A new GPU is a significant investment, so understanding its specifications is crucial. While the terms “GPU” and “graphics card” are often used interchangeably, they aren’t synonymous. This guide breaks down the essential technical specifications of a GPU to help you make an informed purchase.
(Further reading: 4 things to consider before buying a GPU)
A graphics card houses the GPU die (the actual processor) on a circuit board, surrounded by memory modules. This assembly is integrated with a heatsink, cover, and fan to form the complete graphics card. Manufacturers like AMD and Nvidia produce various GPU dies within a generation, leading to different models with customized specifications. Generally, lower numbers in die designations (e.g., AD102 vs. AD103 in Nvidia’s lineup) indicate larger, more powerful dies. Modern GPUs leverage smaller manufacturing processes, packing more performance into the same physical space.
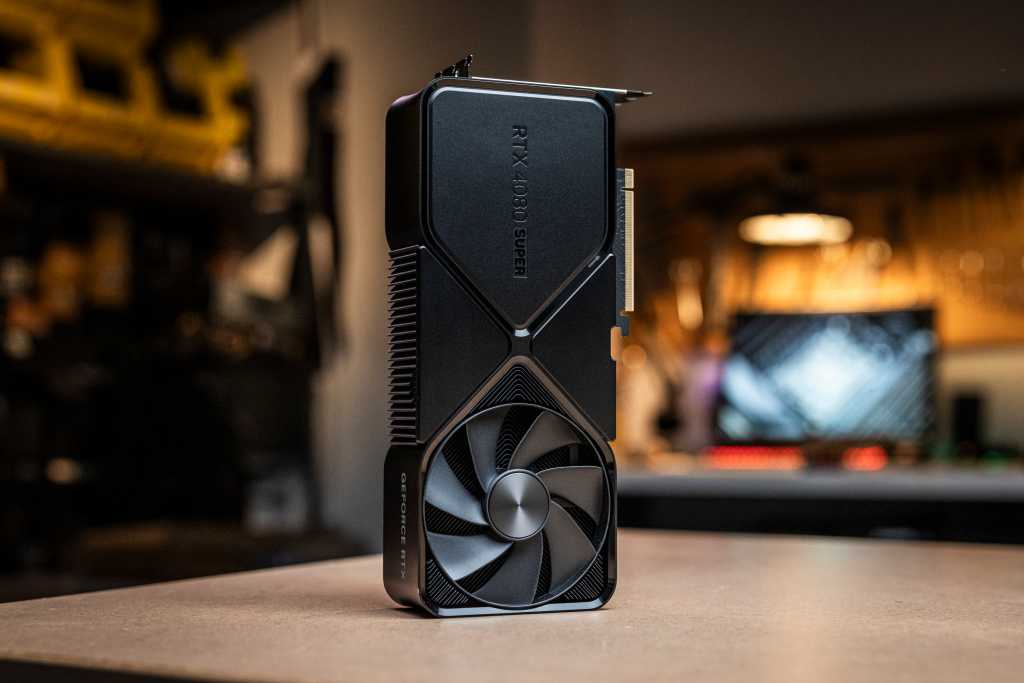
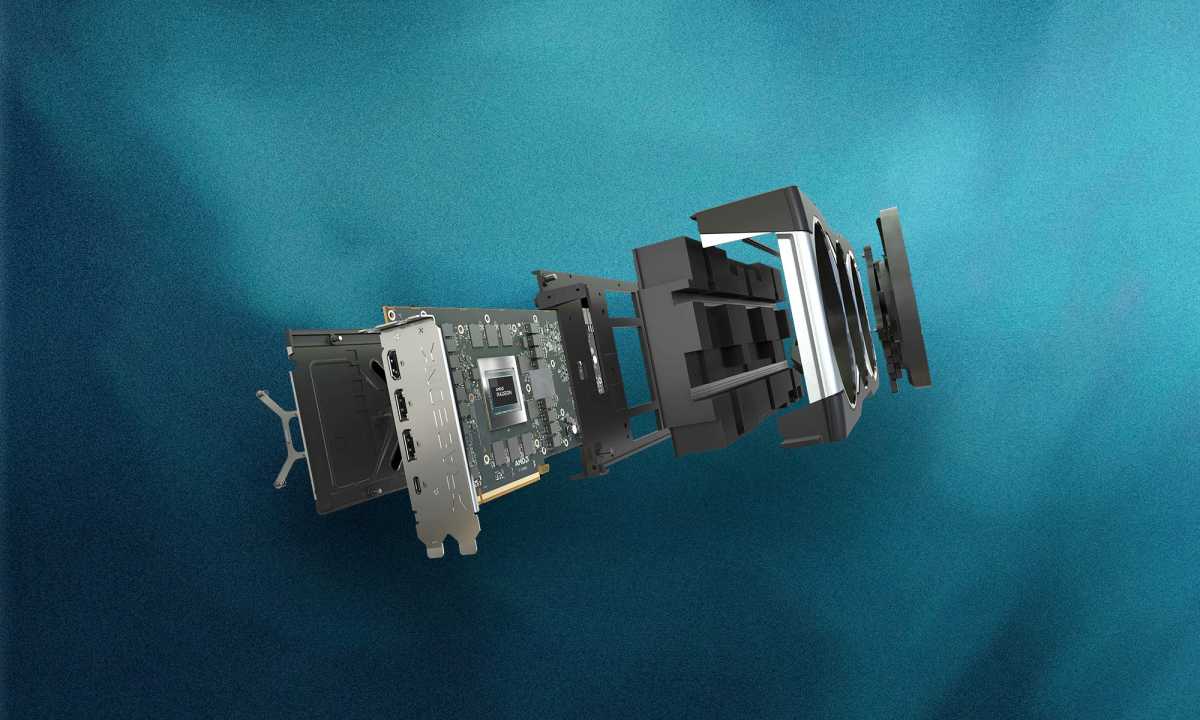 AMD GPUThe GPU is the graphics processor itself (pictured here is an AMD GPU). It becomes a graphics card when combined with other components.
