Google Chrome, the dominant web browser for desktop users, offers a fast and responsive browsing experience out of the box. However, over time, performance can degrade due to accumulated cache files, extensions, and resource-intensive processes. Fortunately, there are several straightforward methods to optimize Chrome’s performance and maintain a snappy browsing experience. Here are nine practical tips to keep Google Chrome running at its best.
 Updating Chrome
Updating Chrome
Regularly Update Chrome
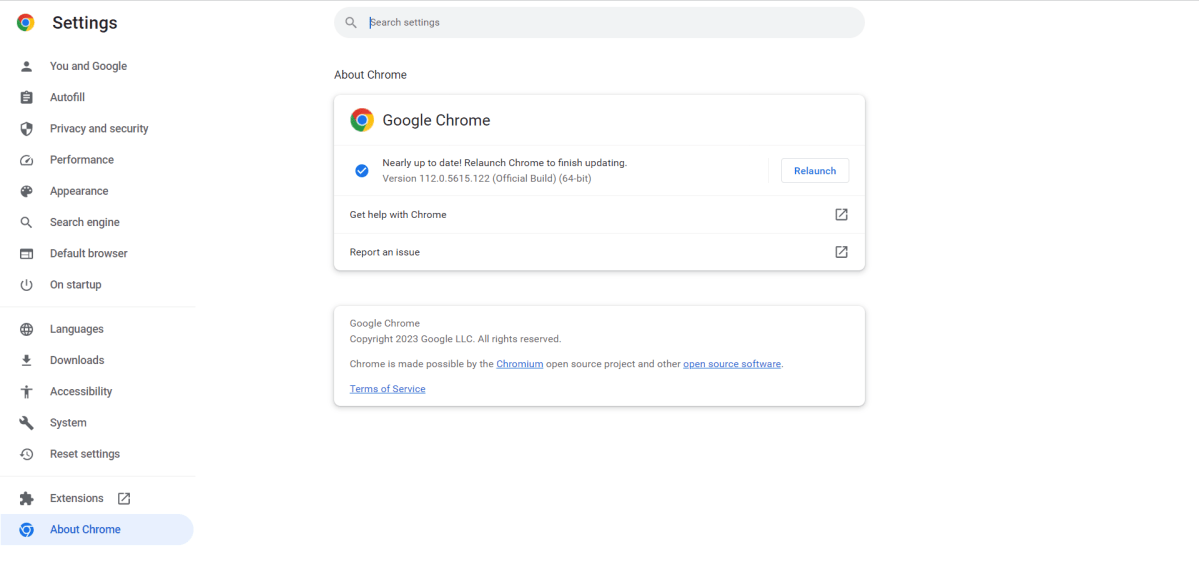
Keeping Chrome updated is crucial for optimal performance. Updates deliver performance enhancements, bug fixes, and essential security patches. Google releases frequent updates, so staying current is vital. Chrome typically updates automatically in the background when closed. However, if you rarely close your browser, manually checking for updates is recommended. An update button will appear in the top-right corner when an update is available. Clicking this button initiates the update process. Alternatively, click the three vertical dots > Help > About Google Chrome to manually check for and install updates. Relaunch Chrome after the update to finalize the process. Ensure all unsaved work is saved before relaunching.
 Managing Tabs
Managing Tabs
Manage Your Tabs Effectively
Numerous open tabs consume significant RAM and CPU resources. As the number of tabs increases, so does the strain on your system, potentially leading to slower performance, extended page load times, or even browser crashes. Closing unused tabs can significantly improve Chrome’s responsiveness.
