Staying safe online doesn’t require advanced coding skills. Simple precautions can significantly enhance your security. Based on recommendations from Germany’s Federal Office for Information Security, this guide expands on ten crucial tips to protect yourself from online threats like fraud and viruses.
Keeping your software updated, using strong passwords, and being cautious about emails and downloads are just a few of the key practices we’ll cover. We’ll also recommend specific tools and security settings to bolster your online defenses.
Update Everything Regularly
Keeping your operating system, browser, and applications up-to-date is paramount for online security. Automatic updates are the easiest way to ensure you have the latest security patches.
Most modern browsers, including Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Mozilla Firefox, automatically check for and install updates upon startup. This applies to desktop as well as mobile devices. Stick to reputable browsers from established developers to avoid security risks associated with less-maintained alternatives.
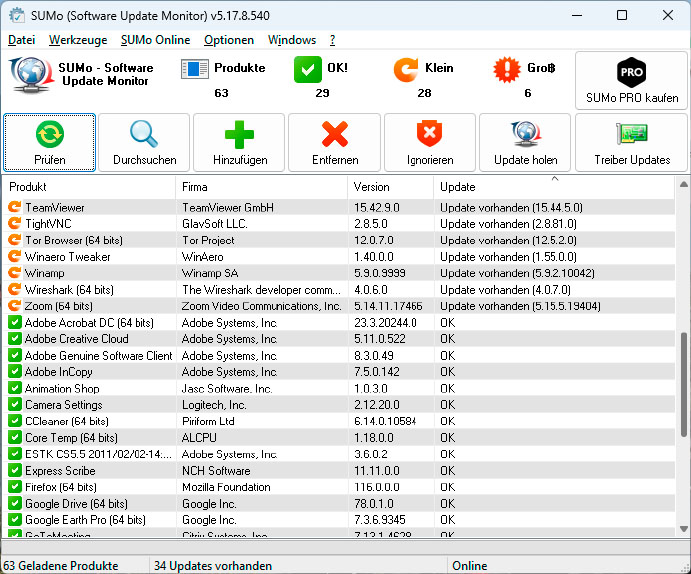 The update manager Sumo determines the version numbers of the installed programs and compares them with its database to detect outdated issues.
The update manager Sumo determines the version numbers of the installed programs and compares them with its database to detect outdated issues.
Beyond browsers, ensure your operating system and other software are also updated. Windows and Microsoft 365 offer automatic updates. For other programs, tools like Sumo or Iobit Software Updater can help manage updates by checking version numbers and notifying you of available updates. Activating your operating system’s built-in antivirus and firewall is crucial, though consider a robust third-party antivirus suite for enhanced protection against ransomware, phishing, and identity theft. Our recommendation for comprehensive protection is Norton 360 Deluxe.
Secure Your Accounts and Data
Create separate user accounts on your computer and avoid using an administrator account for everyday tasks. This limits the potential damage from malware, as it will only have the permissions of the currently active user. Windows User Account Control provides an added layer of security by requiring permission for actions that require administrator privileges. Set the slider to the highest level in the User Account Control Settings for maximum protection.
Strong passwords are essential for all your accounts, both local and online. Aim for at least 16 characters with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. A password manager is highly recommended to securely store and manage your passwords, eliminating the risk of using the same password across multiple services.
Two-factor authentication (2FA) provides an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification step, such as a code from an authentication app. Enable 2FA whenever possible, especially for critical accounts like online banking. Emerging technologies like passkeys, supported by major tech companies and password managers, offer a more secure alternative to traditional passwords by using cryptographic keys.
Exercise Caution Online
Be vigilant about emails and attachments, as they can be used to spread malware or steal data. Phishing emails often contain malicious links or attachments disguised as legitimate files. Tools like Attachment Scanner for Outlook can help you scan attachments for malware using multiple antivirus engines. Learn to identify scam emails and texts to avoid falling victim to phishing attacks.
Download programs only from trusted sources, such as the official manufacturer’s website. Avoid websites offering cracked or pirated software, as they are often bundled with malware. Scan downloaded files with your antivirus program before opening them. Download managers like Free Download Manager can even automate this process. Never click on Google ads for antivirus downloads, as these can be misleading and potentially dangerous.
 Lock on a keyboard security
Lock on a keyboard security
Be mindful of sharing personal information online. Limit the information you share on social media and avoid posting sensitive details like your address, phone number, financial information, or travel plans. This helps protect you from social engineering attacks, where criminals gather information about you to gain your trust and then attempt to steal your data.
