Google is strengthening its digital certificate security protocols, impacting websites using certificates from Entrust and AffirmTrust. This move, announced on Google’s Security blog, stems from these Certificate Authorities (CAs) exhibiting recurring security lapses, unmet improvement commitments, and inadequate incident response times.
What are Digital Certificates and Why Does This Matter?
Digital certificates are essential for online security. They authenticate websites and encrypt data transmitted between the site and users. Compromised certificates can expose sensitive information to hackers, making robust certificate management crucial. Google’s decision to distrust Entrust and AffirmTrust highlights the importance of maintaining high security standards for CAs.
Impact on Chrome Users and Website Owners
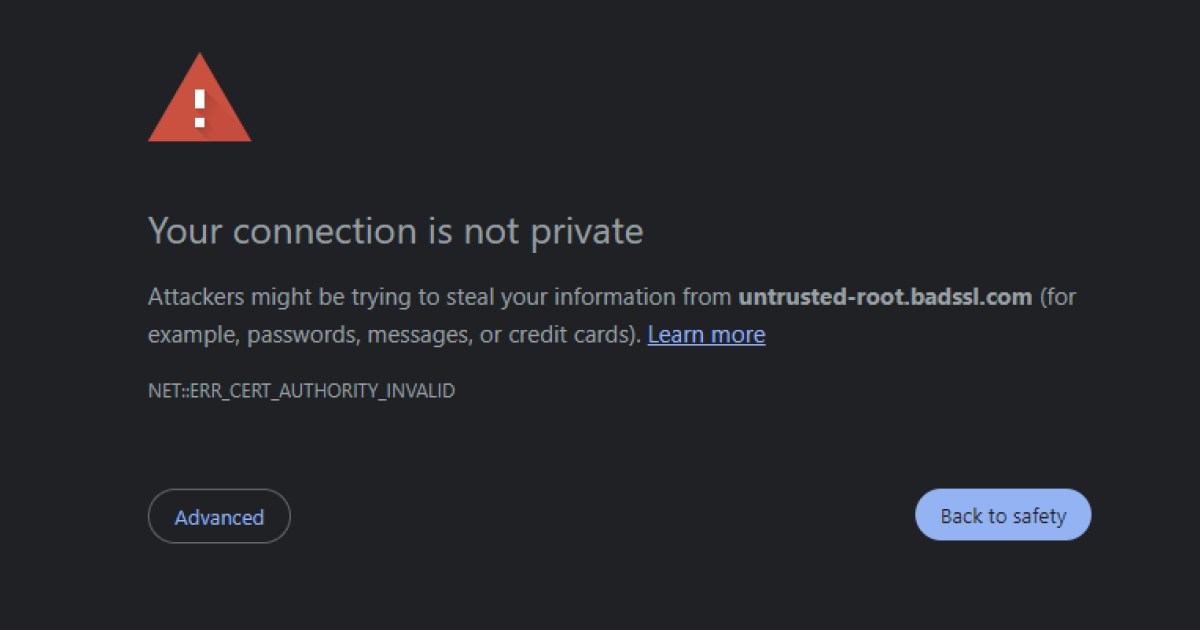
Starting October 31, 2024, Chrome users visiting websites with affected certificates will encounter warnings about untrusted connections (Chrome 127+). Specifically, users will see the “ERR_CERT_AUTHORITY_INVALID” error. Websites like merrilledge.com, moneygram.com, and ey.com, which utilize Entrust certificates, will be affected.
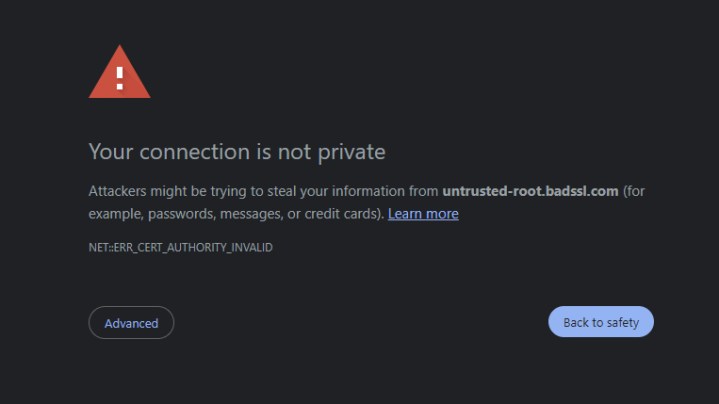 Connection is not private warning from Google.
Connection is not private warning from Google.
Example of an untrusted connection warning in Google Chrome.
To verify a connection’s security in Chrome, click the “Tune” icon to the left of the address bar, then navigate to “Connection is secure” and “Certificate is valid.” Website owners can check if their certificate is issued by Entrust or AffirmTrust under the “Issued By” section.
Google’s Recommendations and Future Implications
Google urges website owners using Entrust or AffirmTrust certificates to switch to a new, publicly trusted CA before the deadline. This action might signal Google’s future approach to digital certificate security across its products. Enterprise customers, however, retain the option to continue trusting Entrust.
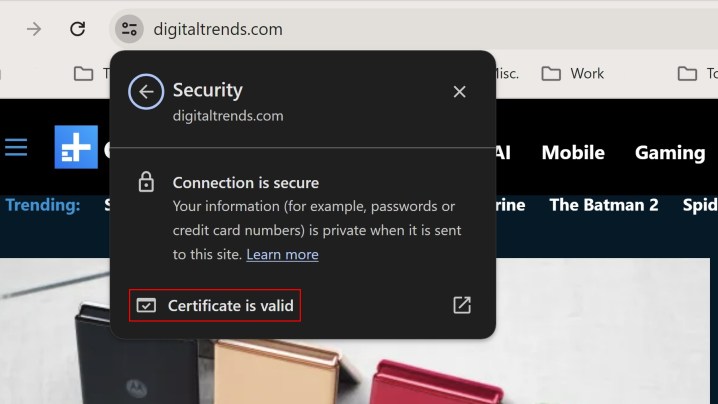 Valid certificate on MaagX.
Valid certificate on MaagX.
Example of a valid certificate verification in Chrome.
A History of Security Enforcement
This isn’t Google’s first intervention regarding certificate security. In 2015, Google issued an ultimatum to Symantec concerning unauthorized HTTPS certificates. While this news might raise concerns, users can enhance their Chrome security through various measures, such as encrypting passwords.
Conclusion
Google’s move underscores the critical role of digital certificate security in maintaining a safe online environment. By distrusting CAs with security lapses, Google aims to incentivize better security practices and protect users from potential threats. Website owners should proactively address this change to ensure uninterrupted access for their users.