Google’s commitment to AI is evident across its product range, and Google Photos is a prime example. Now, Google is increasing transparency about AI’s role in image editing. AI-edited images using the Magic Editor’s Reimagine tool will now include an invisible watermark.
Reimagine empowers users to edit photos with natural language commands. By selecting elements and describing desired changes, users can alter backgrounds, remove objects, and add new elements.
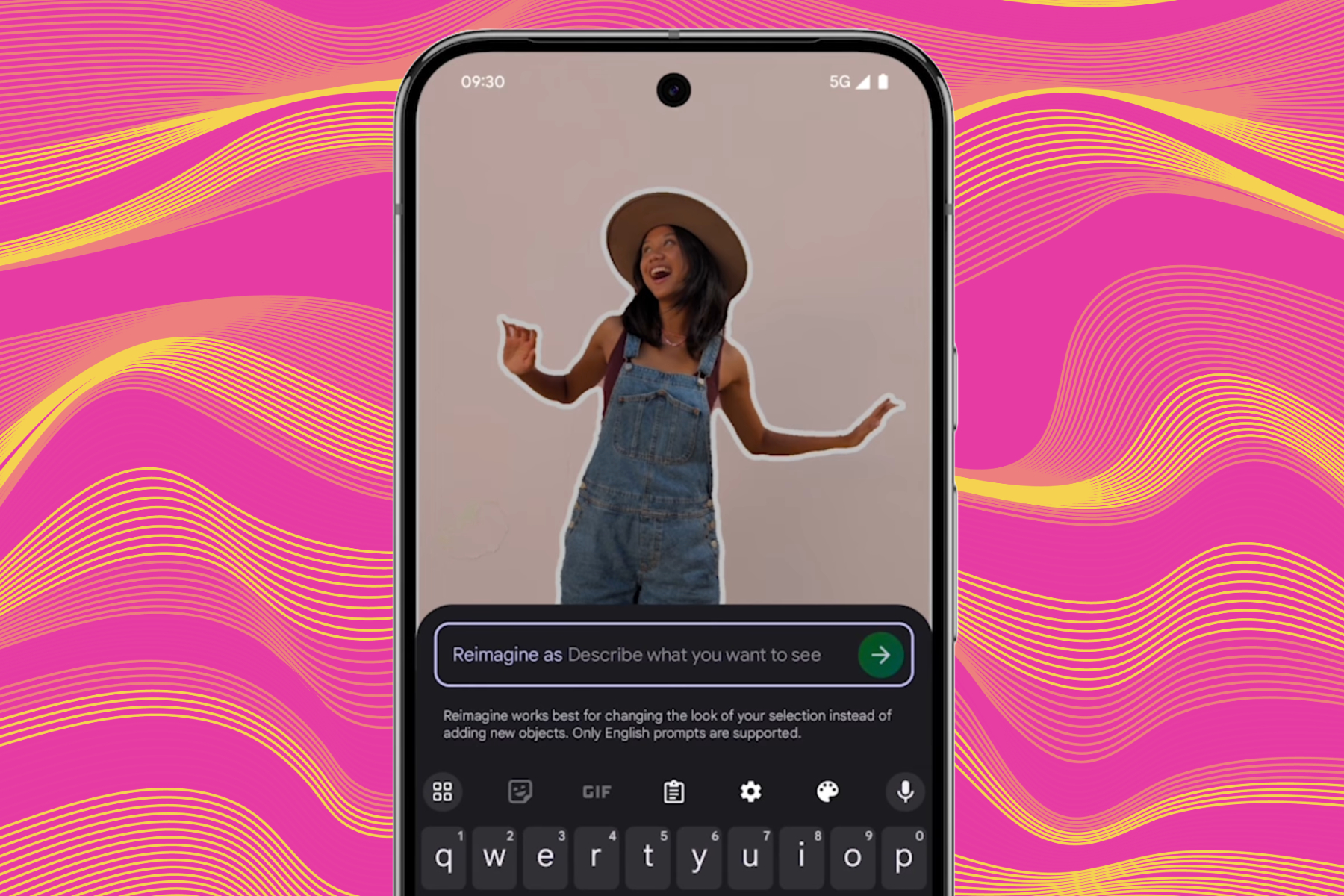
This watermark, imperceptible to the human eye, is embedded at the pixel level using Google’s SynthID digital watermarking technology. SynthID flags AI-edited photos without affecting image quality.