Disable Unnecessary Extensions
 Disabling Extensions
Disabling Extensions
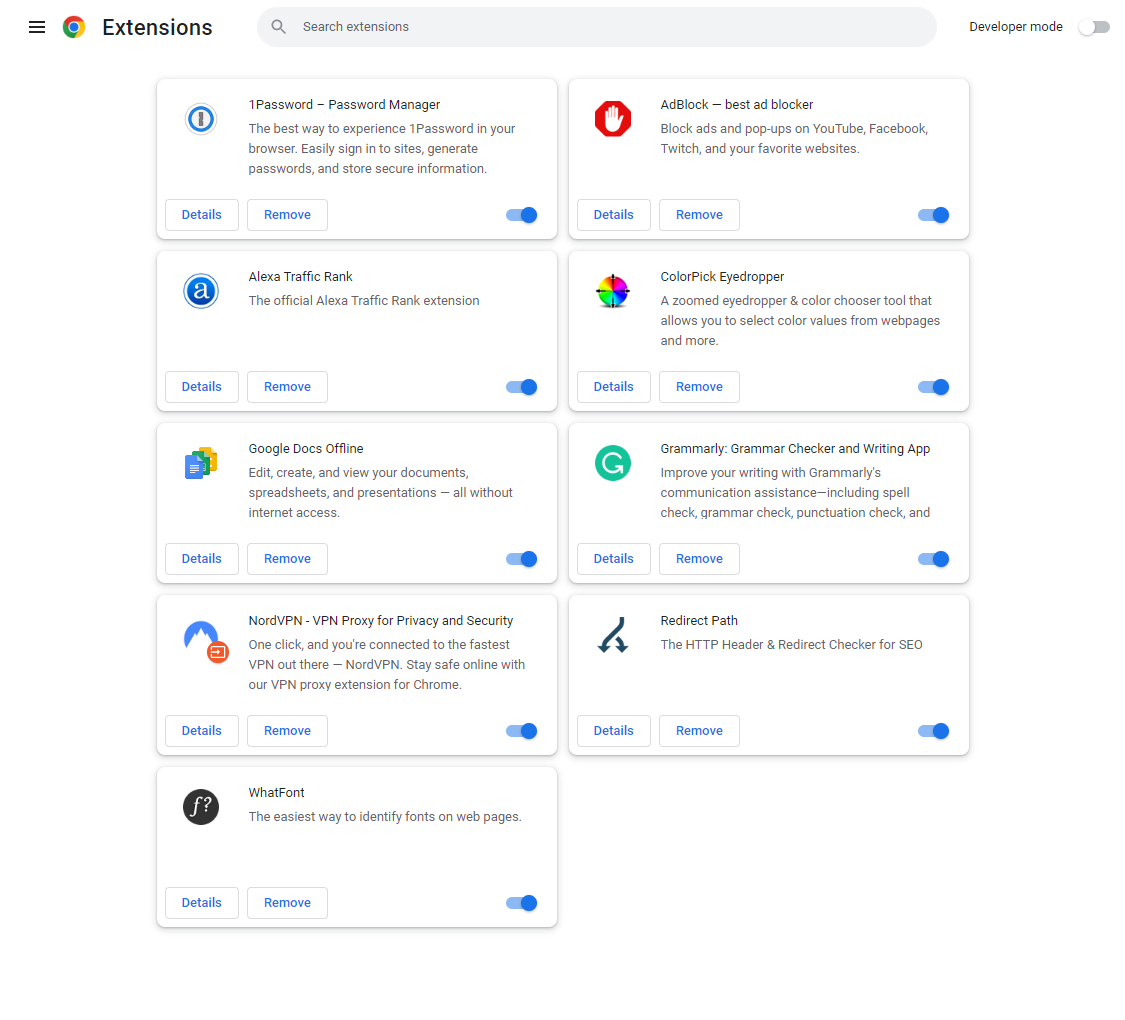
Browser extensions enhance functionality but can also impact performance. Having too many extensions installed, especially resource-intensive ones, can slow down Chrome. Disabling unused extensions is a simple way to reclaim system resources. Navigate to chrome://extensions and toggle the extension’s slider to the Off position or click Remove to uninstall.
