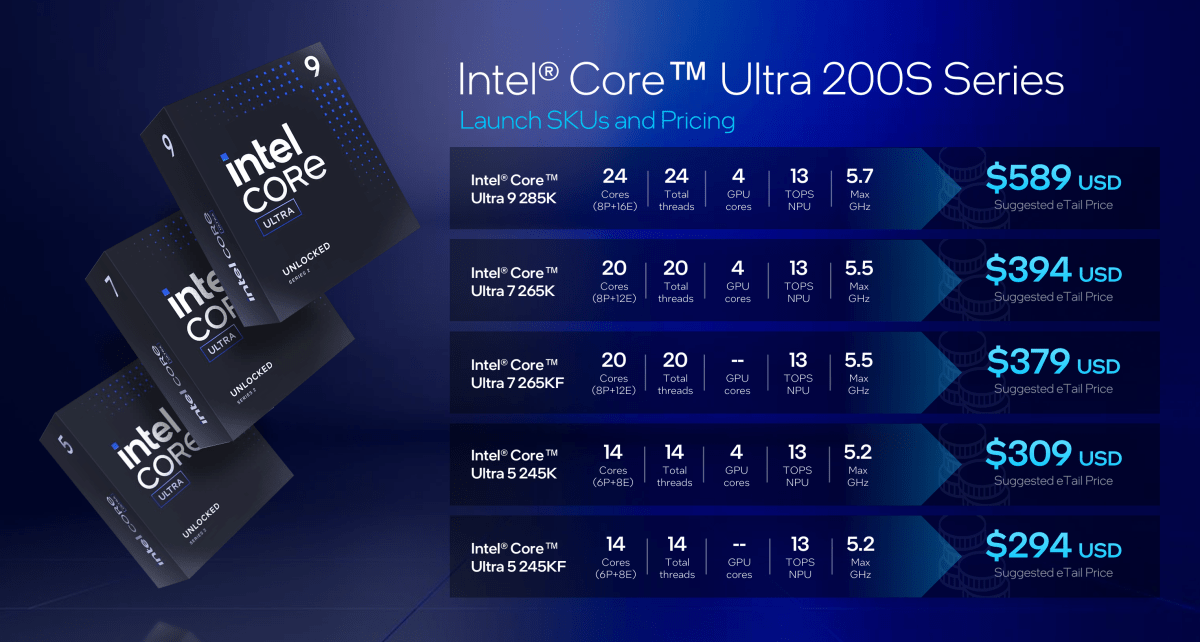 Intel Arrow Lake pricing
Intel Arrow Lake pricing
The Core Ultra 200S series includes five CPUs:
- Intel Core Ultra 9 285K: 24 cores (8 P-cores, 16 E-cores, 5.7GHz max); 4 GPU cores, 13 TOPS NPU, $589
- Intel Core Ultra 9 265K: 20 cores (8 P-cores, 12 E-cores, 5.5GHz max); 4 GPU cores, 13 TOPS NPU, $394
- Intel Core Ultra 9 265KF: 20 cores (8 P-cores, 12 E-cores, 5.5GHz max); 0 GPU cores, 13 TOPS NPU, $379
- Intel Core Ultra 9 245K: 14 cores (6 P-cores, 8 E-cores, 5.2GHz max); 4 GPU cores, 13 TOPS NPU, $309
- Intel Core Ultra 9 245KF: 14 cores (6 P-cores, 8 E-cores, 5.2GHz max); 0 GPU cores, 13 TOPS NPU, $294
The Demise of Hyperthreading
Hyperthreading, Intel’s technology enabling a single core to run two threads concurrently, is absent in Arrow Lake. This decision aims to enhance power and space efficiency. While hyperthreading is gone, the Core Ultra 200S processors still offer a substantial core count, with the 285K boasting 8 P-cores and 16 E-cores.
