Looking to take your home network to the next level? Whether you’re already running a NAS, a home server, or a suite of smart home devices, these advanced networking tips will help you gain more control and optimize your setup. This guide builds upon basic networking principles and explores techniques for enhancing both performance and security.
(Related articles in this series):
- How to choose a new router and get started with important settings
- Solve your Wi-Fi problems with these smart router settings
- Protect your home network with these essential router tweaks
- More than Internet: 9 tips to maximize your home network
1. Exploring Alternative Router Software
If you’re feeling limited by your router’s built-in features, alternative software can unlock a world of possibilities without requiring new hardware.
OpenWrt, a continuously developed open-source project, offers compatibility with numerous router models. It’s a powerful option with support for advanced features like VLAN and Smart Queue Management (SQM). While it boasts extensive capabilities, it also has a steeper learning curve.
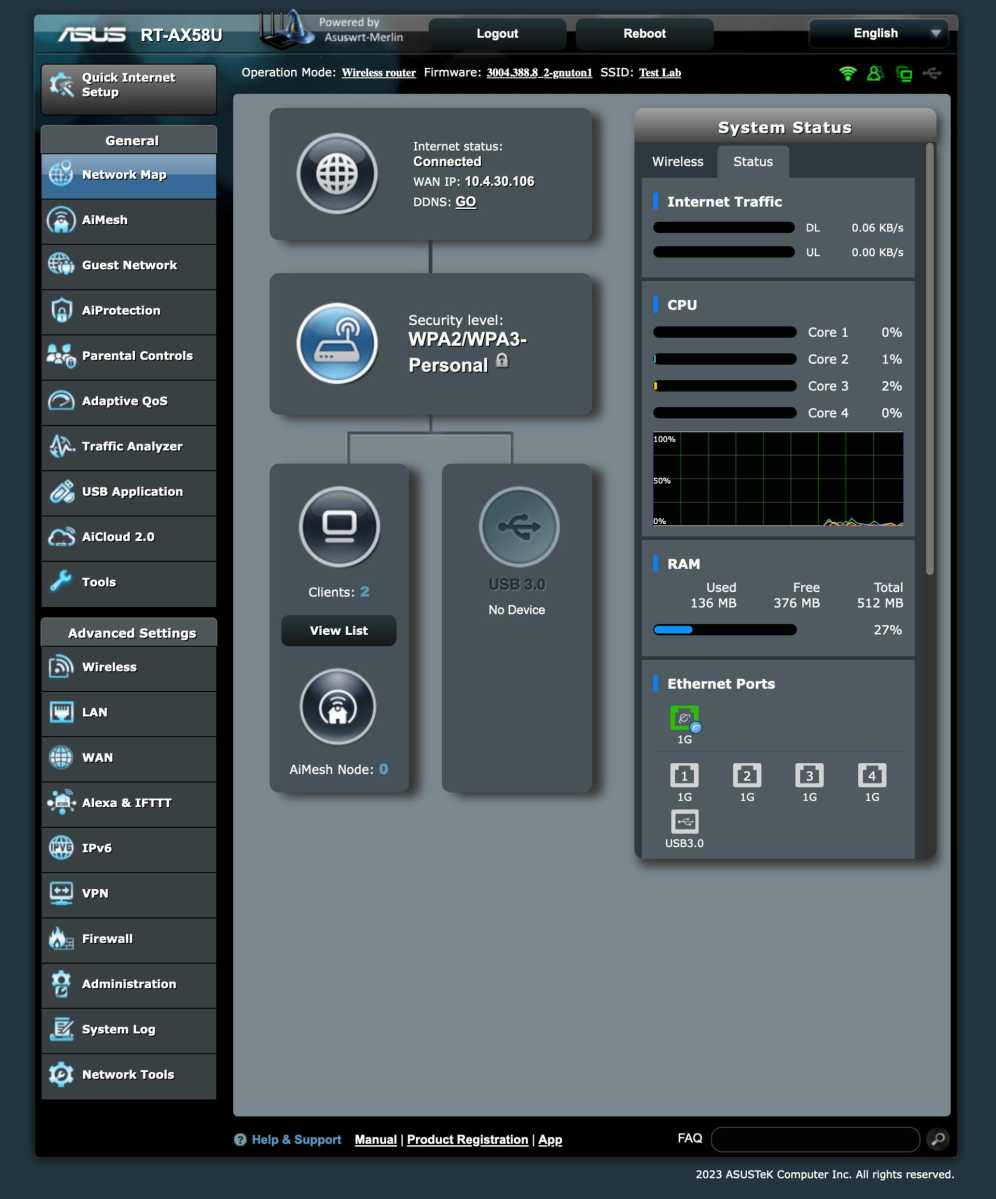 Asuswrt-Merlin
Asuswrt-Merlin
For Asus router owners, Asuswrt-Merlin provides a familiar interface with added functionality, making it an easy entry point to alternative firmware. While older alternatives like DD-WRT and Tomato are largely outdated, FreshTomato, a Tomato variant, remains a viable option for some.