 Clearing Browsing Data
Clearing Browsing Data
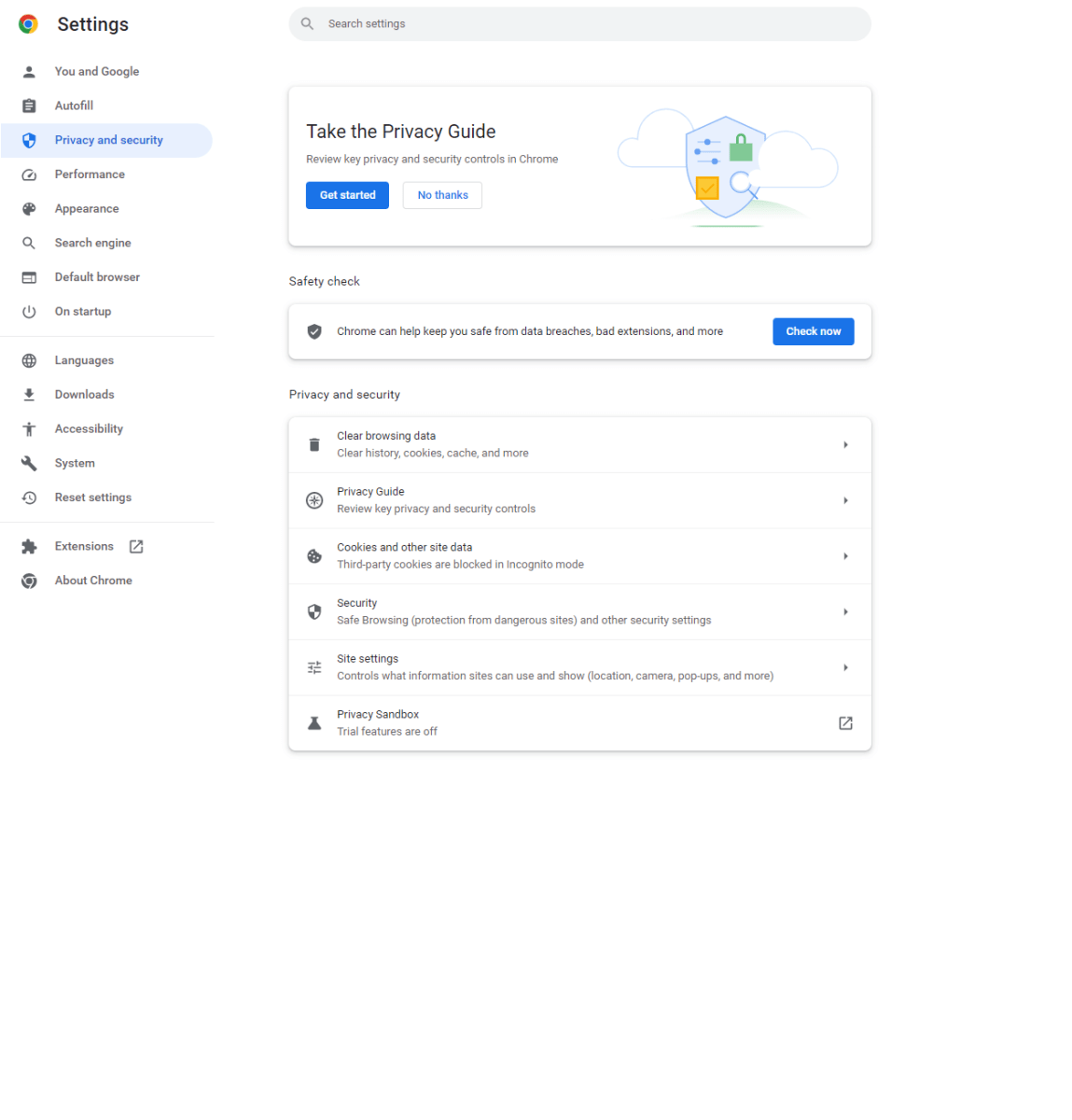
Clear Browsing Data
Clearing browsing data, including history, cookies, and cached files, liberates disk space and resolves website issues stemming from outdated or corrupted data. This action not only enhances performance but also improves privacy and security. Clearing browsing data reduces RAM usage, resulting in smoother browsing and faster page loads, especially on devices with limited memory. Access browsing data settings via three vertical dots > Settings > Privacy and Security. Select the desired data types and click “Clear data.”