However, the watermarking isn’t always foolproof. Google acknowledges that subtle changes, such as altering a small flower’s color, might be too minor for SynthID to detect and label.
Developed by Google DeepMind, SynthID is designed to watermark AI-generated visual content. This technology allows machines and systems, including Google Search, to identify AI-edited images.
Even after cropping, color adjustments, filtering, or compression, the SynthID watermark persists, maintaining the AI signature. Beyond images from Google’s Imagen model, SynthID is also integrated into videos created by the Veo video generation model.
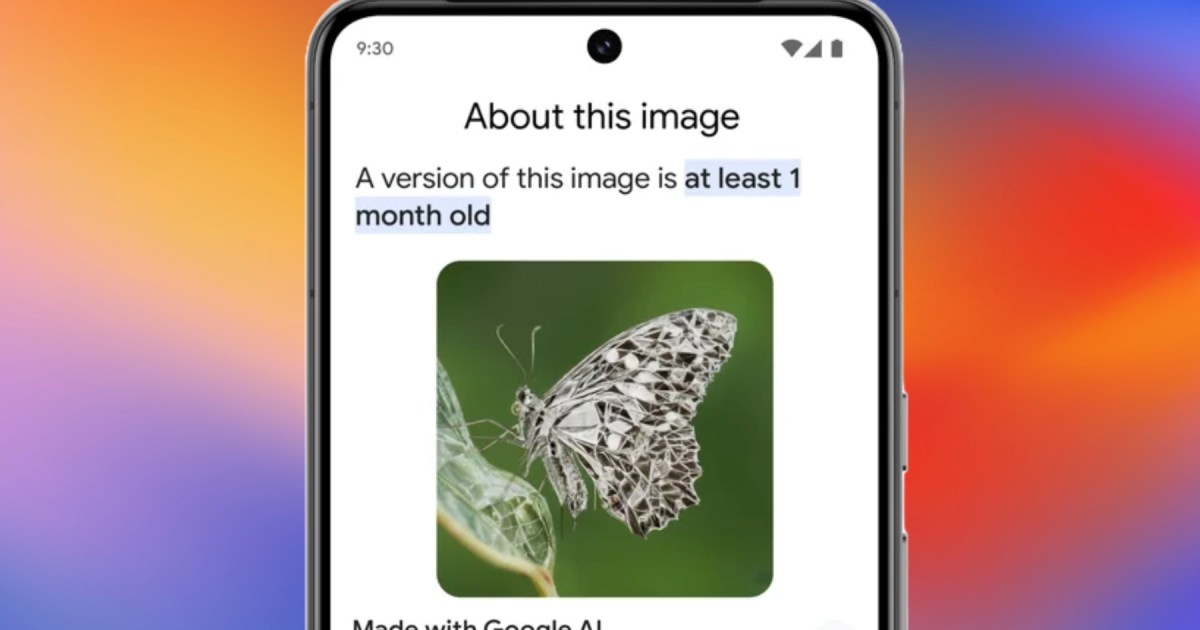
Users can verify AI involvement by accessing the “About this image” data. This information is accessible for online images via Chrome and Google Image Search.
“About this image” details the image’s first indexing date by Google Search, its initial online appearance, and its AI origins. This section is also available through the Circle to Search feature on smartphones and Google Lens within the Google mobile app for Android and iOS. Copyright protection for these images depends on the extent of AI utilization.