2. Decoupling Router/Firewall and Wi-Fi
Enterprise networks often utilize separate devices for routing, firewalling, and Wi-Fi. This modular approach can also benefit home networks, particularly those with numerous devices.
You can achieve this by repurposing your existing router (or mesh system) as an access point and installing a dedicated router operating system on a separate device like a Raspberry Pi (using OpenWrt) or a mini PC (using pfSense or OPNsense).
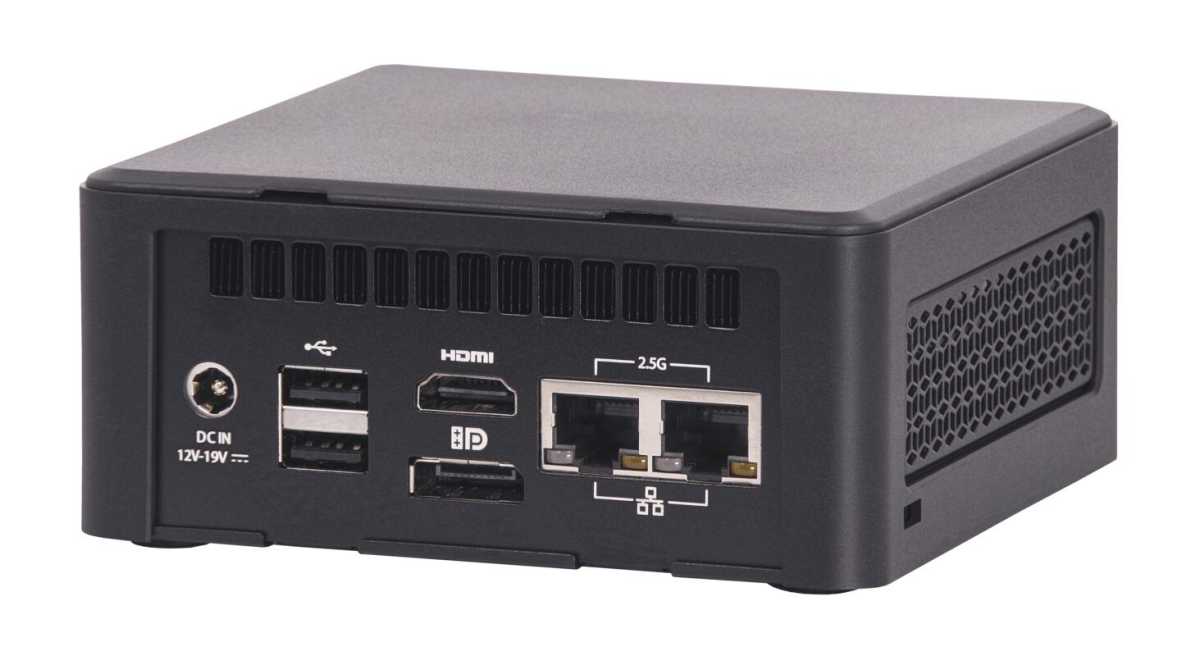 Intel Nuc som router
Intel Nuc som router
Connect both your old router and the new router to a switch. Connect the internet feed to the WAN port of the new router and configure the LAN and WAN interfaces within the chosen operating system. This setup allows for more powerful hardware and advanced security features.
3. Implementing Network Segmentation with VLAN
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows for separating network traffic, similar to guest networks but with greater control. This enables isolating devices into different address spaces with distinct firewall rules.