Leverage Preloading
 Preloading Pages
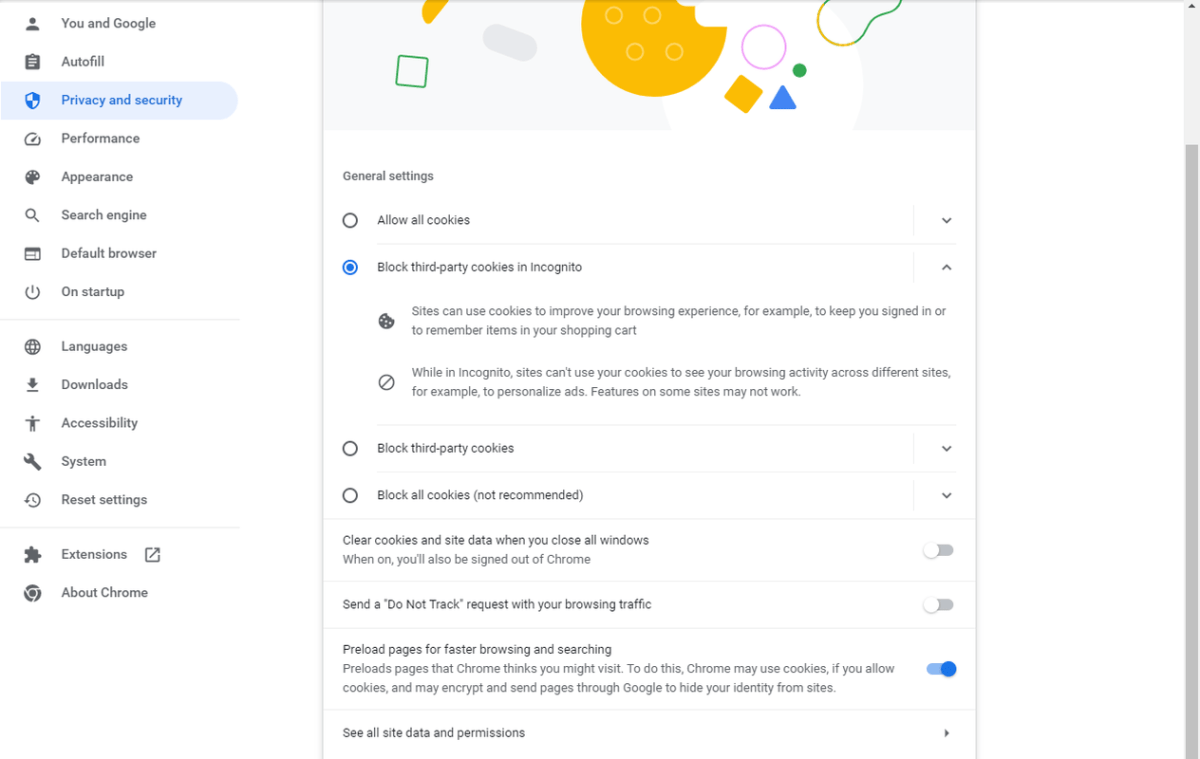
Preloading Pages
Preloading accelerates page loading by preemptively fetching resources before navigation. When hovering over a link or predicting user behavior, Chrome preloads resources like images, CSS, and JavaScript. This background fetching significantly reduces perceived load times. Enable preloading by navigating to three vertical dots > Settings > Privacy and Security > Cookies and other site data and toggling “Preload pages for faster browsing and searching” to the On position.