Content Creation Performance Boost
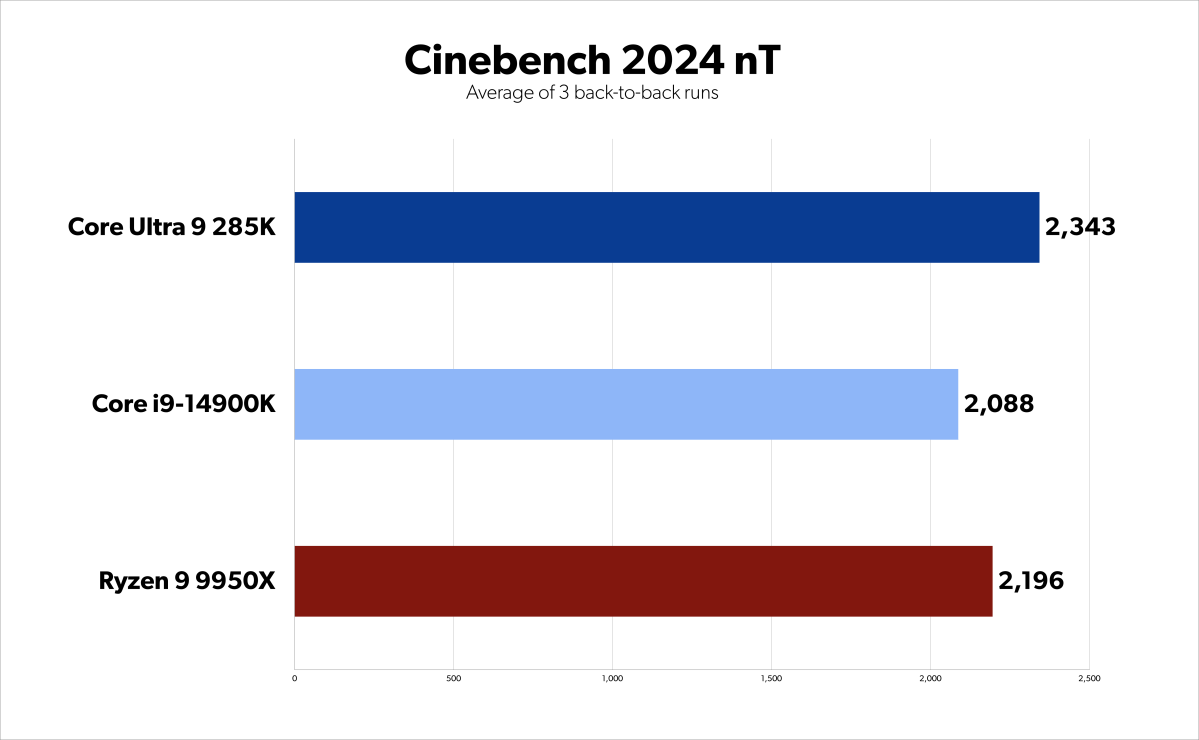 Arrow Lake 285K benchmarks – Cinebench nT
Arrow Lake 285K benchmarks – Cinebench nT
Arrow Lake delivers performance improvements for content creators, although the gains may not warrant an immediate upgrade from the Core i9-14900K. In rendering and encoding benchmarks, the 285K outperforms the 14900K and Ryzen 9 9950X, with improvements between 2% and 21%, except in DaVinci Resolve where it trails slightly.
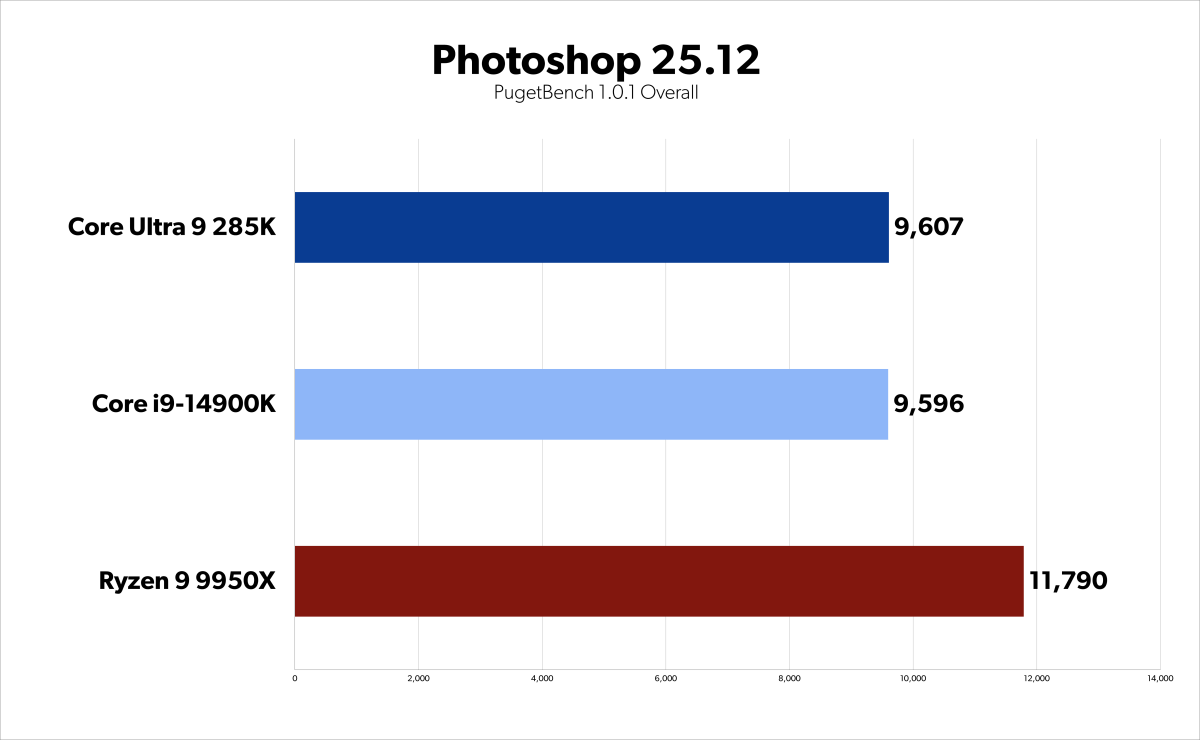 Arrow Lake 285K benchmarks – Photoshop Overall