A common use case is creating a VLAN for IoT devices, enhancing security by containing potential threats from compromised gadgets.
 Wifi-accesspunkt
Wifi-accesspunkt
Another application is establishing a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) for publicly accessible servers, like a Minecraft server, while restricting their access to the internal network.
Getting Started with VLAN
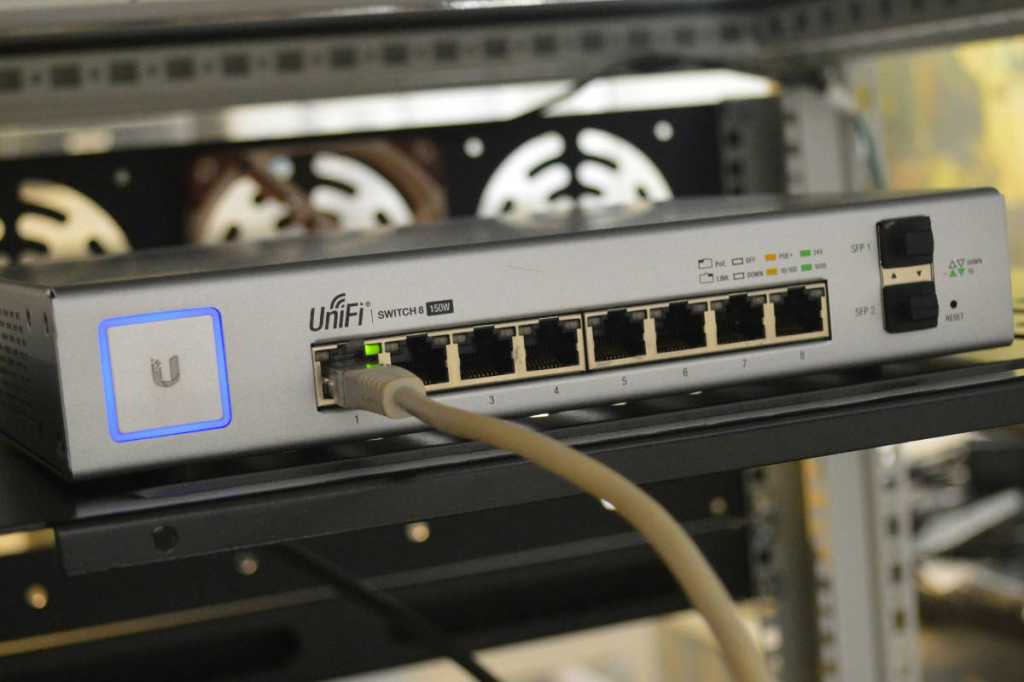
VLAN setup varies depending on the router operating system. Consult specific guides for your system, such as the