Utilize Chrome’s Energy Saver
 Energy Saver
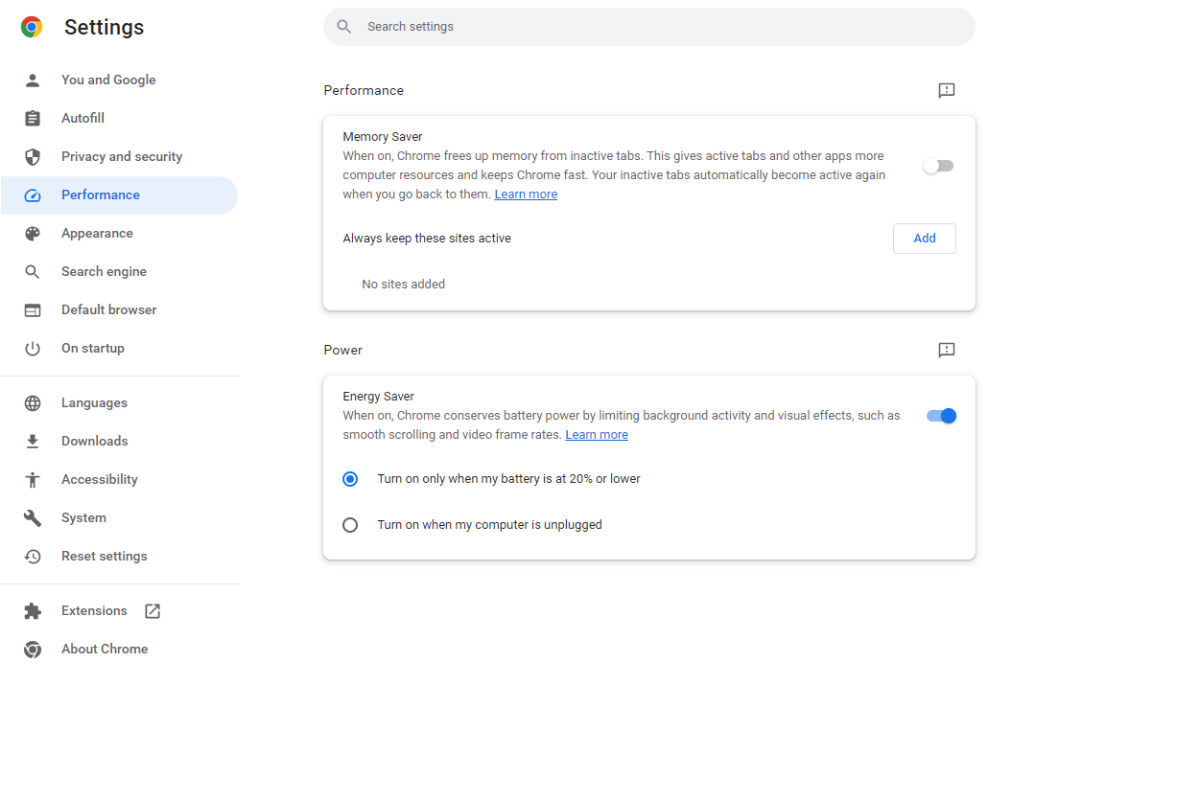
Energy Saver
While primarily designed to extend battery life, Energy Saver also improves performance by limiting background activity. Configure Energy Saver to activate at a specific battery threshold or when unplugged. Enable Energy Saver via three vertical dots > Settings > Performance and toggle the “Energy Saver” slider to the On position. Choose the desired activation trigger.