Secure Your Connections and Back Up Your Data
Always ensure you’re using a secure connection (HTTPS) when browsing the web. Look for the lock symbol in the address bar to confirm the connection is encrypted. This prevents eavesdropping on your data by encrypting the information transmitted between your browser and the website. Modern browsers like Chrome and Edge warn you about insecure HTTP connections, while Firefox can automatically redirect you to the HTTPS version of a website.
Regular backups are essential to protect your data from ransomware attacks, which encrypt your files and demand a ransom for decryption. Back up your important data to an external storage device that is not permanently connected to your computer. This prevents the ransomware from encrypting your backups as well. Simple file copying can suffice, but consider dedicated backup software for more comprehensive protection, including system image backups. R-Drive Image is a robust option for creating restorable system images.
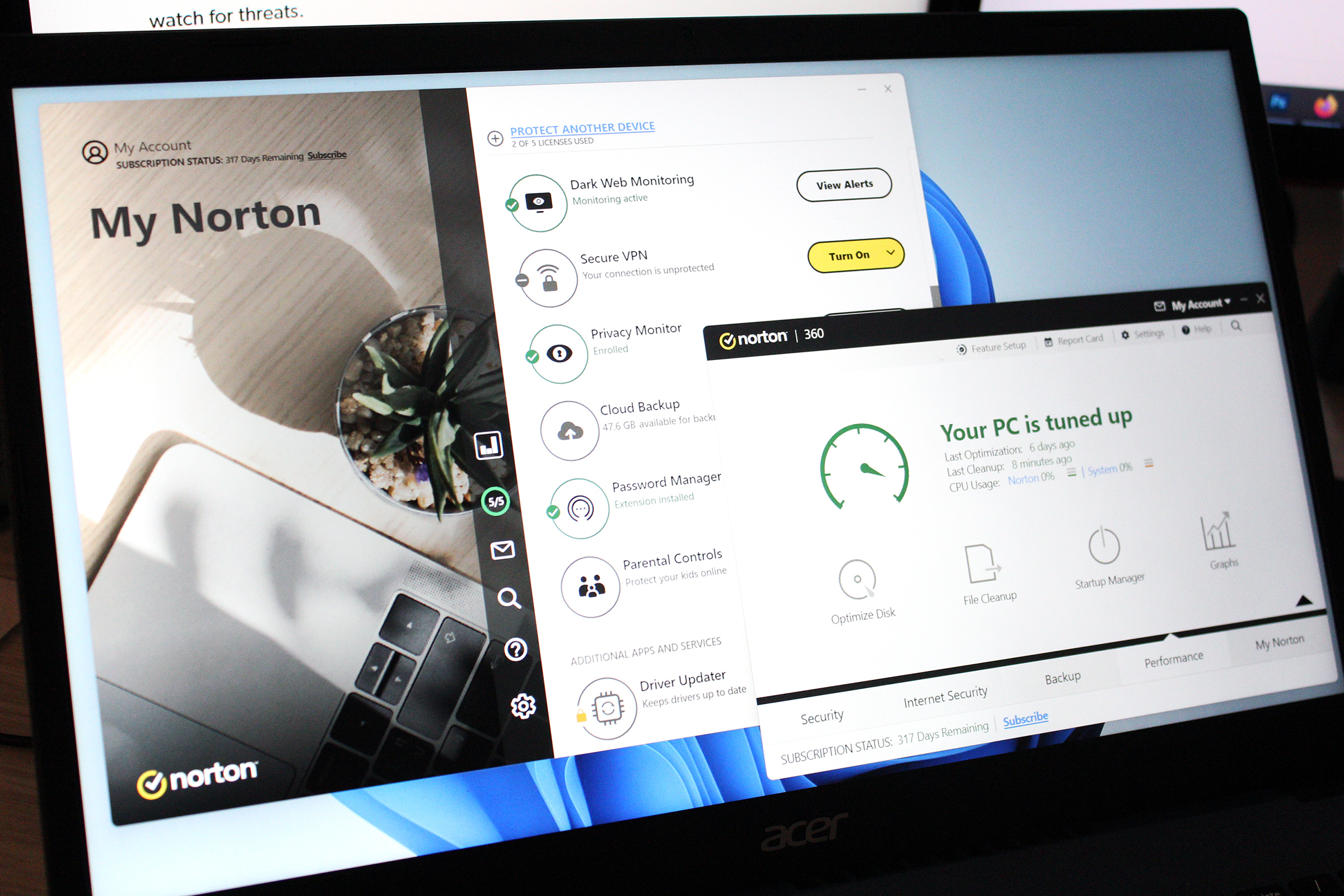 Norton 360 Deluxe
Norton 360 Deluxe
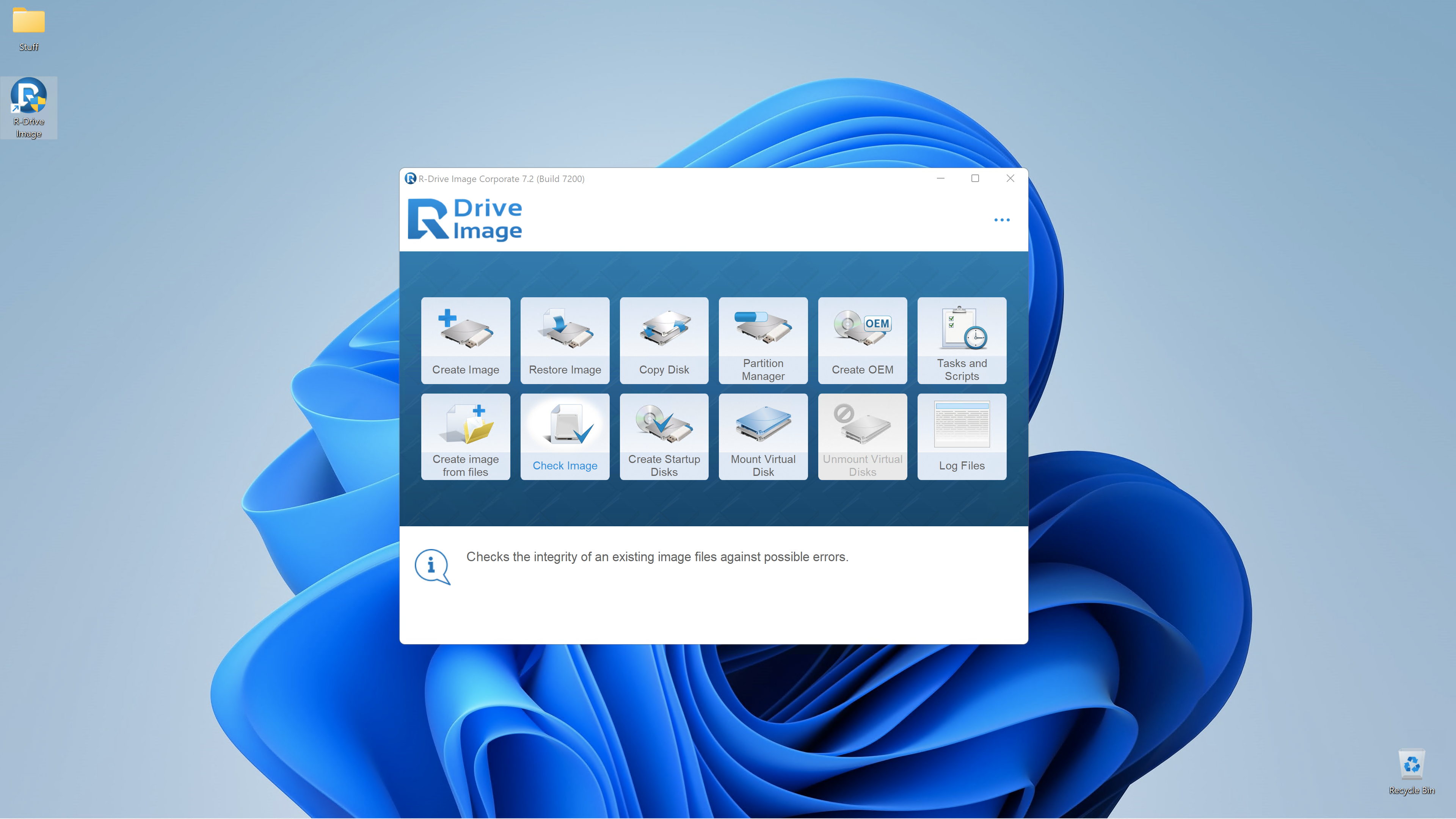 R-Drive Image
R-Drive Image