Open Source guide for OpenWrt. Managed switches are recommended for connecting wired devices to VLANs. Ubiquiti’s Unifi product line offers switches and access points for creating separate wireless networks with customized rules.
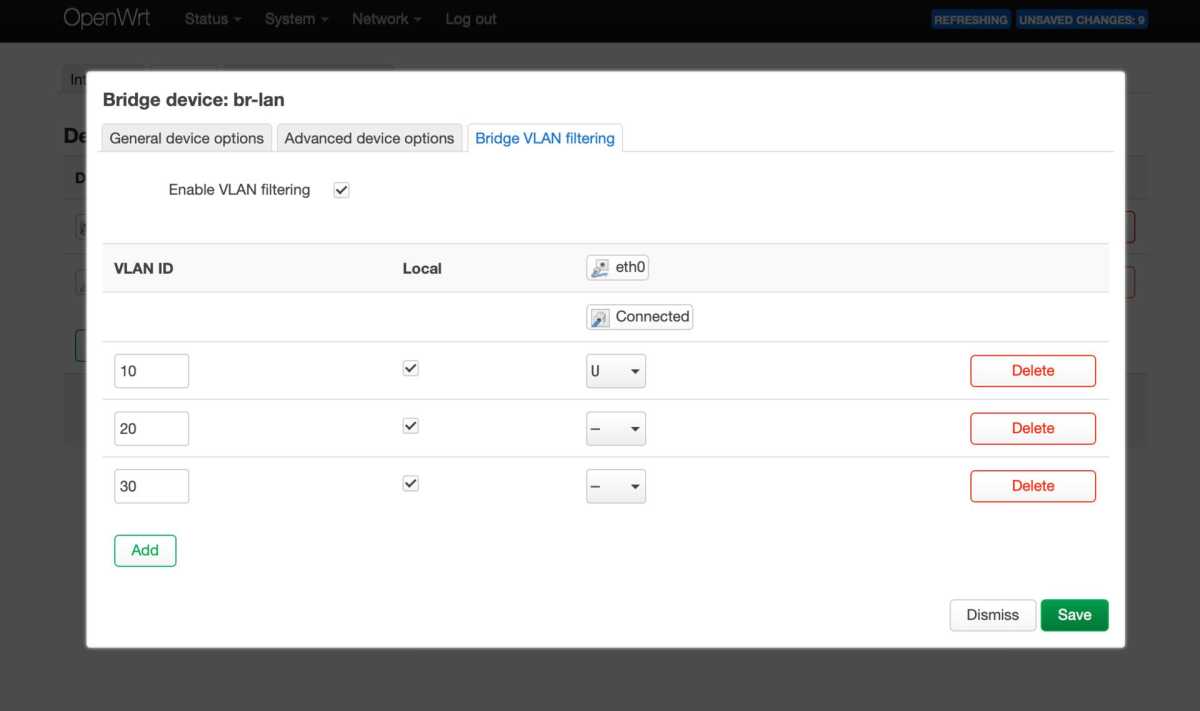 Vlan på Openwrt
Vlan på Openwrt
4. Network-wide Ad and Tracker Blocking with Pi-Hole
Pi-Hole acts as a local DNS server, blocking unwanted domains by referencing blocklists for advertising, tracking, malware, and more. Its low system requirements make it ideal for a Raspberry Pi.
