Apple’s philosophy for new features often centers on robust safety and effortless user convenience. AirPlay, the company’s proprietary wireless protocol for streaming audio and video between devices, exemplifies this. While AirPlay functions seamlessly across Apple’s ecosystem and on many third-party TVs and speakers, this widespread compatibility also presents an attractive target for malicious actors. Recent findings indicate that vulnerabilities within AirPlay could potentially allow attackers to distribute malware and compromise connected devices, highlighting critical AirPlay security vulnerabilities that users need to address.
Understanding the “Airborne” AirPlay Risk
Security researchers at Oligo recently detailed a set of flaws, collectively named “Airborne,” affecting Apple’s AirPlay Protocol and its Software Development Kit (SDK). These vulnerabilities could enable hackers to execute code remotely, potentially taking control of AirPlay-enabled devices and using them as a gateway to cause broader network damage.
“An attacker can take over certain AirPlay-enabled devices and do things like deploy malware that spreads to devices on any local network the infected device connects,” Oligo explained. The potential impact is significant, given the billions of AirPlay-compatible Apple devices in use and the millions of certified third-party products.
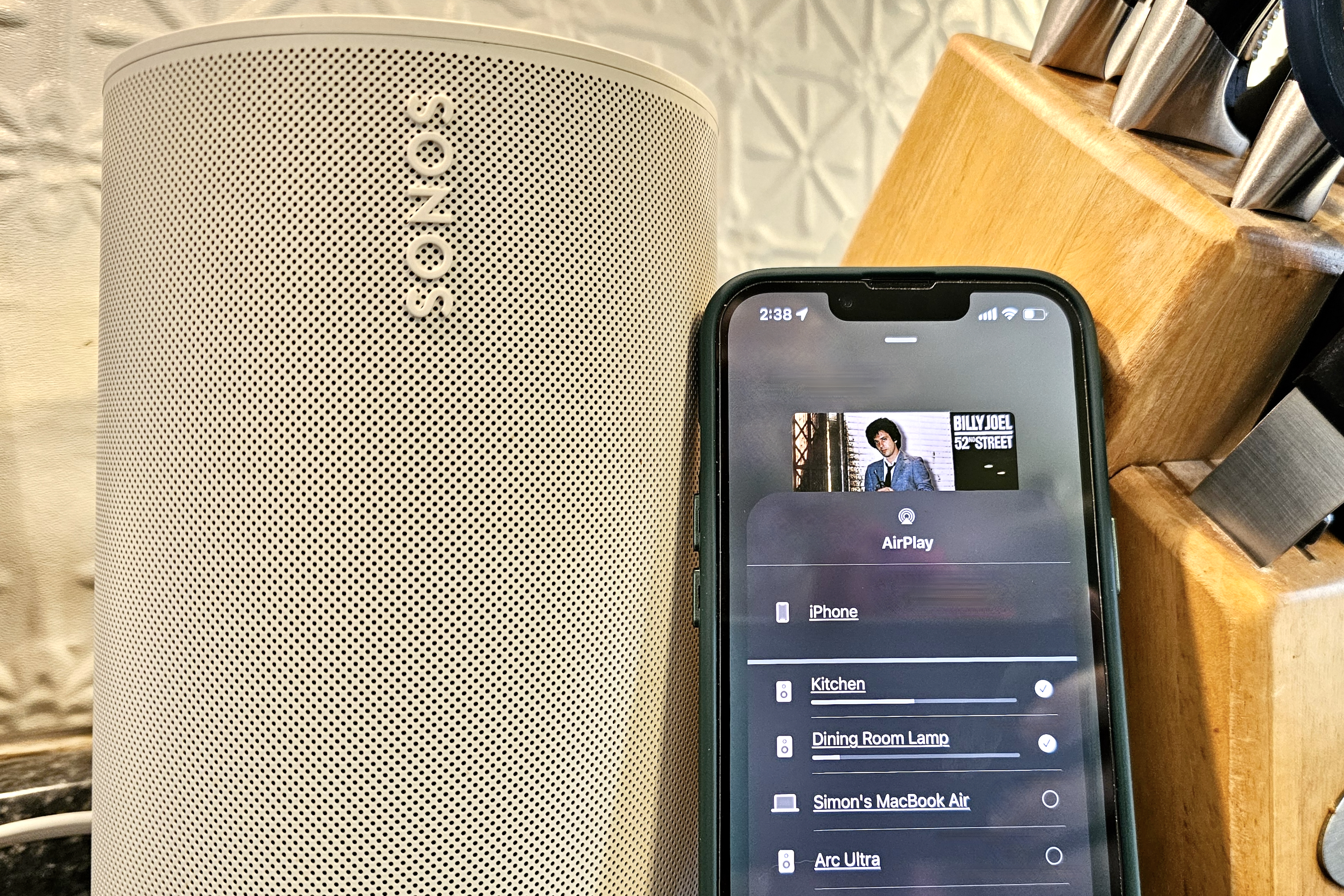 iPhone displaying AirPlay speaker selection menu next to a Sonos Era 100, illustrating broad device compatibility and potential AirPlay security vulnerabilities.