 Hardware Acceleration
Hardware Acceleration
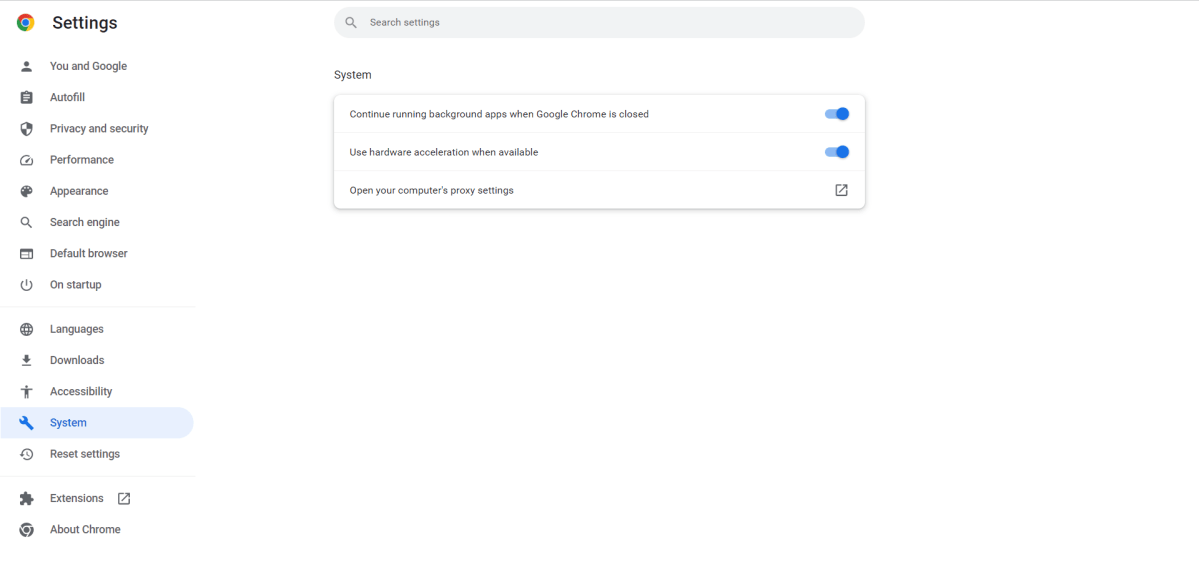
Enable Hardware Acceleration
Hardware acceleration leverages your GPU for tasks that benefit from parallel processing, such as rendering graphics, animations, and video. Offloading these tasks from the CPU to the GPU improves performance, smooths web content rendering, and reduces resource consumption. This is particularly advantageous for systems with powerful GPUs or when browsing graphically rich websites. Enable hardware acceleration through three vertical dots > Settings > System and toggling “Use hardware acceleration when available” to On.
Consider GPU Rasterization (Experimental)
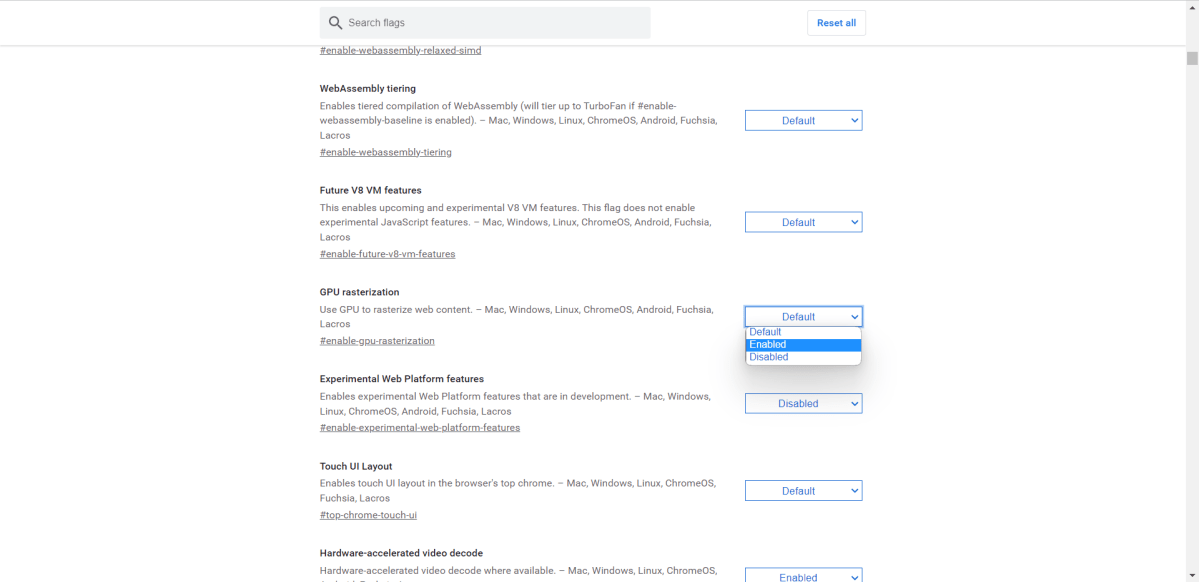 GPU Rasterization
GPU Rasterization
GPU rasterization offloads the process of converting vector graphics to pixels from the CPU to the GPU. This can improve rendering speed, but it’s an experimental feature. Enable this by typing chrome://flags in the address bar, searching for “GPU Rasterization,” and setting it to “Enabled.” Proceed with caution as this is an experimental feature.