Arrow Lake 285K benchmarks – Photoshop Overall
Gaming Performance: Less Impressive
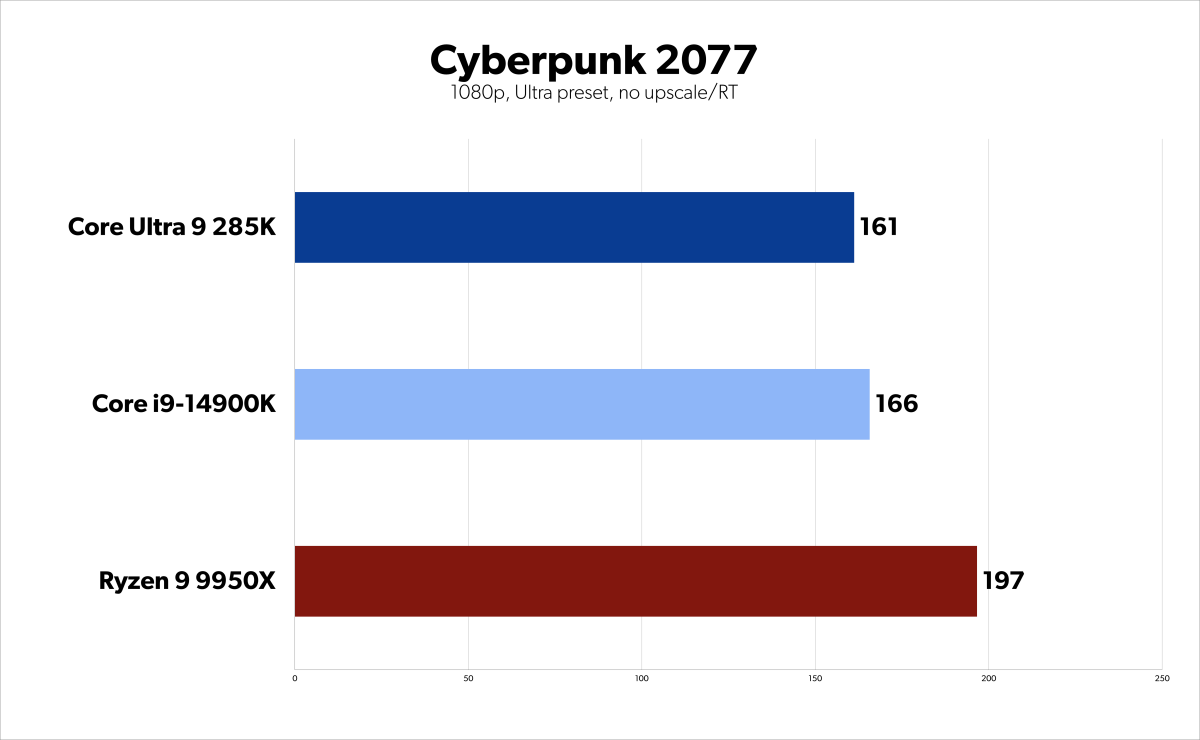 Arrow Lake 285K benchmarks – Cyberpunk 2077
Arrow Lake 285K benchmarks – Cyberpunk 2077
Gaming performance on the 285K is less remarkable. While it performs comparably to the 14900K in some games, it often lags behind the Ryzen 9 9950X. Even with faster CU-DIMM memory, the performance uplift isn’t substantial. While not a poor gaming CPU, the 285K doesn’t deliver a groundbreaking gaming experience.