iPhone displaying AirPlay speaker selection menu next to a Sonos Era 100, illustrating broad device compatibility and potential AirPlay security vulnerabilities.
One specific vulnerability could allow an attacker to compromise a single device and then leverage it to access the wider network, thereby targeting other connected devices. The consequences vary depending on the target, ranging from eavesdropping on conversations and tracking a vehicle’s location to accessing sensitive data, executing ransomware attacks, or causing denial of service.
Apple has addressed these vulnerabilities through updates in macOS Sequoia 15.4, tvOS 18.4, macOS Ventura 13.7.5, iPadOS 17.7.6, macOS Sonoma 14.7.5, iOS 18.4, iPadOS 18.4, and visionOS 2.4. However, a considerable number of older devices may not receive these patches, leaving them susceptible to these AirPlay security vulnerabilities.
What Steps Do Experts Suggest?
The primary defense against these threats is to install the security fixes released by Apple. Yet, this is only part of the solution. Trevor Horwitz, CISO and founder of TrustNet, emphasizes that patches are only effective if users actively install them once downloaded.
“The simplest and most effective thing you can do is keep your devices updated. That sounds basic, but it’s often overlooked,” he advises. To install updates on an iPhone or iPad, navigate to Settings > General > Software Update. For macOS users, the path is Apple menu > System Settings > General > Software Update.
 macOS System Settings dialog for AirPlay, showing options to control access and require a password to enhance AirPlay security.
macOS System Settings dialog for AirPlay, showing options to control access and require a password to enhance AirPlay security.
Since attack vectors like Airborne can exploit Wi-Fi networks to propagate, network security is also paramount. Oleh Kulchytskyi, Senior Malware Reverse Engineer at MacPaw’s Moonlock, told DigitalTrends that a Zero-Click Remote Code Execution (RCE) represents the highest level of security breach.
While companies should patch such vulnerabilities immediately, users must also take network-related precautions. “To stay safe at home, ensure that your router has a strong password and there are no suspicious connections to your network,” Kulchytskyi adds. [internal_links]
A Safe Way to AirPlay
Matthias Frielingsdorf, an experienced iOS researcher and cofounder of iVerify, recommends adhering to fundamental digital security practices. These include promptly installing updates, maintaining strong network passwords, and, crucially, minimizing the potential attack surface.
Given that AirPlay is the threat vector, users should adopt proactive measures. ”Disabling this on iOS / macOS / tvOS devices that don’t need to be an AirPlay receiver would limit some of the attacks. In public spaces, disabling WiFi on the Mac and iPhone would stop those attacks as well,” says Frielingsdorf.
