Knowing your CPU’s temperature is crucial for ensuring optimal performance. An overheating CPU can lead to various issues, from performance throttling and system instability to crashes, even with a top-tier processor. Fortunately, there are several ways to check your CPU temperature, and some of the necessary applications might already be installed on your system. This guide outlines the most effective methods for monitoring your CPU temperature, regardless of whether you’re troubleshooting or simply curious about your processor’s performance.
Checking CPU Temperature on Windows
HWInfo is a comprehensive PC monitoring solution that provides detailed information about your system’s components, including CPU temperature. It offers a simple interface without overclocking tools, focusing on delivering accurate data. Whether you need an overall CPU temperature or per-core readings, HWInfo presents the information clearly.
-
Download and Install: Download HWInfo from the official website and install it.
-
Launch and Select Sensors: Upon launching, choose “Sensors Only” for temperature-specific data. Alternatively, explore the full suite of tools for a complete system overview.
-
Locate CPU Section: Scroll down to the CPU section, which displays your CPU model. Ensure you know your CPU model beforehand. Temperatures are displayed in Celsius, showing Current, Minimum, Maximum, and Average readings, illustrating temperature fluctuations over time and workload. You’ll also find Tdie (CPU die average), core-specific temperatures (Intel), or core complex die temperatures (AMD multi-die processors). Depending on your CPU, you might also see hotspot, L3 cache, and IOD temperatures. Expand the “Core Temperatures” section for individual core readings.
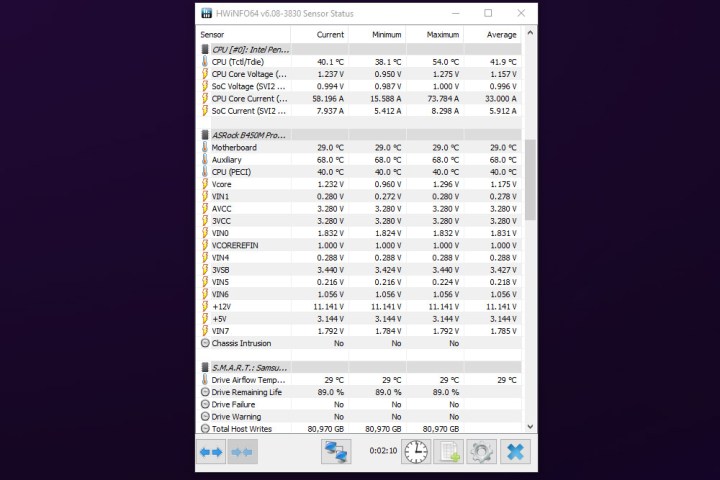 HWInfo sensor status page.Screenshot of HWInfo sensor status page.
HWInfo sensor status page.Screenshot of HWInfo sensor status page.
Monitoring CPU Temperature on macOS
TG Pro is a recommended application for monitoring CPU temperature on Macs. It allows temperature tracking and fan control, offering comprehensive thermal management. The app is verified by Apple and compatible with macOS updates, including the latest Apple Silicon and Intel-based Macs.
-
Download and Install: Download TG Pro from the official website and install it.
-
Utilize Monitoring and Control Features: TG Pro enables real-time temperature monitoring and manual fan curve adjustments, providing precise control over your system’s cooling.
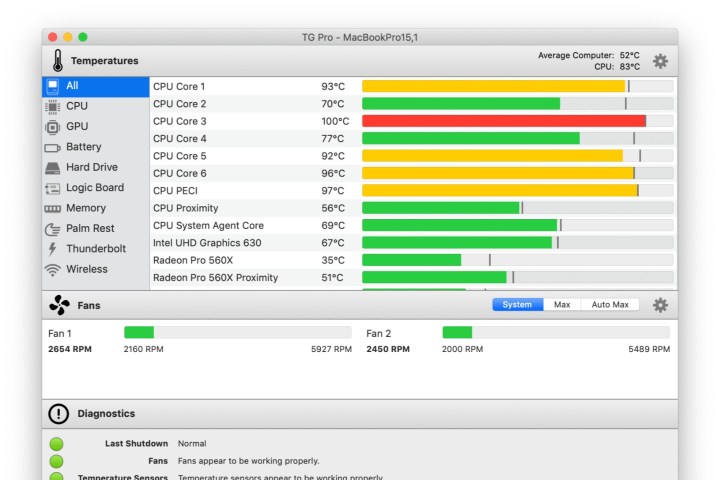 TG Pro tracking application.Screenshot of TG Pro tracking application.