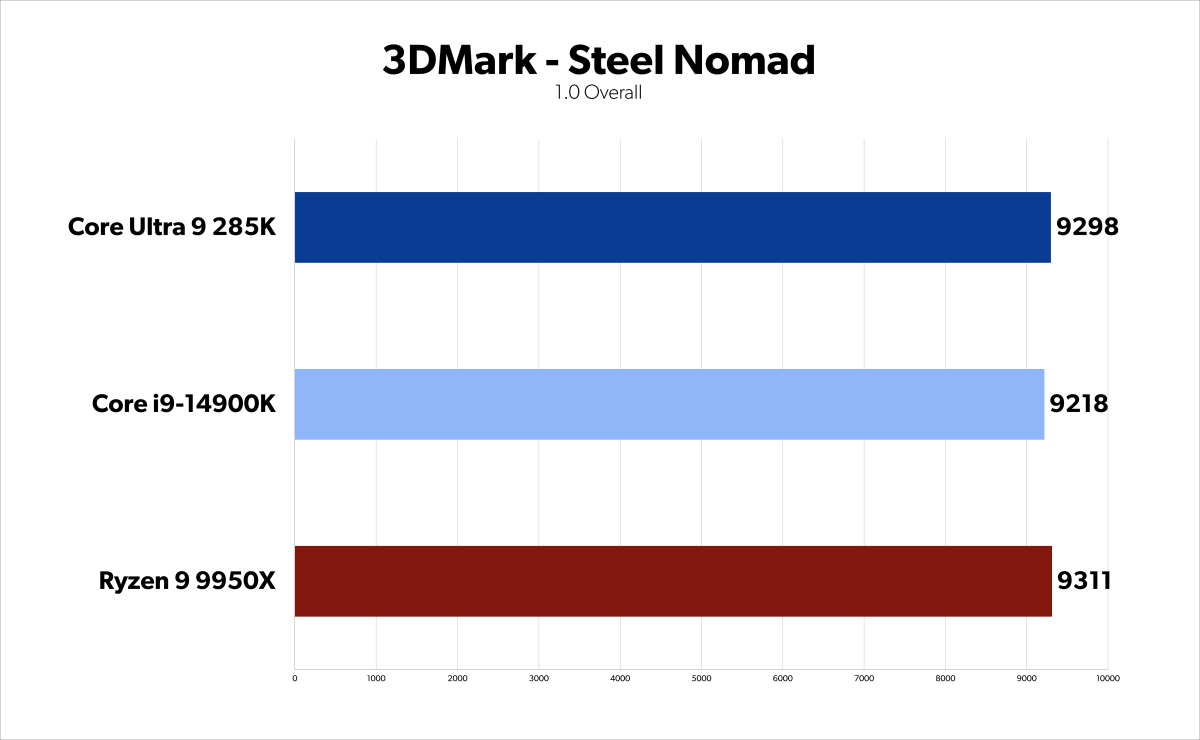 Arrow Lake 285K benchmarks – 3DMark Steel Nomad
Arrow Lake 285K benchmarks – 3DMark Steel Nomad
Improved Power Efficiency, With a Caveat
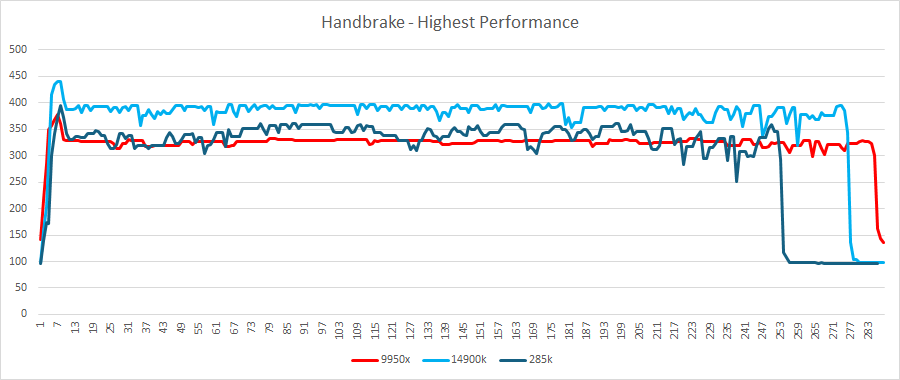 arrow lake power draw – handbrake highest performance
arrow lake power draw – handbrake highest performance
Arrow Lake boasts improved power efficiency. Our tests revealed a 17% reduction in power consumption during Handbrake encoding and a 16% decrease during Cinebench 2024’s single-core benchmark compared to the 14900K. However, idle power draw saw a slight increase. Compared to the 9950X, the 285K shows even better power efficiency.