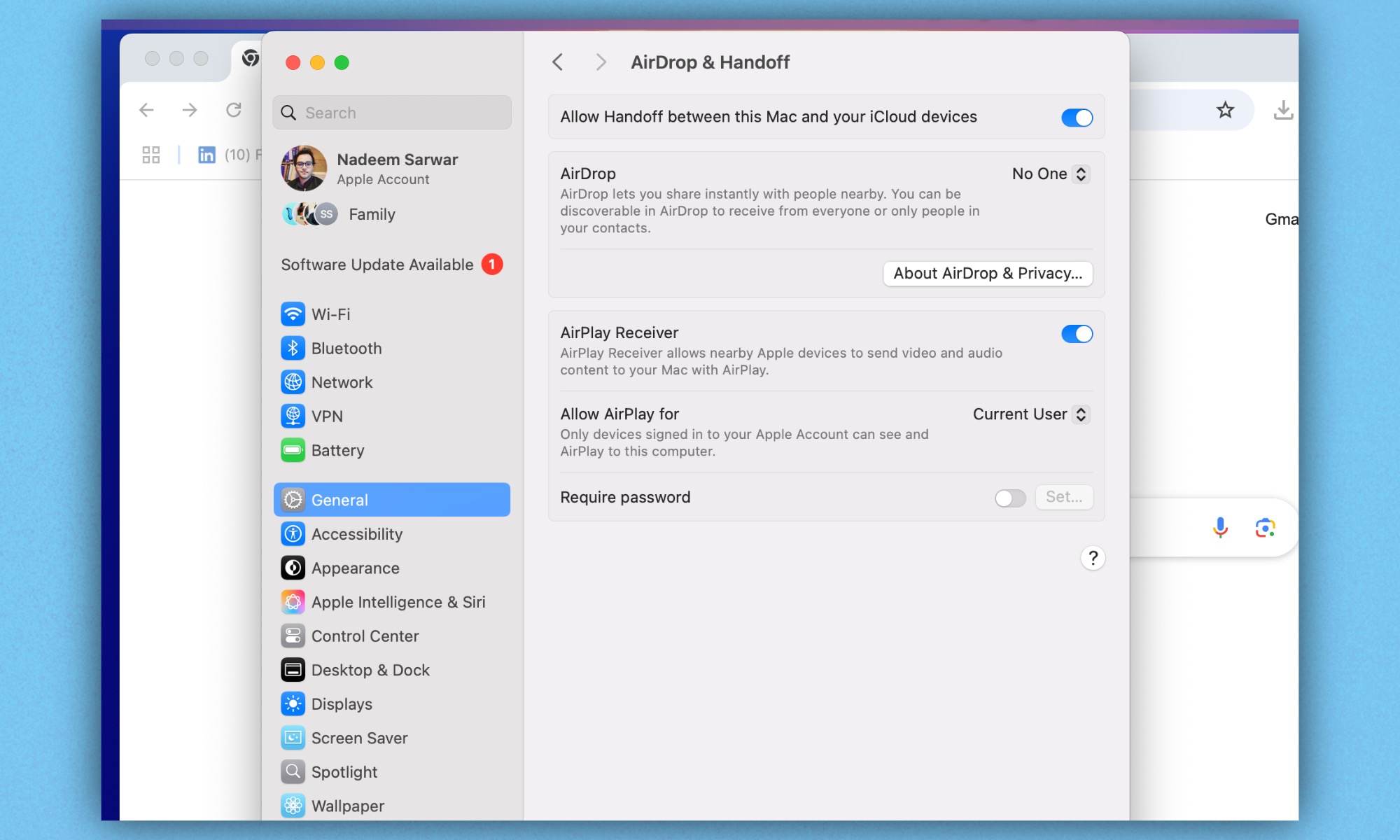 Adjusting AirPlay Receiver settings on a Mac, including the toggle switch and user access permissions to prevent unauthorized AirPlay connections.
Adjusting AirPlay Receiver settings on a Mac, including the toggle switch and user access permissions to prevent unauthorized AirPlay connections.