TG Pro tracking application.Screenshot of TG Pro tracking application.
Checking AMD CPU Temperature
AMD Ryzen Master is a dedicated tool for monitoring and overclocking AMD Ryzen processors. It offers a convenient way to check CPU temperature and other vital statistics.
-
Download and Install: Download and install Ryzen Master from the official website.
-
Access CPU Statistics: Upon launching, the top section displays key processor statistics, including temperature, voltage, usage, and more. Individual core clock and temperature details are also available for in-depth analysis.
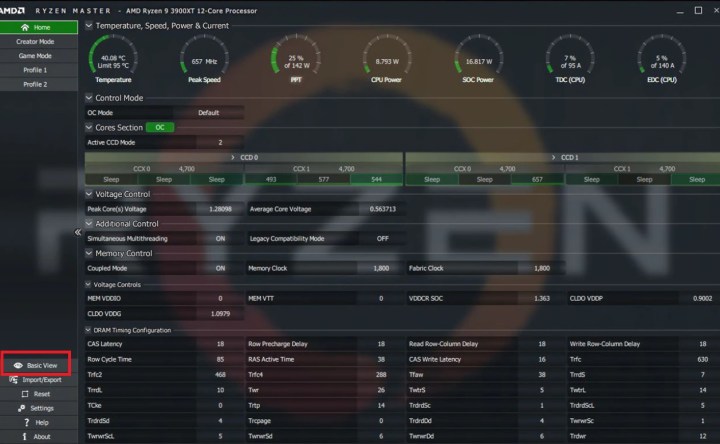 AMD Ryzen Master settings.Screenshot of AMD Ryzen Master settings.
AMD Ryzen Master settings.Screenshot of AMD Ryzen Master settings.
Monitoring Intel CPU Temperature
Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) is a powerful tool for monitoring and overclocking Intel Core processors. While primarily for overclocking, it provides valuable monitoring features, including CPU temperature tracking.
-
Download and Install: Download and install Intel XTU from the official website
-
Check Package Temperature: The main screen’s lower panel displays crucial CPU information, including the package temperature (your CPU temperature) and its corresponding graph. A “Yes” under “Thermal Throttling” indicates that your CPU is slowing down to manage excessive heat, suggesting the need for improved cooling. Consider upgrading to a better cooler, such as an all-in-one liquid cooler if feasible. CPU Utilization percentage indicates workload intensity. Use XTU’s built-in CPU benchmark for stress testing.
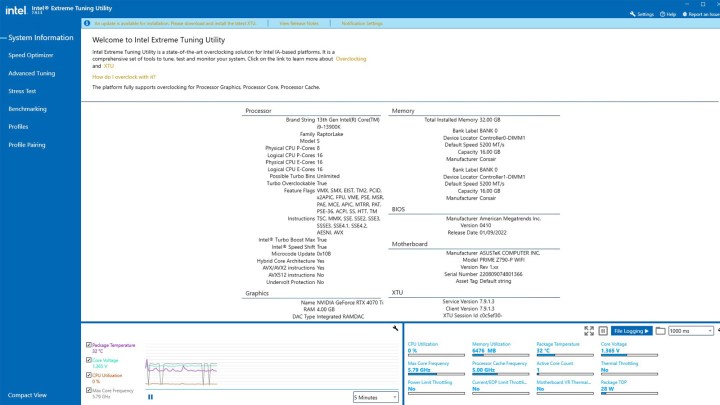 Intel XTU status screen.Screenshot of Intel XTU status screen.
Intel XTU status screen.Screenshot of Intel XTU status screen.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s a Safe CPU Temperature?
Ideal CPU temperatures vary depending on the specific CPU model, its thermal thresholds, and throttling behavior. Generally, temperatures below 80°C under full load are considered safe. Newer CPUs can often operate at up to 95°C without performance degradation. For detailed information, consult our guide on safe CPU temperatures.
How Can I Lower CPU Temperature?
Improving CPU cooling involves enhancing heatsink effectiveness, optimizing airflow, or reducing CPU workload. This can be achieved by upgrading to a larger heatsink, increasing fan speeds, improving cable management, adding more case fans, underclocking, or undervolting.