Windows Optimization Concerns
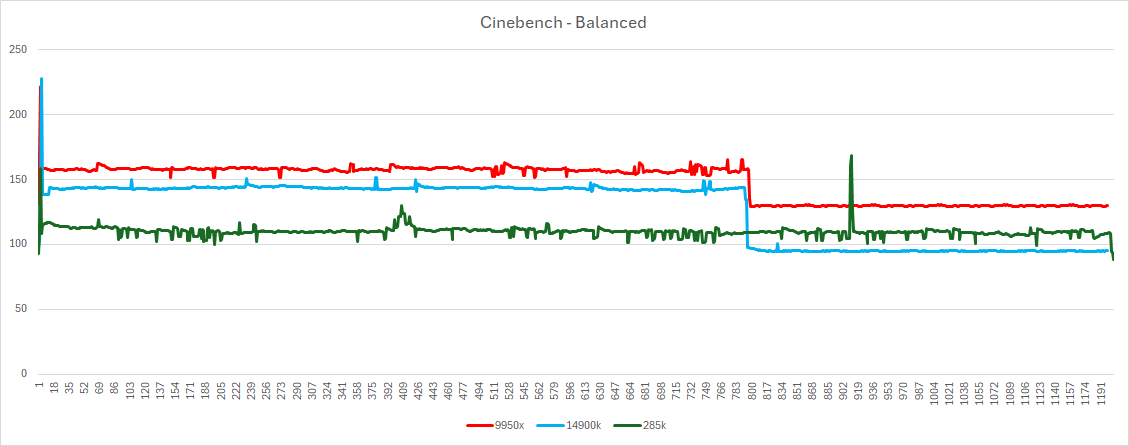 arrow lake power draw – handbrake power savercinebench balanced
arrow lake power draw – handbrake power savercinebench balanced
Surprisingly, the 285K’s performance significantly degrades on Windows 11’s Balanced and Power Saver plans. Benchmark scores showed a substantial drop compared to the 14900K and 9950X on these power plans. This issue raises concerns about Windows optimization for Arrow Lake.
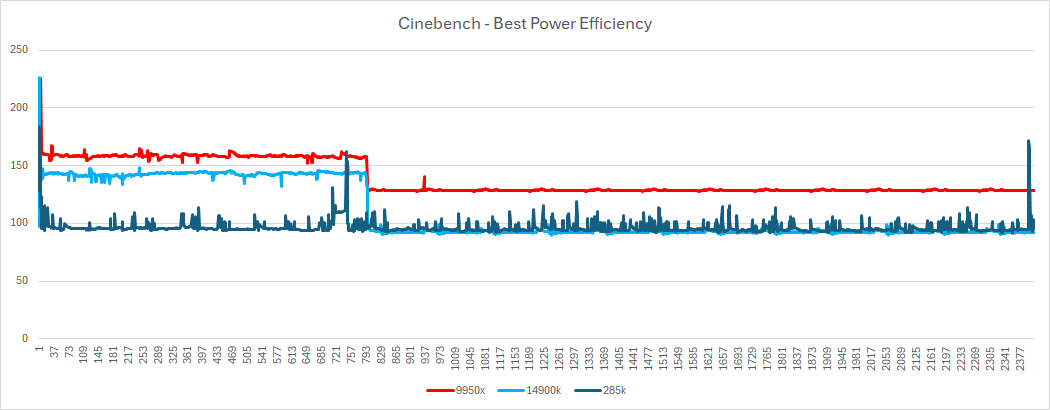 arrow lake power draw – handbrake power savercinebench power saver
arrow lake power draw – handbrake power savercinebench power saver
A New Chiplet Architecture