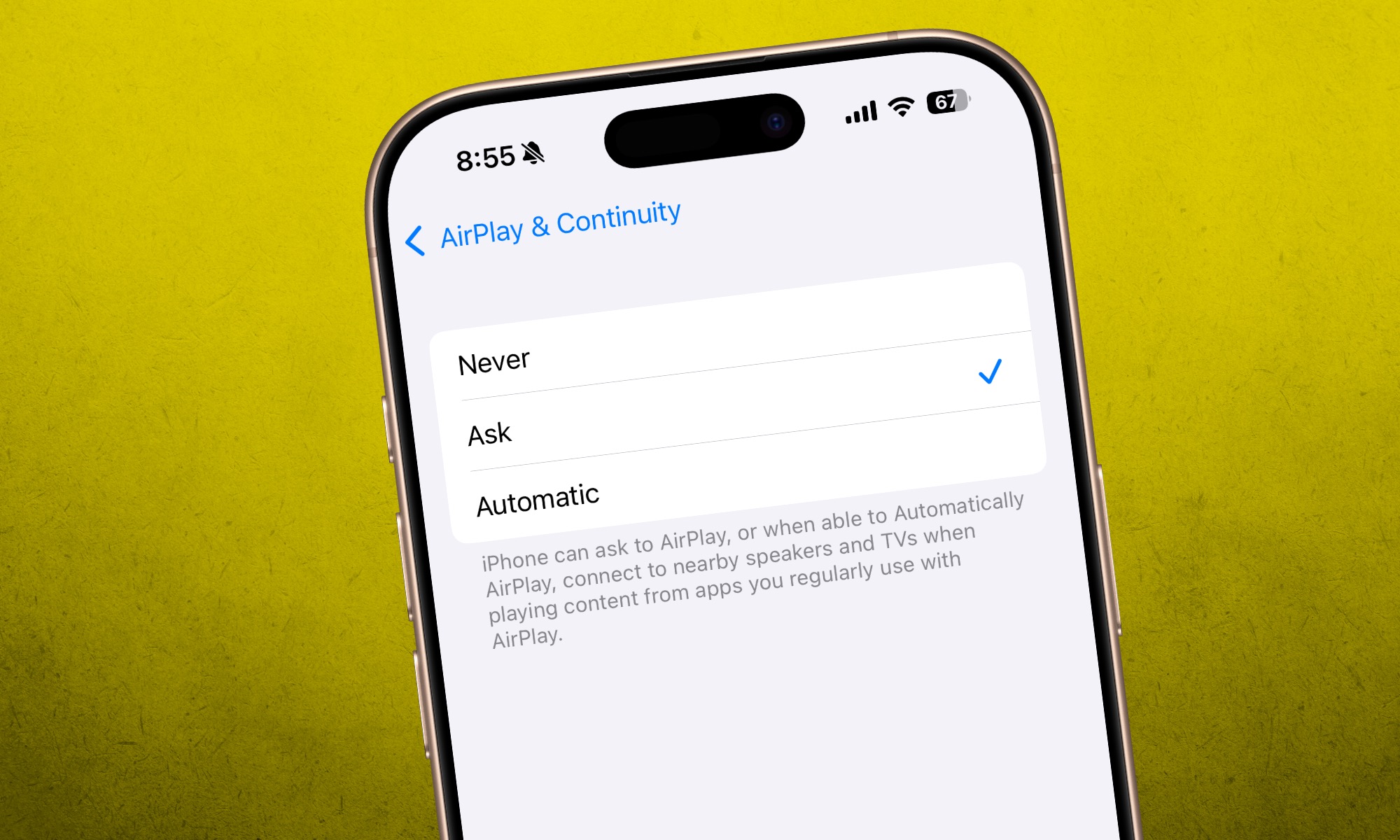
AirPlay streaming is often active by default, so manual disabling may be necessary. On your iPhone or iPad, go to Settings > General > AirPlay & Handoff > Automatically AirPlay. You can set this to Ask or Never if you don’t frequently use the feature. On the same screen (Settings > General > AirPlay & Handoff), you can turn off the AirPlay Receiver toggle if your device doesn’t need to receive AirPlay streams. If you do use it as a receiver, you can restrict access to Current User or Anyone on the Same Network instead of Everyone, and set a password.
For Mac users, configure these settings via Apple Menu > System Settings > General > AirDrop & Handoff > AirPlay Receiver. Here, you can turn AirPlay Receiver off, or restrict who can AirPlay to your Mac and set a password. Since older or discontinued devices may not always receive patches, it’s vital to ensure that currently used machines have appropriate protocols enabled to minimize risks.
The Bottom Line
Security experts have previously highlighted flaws in wireless transmission systems like Bluetooth. However, a vulnerability enabling zero-click remote code execution in AirPlay serves as a significant cautionary tale. The underlying message is clear: Apple’s security measures are robust, but not infallible.
Apple’s security guardrails are solid, but not impenetrable.
“What makes this serious is the integration. AirPlay isn’t just a standalone app. It’s a system-level service built into iOS, macOS, and tvOS. So the moment that layer is compromised, the attacker could potentially affect multiple devices at once,” TrustNet’s Horwitz explained to MaagX.
