Your PC is slowing down. Boot times are creeping up, browser tabs lag, and video editing or gaming performance is sluggish. Every PC eventually reaches its limits, regardless of its purpose. But a new purchase isn’t always necessary. Often, a single component upgrade can revitalize your system. This guide helps you determine whether upgrading or buying a new PC is the best solution.
When Does a PC Upgrade Make Sense?
Desktop PCs are modular, making component replacement relatively straightforward for those with some technical knowledge. If you’re comfortable doing the upgrade yourself or can enlist expert help, upgrading is a viable option. It’s particularly beneficial when you can achieve significant performance gains by replacing just a few components at a low cost.
For instance, swapping an old HDD for an SSD dramatically speeds up boot times and program loading without requiring other component changes. Similarly, adding more RAM if your motherboard has free slots is a simple upgrade. A graphics card upgrade is also worthwhile if the processor isn’t being fully utilized in games, the power supply can handle a more powerful GPU, and the case has sufficient space.
Advantages of Upgrading:
- Cost-Effective: Replacing one component is significantly cheaper than a new PC.
- Time-Saving: Avoids the hassle of setting up a new system, reinstalling software, and migrating data.
- Sustainable: Reduces electronic waste by replacing only necessary parts.
When Should You Buy a New PC?
While upgrading is often preferable, sometimes a new PC is the better choice. If your system is severely outdated and requires multiple upgrades, the cumulative cost can exceed half the price of a new machine. In such cases, a new purchase is more sensible in the long run.
Upgrading individual components isn’t always feasible. A faster graphics card requires a compatible power supply with sufficient wattage and connections, and adequate case space. If these conditions aren’t met, additional component replacements can quickly escalate costs.
Processor upgrades can also be complex. Motherboards with Intel chipsets often require a new socket and chipset after two CPU generations. Upgrading to a newer processor may necessitate a new motherboard and potentially new RAM.
Compatibility with current software is another factor. Windows 11, for example, has specific processor requirements. Meeting these requirements might entail upgrading other components, making a new PC more attractive. Finally, new PCs come with warranties on all components, providing peace of mind.
Advantages of Buying New:
- Warranty: Comprehensive coverage for all components.
- Efficiency: Newer processors and graphics cards are more energy-efficient, reducing electricity costs.
- Future-Proofing: Latest technologies and interfaces ensure compatibility with future software and hardware.
Which Components are Worth Upgrading?
While technically any component can be replaced, upgrading the power supply or case is generally only for efficiency or aesthetic reasons. The components that directly impact system performance are:
- System Storage (HDD or SSD)
- RAM
- Graphics Card
- Processor
- CPU Cooler and Fan
Upgrading System Storage
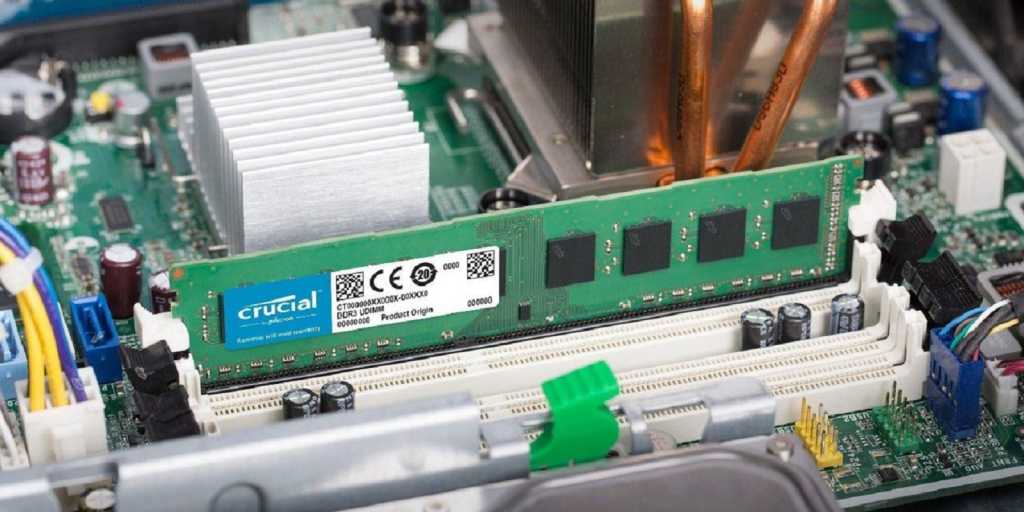
If your PC takes ages to boot or open programs, your operating system might be on an old HDD. Upgrading to an SSD drastically improves system responsiveness. Before upgrading, determine your PC’s available interfaces (SATA or NVMe). Our SSD buying guide helps you choose the right drive. After installation, either reinstall the operating system or clone it from the old drive.