AMD GPUThe GPU is the graphics processor itself (pictured here is an AMD GPU). It becomes a graphics card when combined with other components.
While often called “cores,” the processing units on a GPU differ significantly from CPU cores. GPUs have thousands of smaller processing elements grouped into clusters and then into compute units. These are labeled differently by manufacturers: Compute Units (AMD), Xe Cores (Intel), and Stream Multiprocessors (Nvidia). Faster GPUs typically boast more CUDA cores (Nvidia) or Stream Processors (AMD), but these metrics are only comparable within the same generation and manufacturer.
VRAM (Video RAM) is the dedicated memory on a graphics card. It stores the frame buffer, texture information, and other graphical data. Insufficient VRAM for your game settings and resolution can cause graphical glitches and performance drops. Key VRAM specifications include size, type (GDDR6, GDDR6X, etc.), memory bus width (e.g., 384-bit, 256-bit), and memory bandwidth (GB/s).
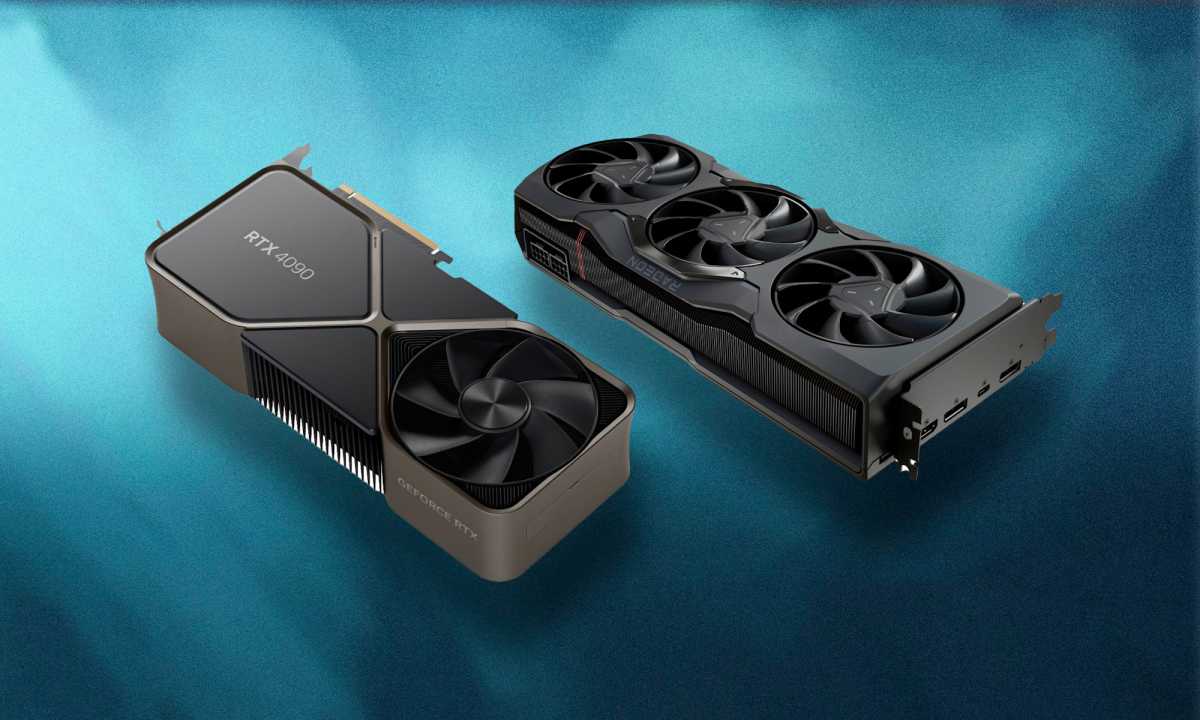 GPUGraphics cards have numerous technical specifications. Understanding the terminology is key to effective comparison.