Preventing Use of Other DNS Services
Blocking devices from using external DNS servers ensures Pi-Hole’s effectiveness. This typically involves firewall rules that block port 53 traffic while allowing traffic to the Pi-Hole’s IP address.
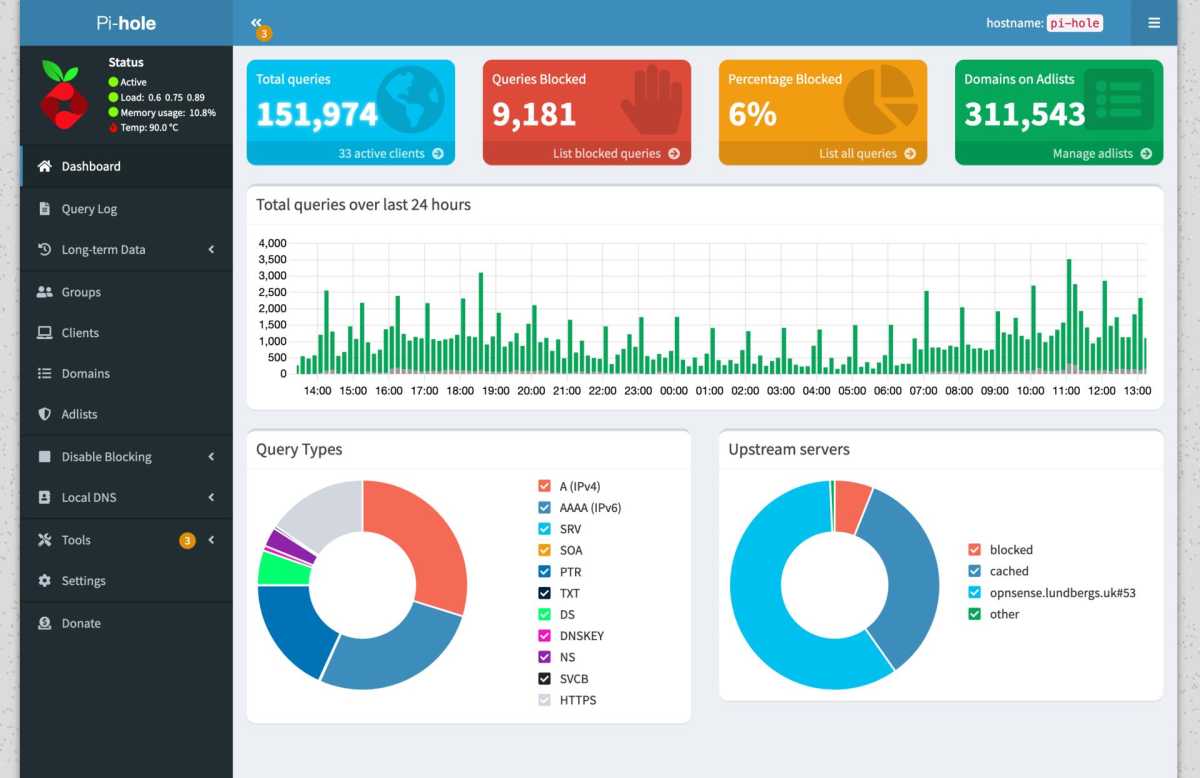 Pi-hole
Pi-hole
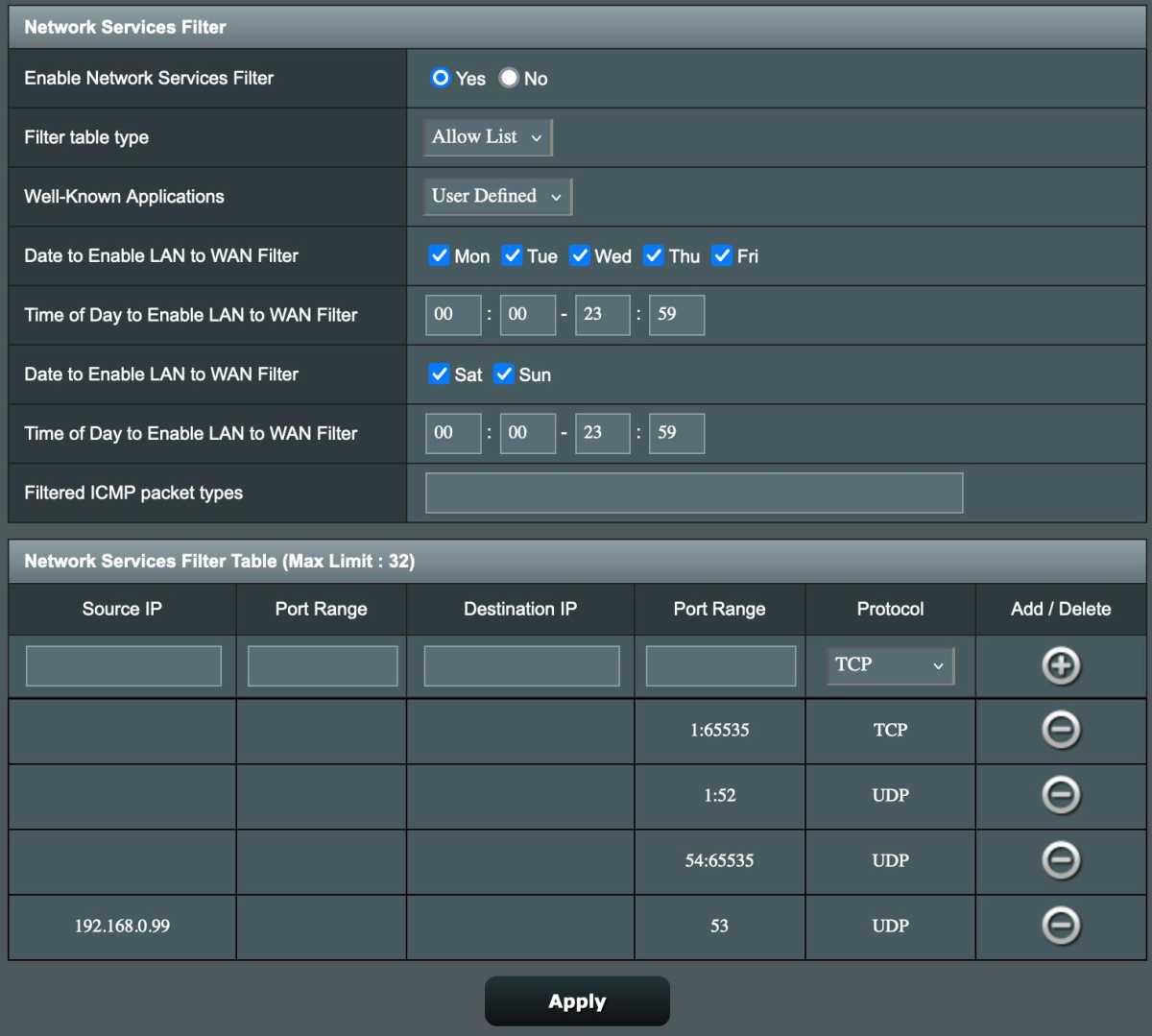 Blockera annan dns
Blockera annan dns
Asuswrt-Merlin offers a more streamlined approach with its DNS Filter function. However, be aware of techniques like DNS over HTTPS (DoH) that can bypass traditional DNS blocking.