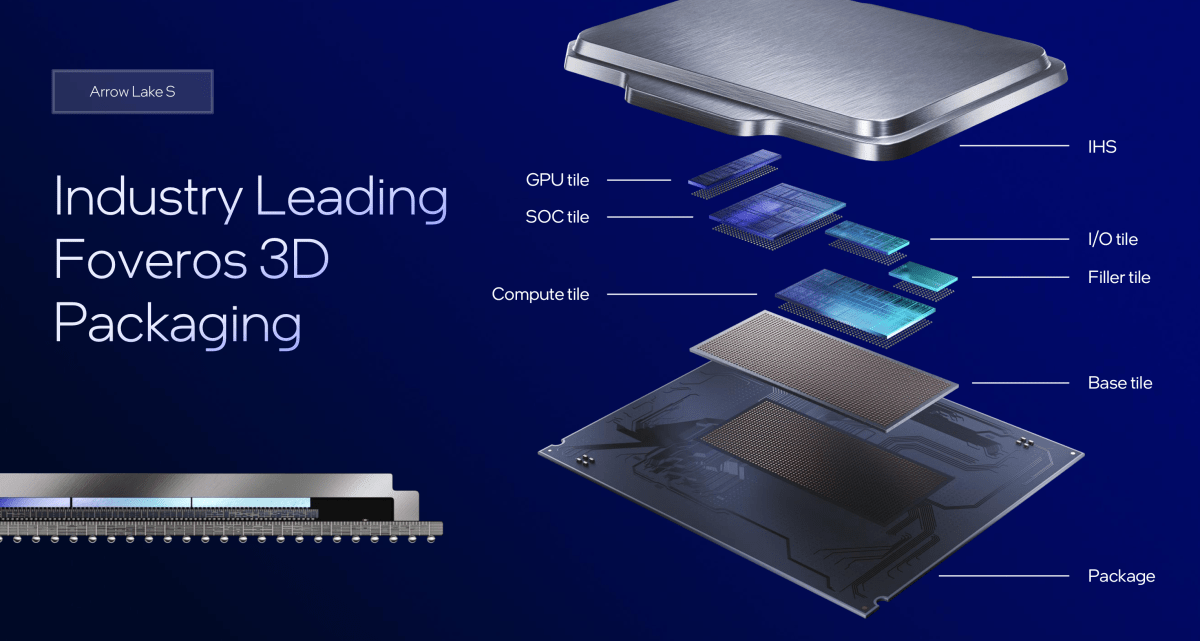 Intel Arrow Lake deep dive tiles
Intel Arrow Lake deep dive tiles
Arrow Lake adopts a chiplet design, a significant departure from Intel’s previous monolithic approach. The processor comprises interconnected chiplets (tiles) for different functions, fabricated on different processes.
New Motherboard Required
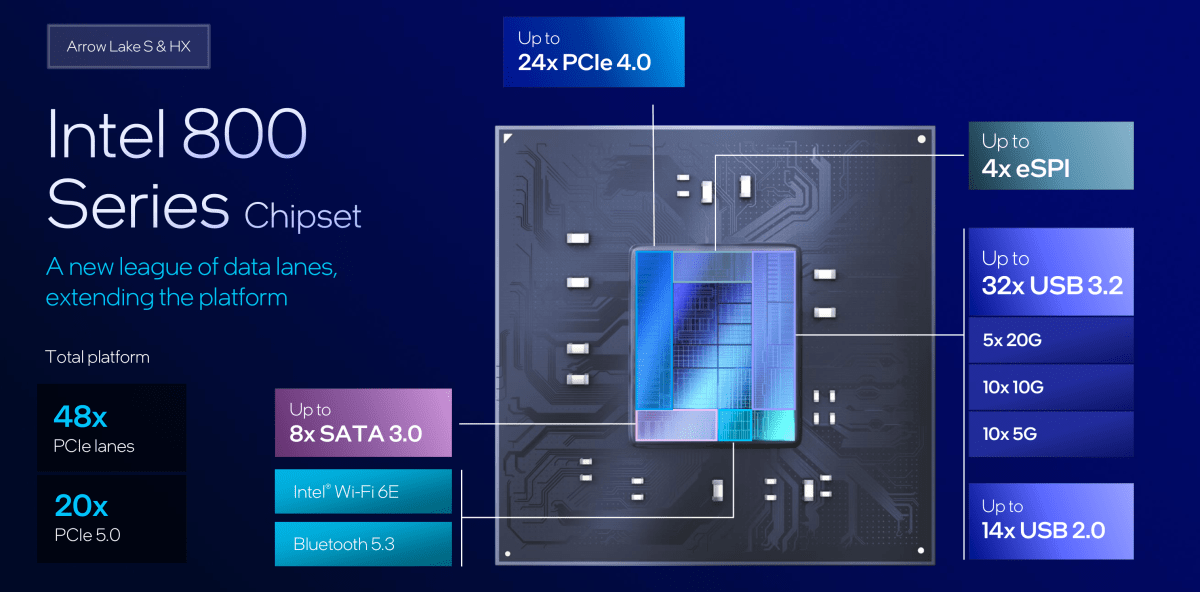 Intel Arrow Lake deep dive 800 series chipset
Intel Arrow Lake deep dive 800 series chipset
Arrow Lake utilizes the new LGA 1851 socket, requiring a new motherboard. The Z890 chipset supports DDR5-6400 memory and CU-DIMM modules. It offers various connectivity options, including PCIe 5.0, Thunderbolt 4/5, and 2.5Gbps ethernet.