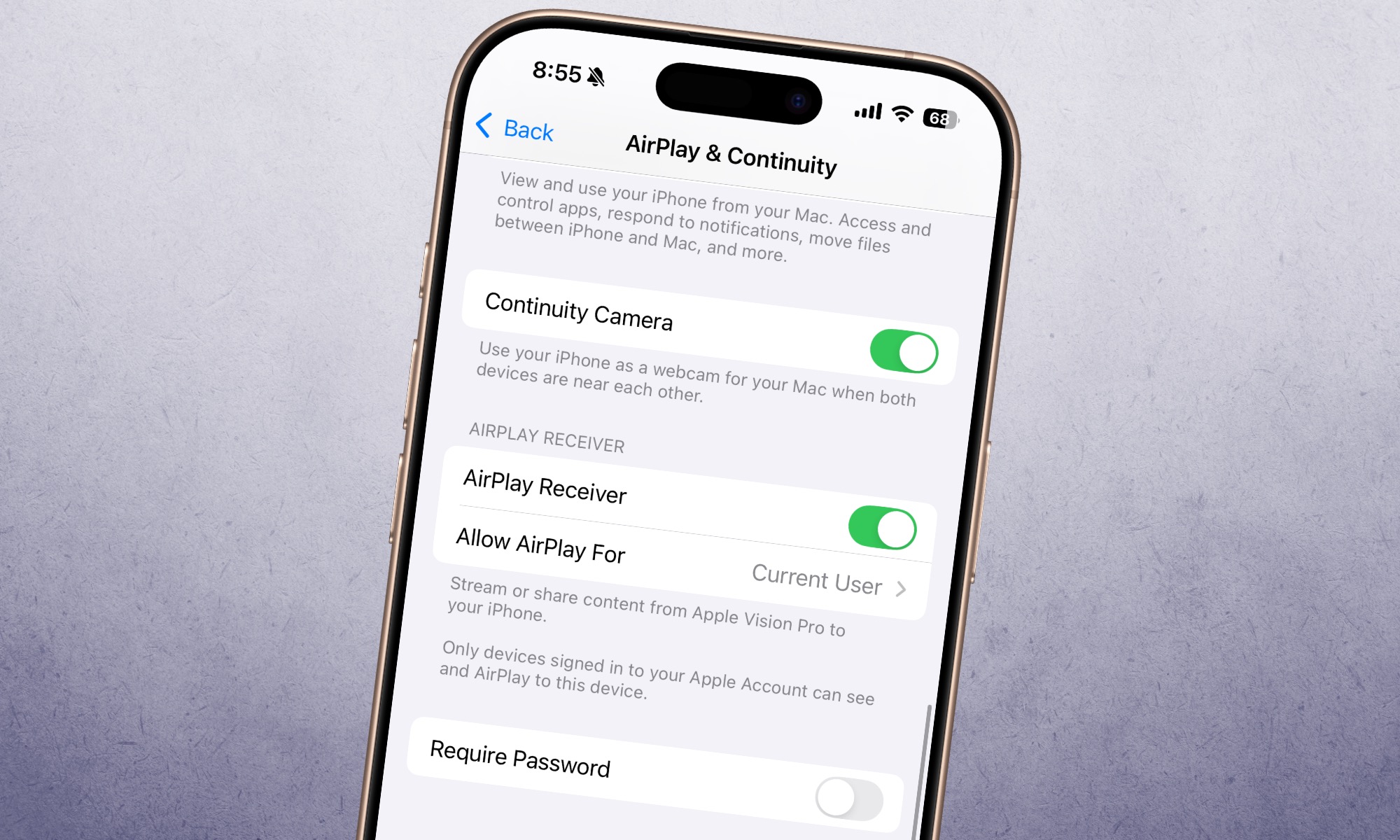 iPhone settings for AirPlay & Handoff, showcasing options to manage automatic AirPlay, HomePod transfers, and the AirPlay Receiver function for improved device security.
iPhone settings for AirPlay & Handoff, showcasing options to manage automatic AirPlay, HomePod transfers, and the AirPlay Receiver function for improved device security.
So, what does this mean for the average user who may not be well-versed in security measures? It’s time to look beyond marketing perceptions. Chris Hill, Chief Security Strategist at BeyondTrust, advises users to understand the evolving threat landscape rather than assuming any single ecosystem is inherently safer.
“Threat actors are opportunistic, looking for the easiest path of least resistance, they will find it, and they did in this case with AirPlay and AirBorne,” he warns. Ultimately, keeping your devices updated, disabling features you don’t use, and remaining vigilant about network security settings are crucial steps to protect yourself from AirPlay security vulnerabilities and other emerging threats.