5. Secure Remote Access with a VPN Server
Hosting services like NAS devices or game servers often necessitates remote access. Opening ports directly poses security risks. A VPN server offers a secure alternative, requiring only one open port.
Modern protocols like OpenVPN and Wireguard are recommended. Many routers offer built-in VPN server functionality.
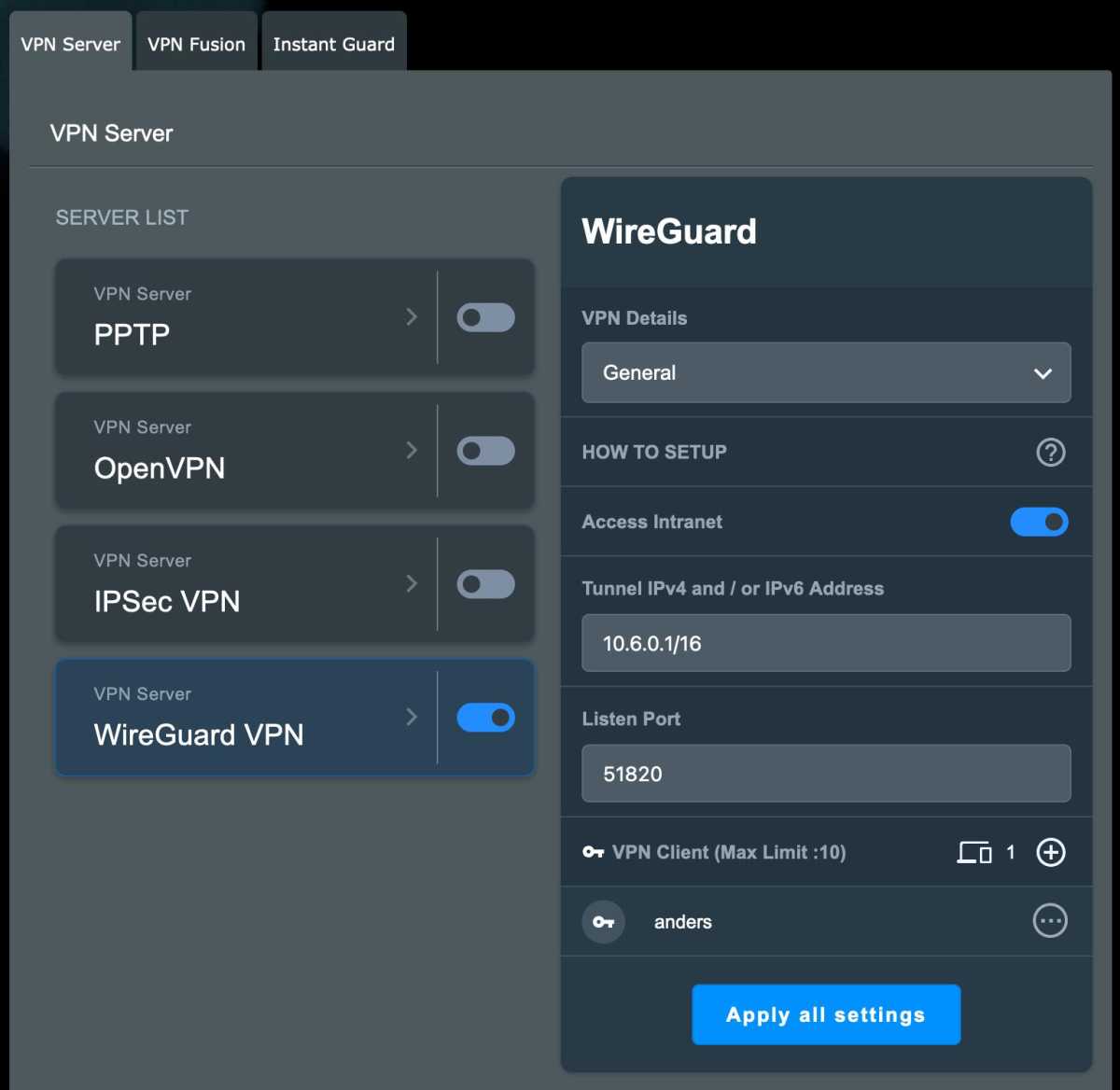 Wireguard
Wireguard
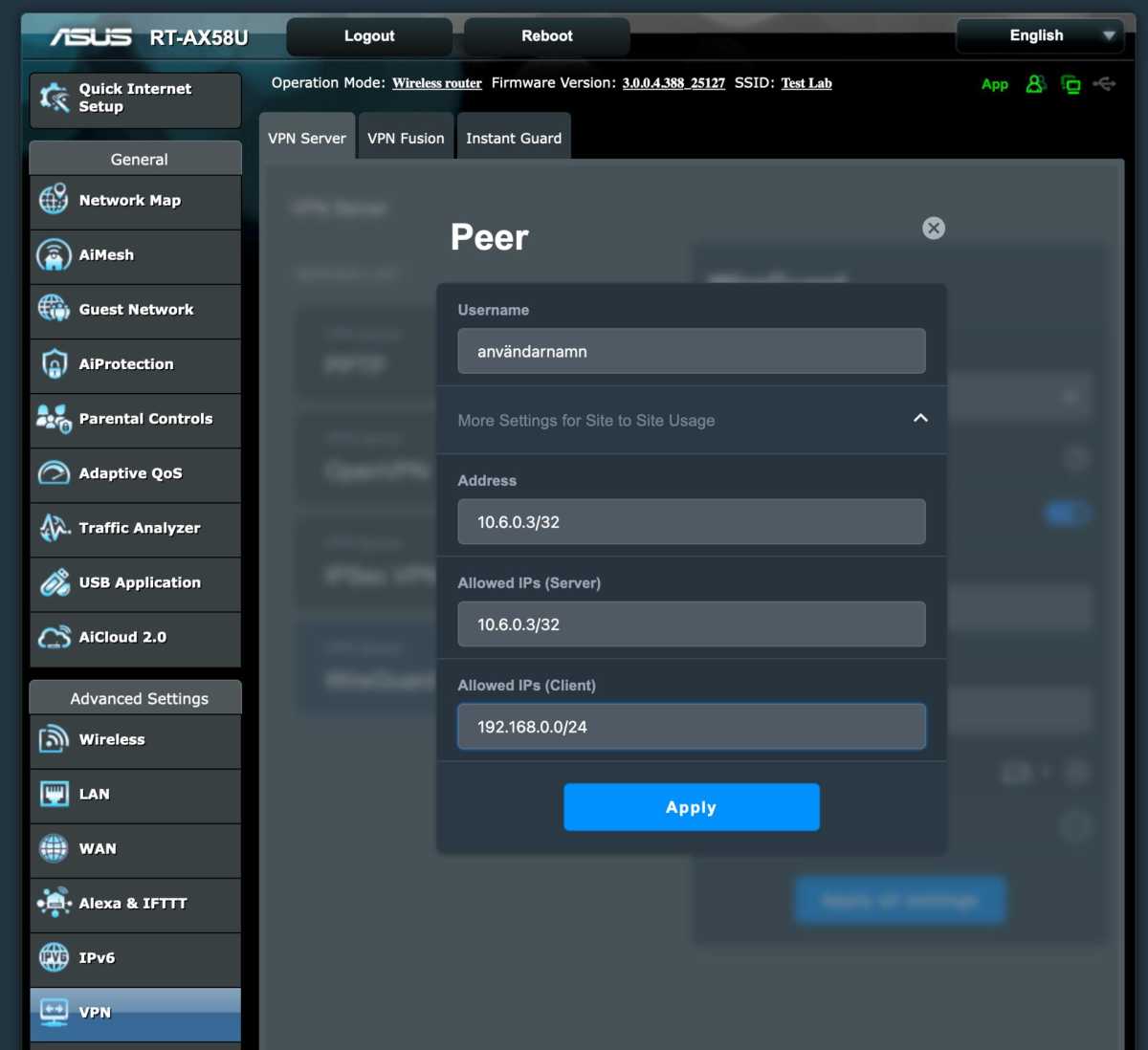 Wireguard
Wireguard
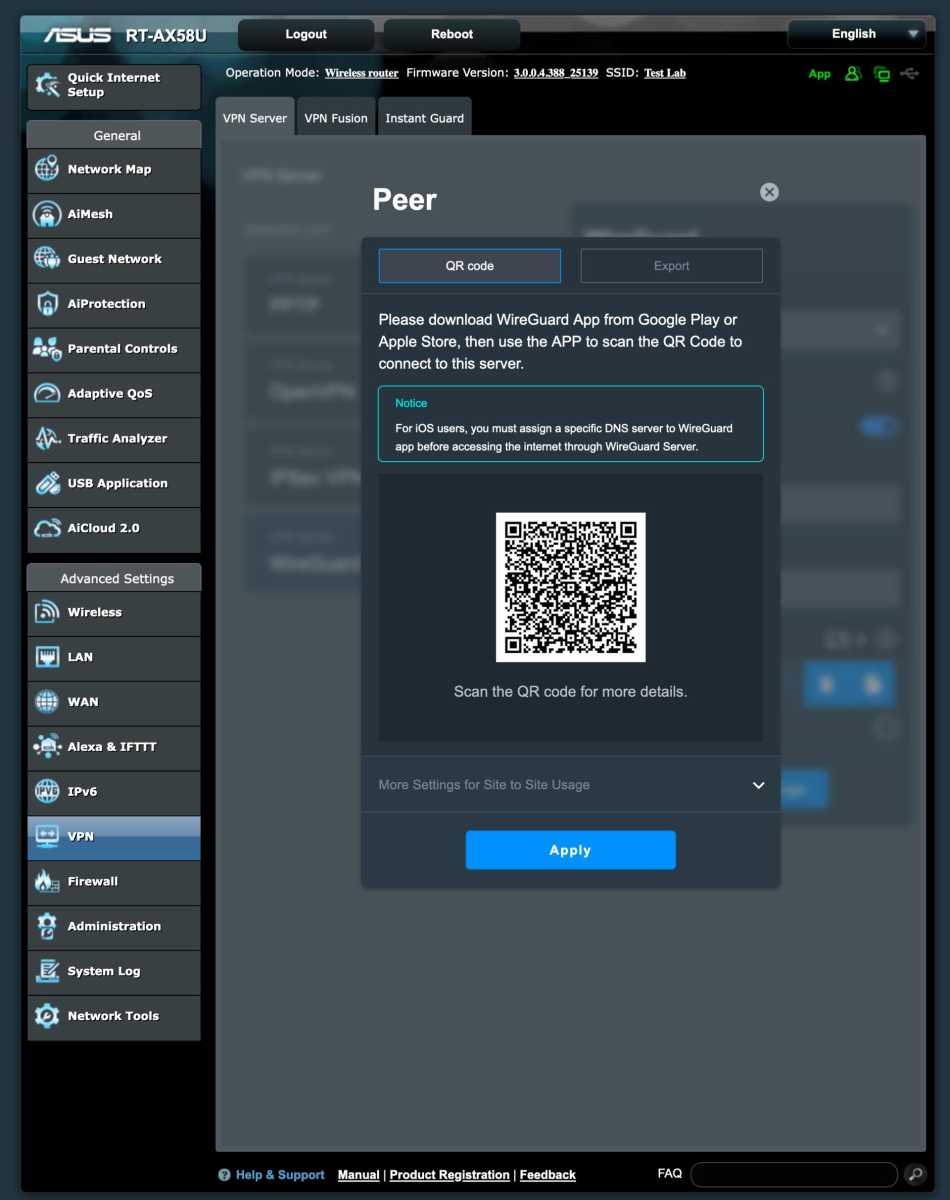 Wireguard
Wireguard
Configuring a VPN server allows secure access to your home network resources without exposing them directly to the internet. You can choose to route all traffic through the VPN or only traffic destined for your local network.