DDR5 and Existing Coolers Compatible
 DDR5 RAM
DDR5 RAM
While CU-DIMM memory is supported, Arrow Lake remains compatible with DDR5 RAM. Existing coolers for 13th and 14th-gen processors are also compatible, though new mounting hardware may be necessary.
No Desktop AI Upgrades
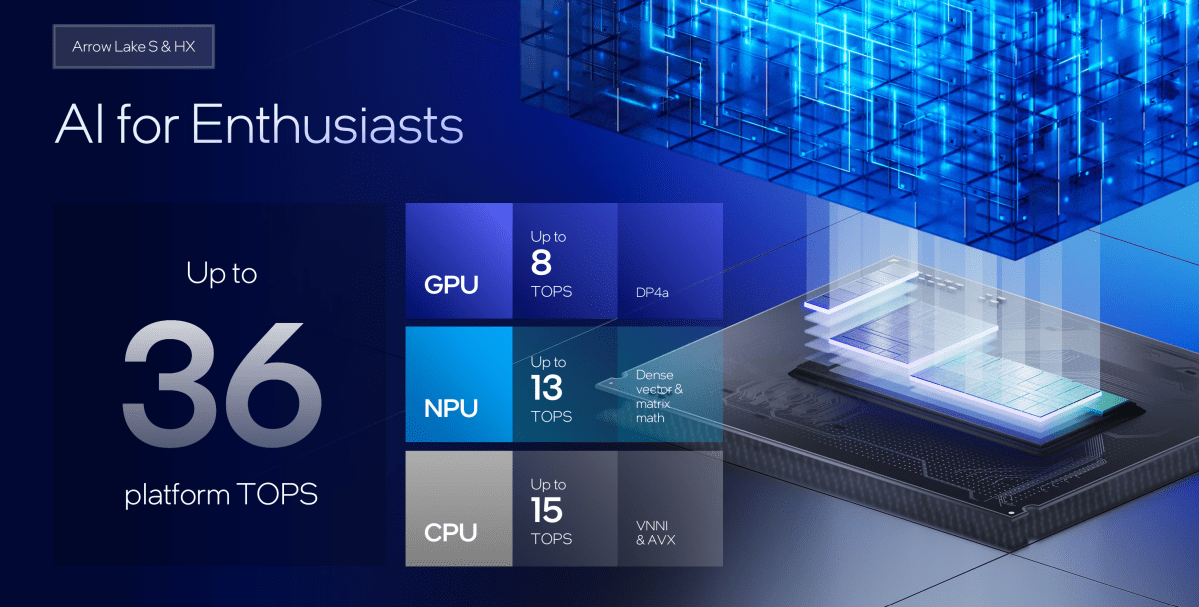 Intel Arrow Lake deep dive AI TOPS NPU
Intel Arrow Lake deep dive AI TOPS NPU
Arrow Lake’s NPU provides 13 TOPS of performance, insufficient for Windows 11’s advanced AI features. This limitation stems from design choices prioritizing gamers, a key demographic for desktop CPUs. While marketed as AI-capable, these PCs won’t offer the full range of Windows 11 AI functionalities.