GPUGraphics cards have numerous technical specifications. Understanding the terminology is key to effective comparison.
Like CPUs, GPUs have clock speeds for both the core and the memory. The core clock dictates instruction processing speed, while the memory clock governs data transfer speed between the GPU and VRAM. Higher clock speeds generally translate to better performance. Overclocking allows users to push these clock speeds beyond factory settings.
TGP (Total Graphics Power), measured in watts, represents a GPU’s maximum power consumption. This metric indicates power demands and provides insights into potential operating temperatures during intensive tasks.
FP32 (Floating-Point Single Precision) measures theoretical GPU performance in TFLOPS (trillion floating-point operations per second). While it’s a useful comparison tool across generations, it doesn’t encompass all performance aspects.
Other vital factors include PCIe generation support and compatibility with graphical APIs like DirectX, Vulkan, and OpenGL, especially for designers and developers. Software features like Nvidia DLSS, AMD FSR, and Intel XeSS also impact performance and game support, so verifying supported versions is essential.
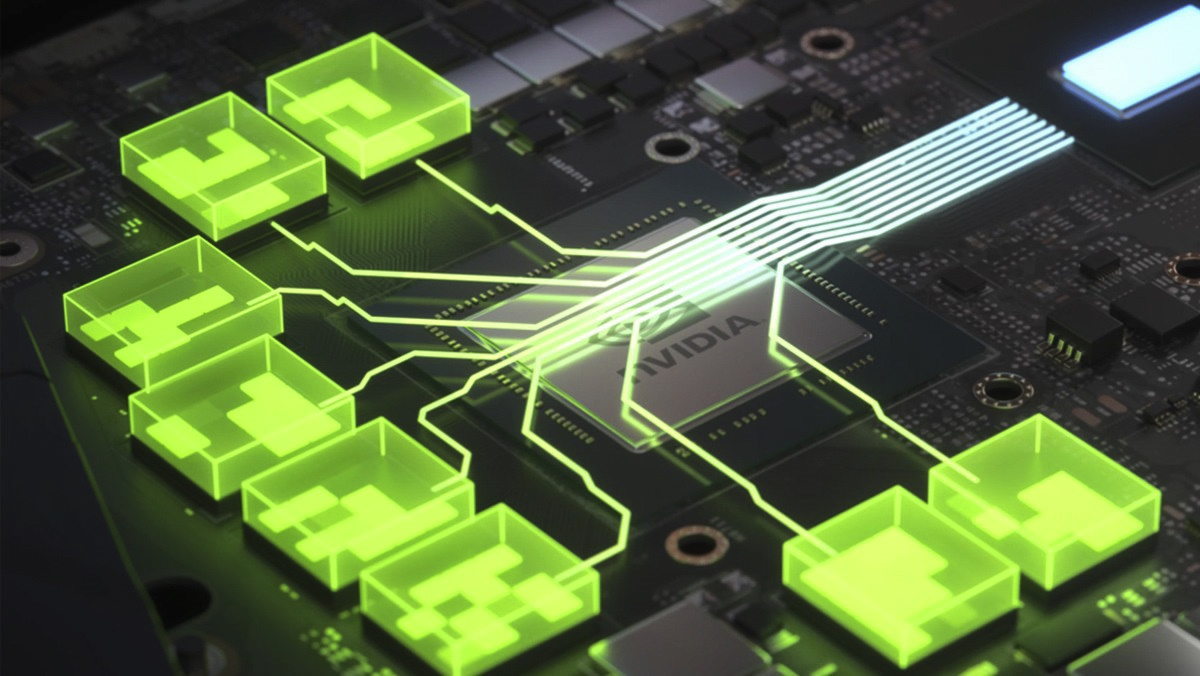 GrafikspeicherGraphics memory (shown in green) is positioned close to the die to minimize communication delays.
GrafikspeicherGraphics memory (shown in green) is positioned close to the die to minimize communication delays.
Before buying a GPU, consult real-world benchmarks and reviews from reputable sources like Reddit communities, YouTube channels, and tech publications. Focus on performance data for your intended games and applications to make the best choice.