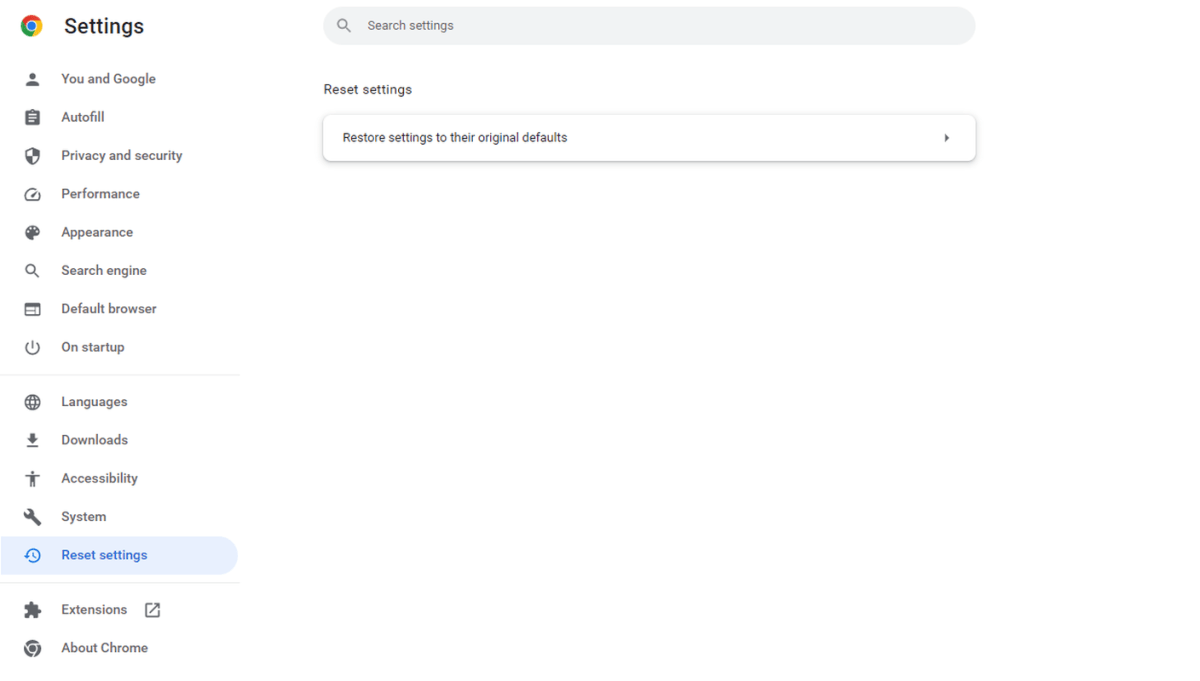 Resetting Chrome
Resetting Chrome
Reset Chrome to Default Settings
Resetting Chrome to its default configuration can resolve persistent performance problems by eliminating problematic customizations, extensions, or settings. This is a useful troubleshooting step if other methods fail. Access reset settings via three vertical dots > Settings > Reset Settings.
Google’s Ongoing Chrome Optimization
Google continually improves Chrome’s performance. Recent updates, like Chrome 112, introduced significant optimizations to JavaScript functions and HTML parsing, resulting in notable speed improvements. Staying updated ensures you benefit from these ongoing enhancements. These updates highlight the importance of keeping Chrome up-to-date to leverage Google’s continuous performance improvements.