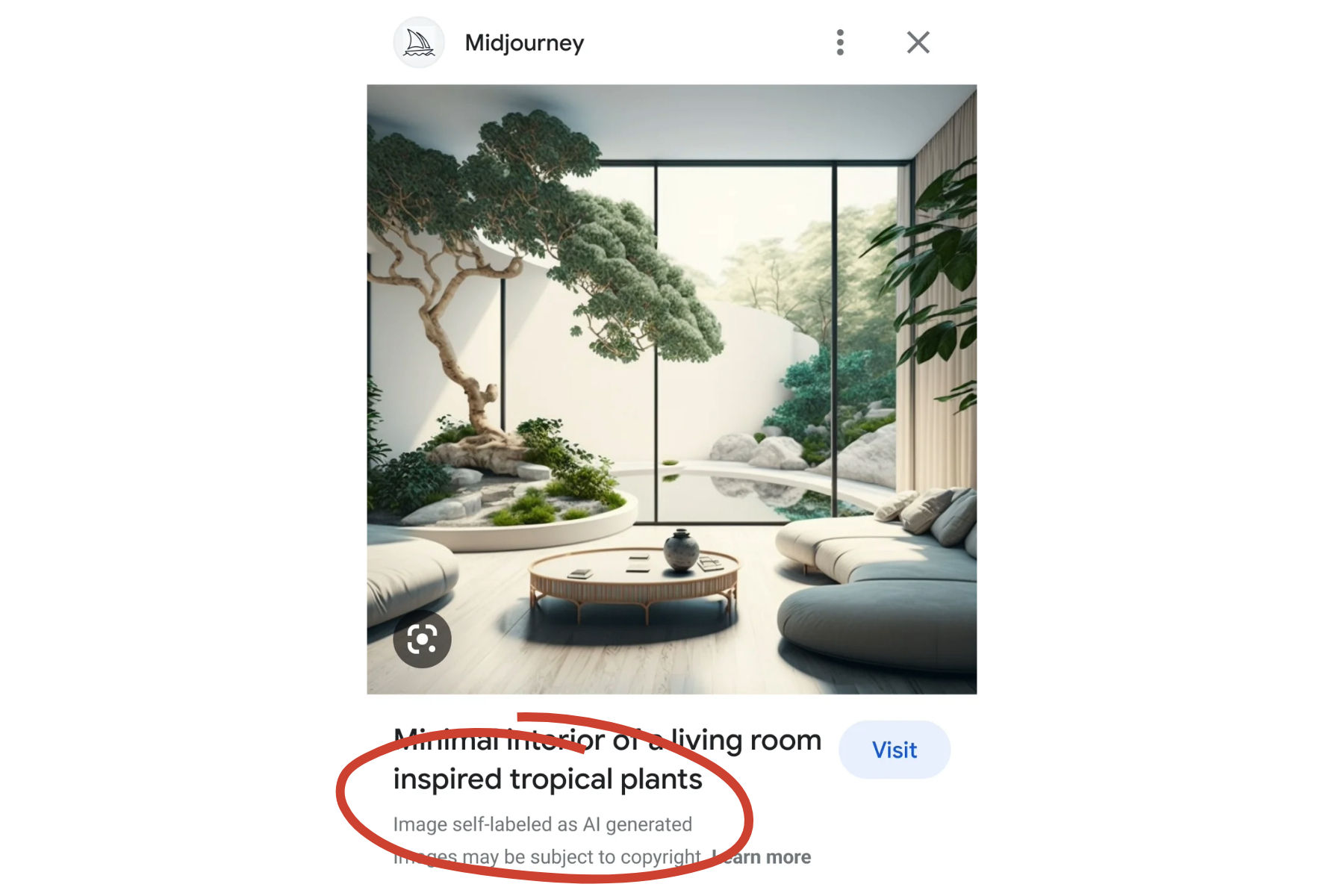
Google’s approach differs from emerging standards like C2PA, which employ cryptographic methods to modify image metadata. Interestingly, Google, alongside Amazon, Meta, OpenAI, and Microsoft, is a member of the Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity (C2PA).