Our Favorite SATA SSD
Samsung 870 EVO SATA SSD
 Samsung 870 EVO SATA SSDEditors
Samsung 870 EVO SATA SSDEditors
Read our review
Price When Reviewed: 250GB/$40, 500GB/$70, 1TB/$130, 2TB/$250, 4TB/$480
Best Prices Today: $64.99 at Walmart | $89.95 at B&H | $99.43 at Amazon
Upgrading RAM
Slow program startup or browser tab loading often indicates insufficient RAM. Check RAM usage in the Windows Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc). Under the Performance tab, select Memory. If RAM usage consistently reaches 90% or higher, consider upgrading.
We recommend at least 8GB of RAM for office PCs, preferably 16GB. Gaming PCs also benefit from 16GB, with 32GB ideal for demanding titles. Creative workloads like video editing and 3D rendering also require ample RAM.
Before upgrading, determine your processor’s supported RAM capacity and speed, available motherboard RAM slots, and the specifications (DDR type, clock rate, latency) of your existing RAM modules.
Upgrading Your Graphics Card
Best GPU for 1080p
Radeon RX 6600 Swft 210
 Radeon RX 6600 Swft 210
Radeon RX 6600 Swft 210
Read our review
Price When Reviewed: $329.99
Best Prices Today: $199.99 at Amazon | $229.99 at Newegg
Graphics card upgrades are crucial for gamers and creative professionals. First, determine whether the GPU, CPU, or RAM is the bottleneck. A faster graphics card won’t help if the processor is limiting performance.
If the GPU is the bottleneck, consider power supply wattage, PCIe power connections, and case space. A more powerful GPU may require a stronger power supply and a larger case. Also, check the PCIe generation supported by your processor and motherboard. While PCIe is backward compatible, using a PCIe 4.0 card in a PCIe 3.0 slot will reduce performance. Our graphics card buying guide assists in selecting the right GPU.
Upgrading the Processor
Processor upgrades are the most complex. First, ensure the CPU is the bottleneck. Then, check your motherboard’s compatibility with different processors, considering the CPU socket, TDP (Thermal Design Power), and BIOS updates. Find your motherboard model in System Information (Windows + R, then type “msinfo32”). Check the motherboard manufacturer’s website for compatible CPUs.
If your motherboard doesn’t support faster processors, you’ll need a new motherboard, possibly new RAM, and perhaps a new power supply. Avoid upgrading to older processors, even if compatible, as they lack modern interfaces (PCIe Gen 4/5, Wi-Fi 6(E), USB4) and may be incompatible with current software. Ensure your CPU cooler can handle a faster processor’s higher TDP. Otherwise, upgrade your cooler. You’ll also need thermal paste for the installation.
Upgrading CPU Cooler and Fan
Sometimes, a slow PC is due to overheating components, causing them to throttle performance. Learn how to monitor and lower CPU temperatures. If your CPU cooler is inadequate, consult our guide on optimizing PC fan setup for maximum cooling.
The best gaming CPU for most people
Intel Core i5-12400
 Intel Core i5-12400
Intel Core i5-12400
Price When Reviewed: $192
Best Prices Today: $132.99 at Amazon | $170.99 at Walmart