The web browser has evolved into the central hub of the modern PC experience. No longer just for websites, browsers now handle everything from office suites like Microsoft Word and Google Docs to streaming entertainment and even basic photo and video editing. The operating system itself has become almost secondary; the browser is key.
This makes choosing the right browser more critical than ever. Your browser choice impacts your online security, privacy, browsing speed, and overall functionality. With options like Microsoft Edge’s AI-powered Copilot and Opera’s built-in VPN, the differences are significant. This article delves into a comprehensive comparison of leading browsers, focusing on security, privacy, and features to help you make the best choice.
Chromium vs. Firefox: Two Browser Families
Today’s browser landscape is dominated by two main technology families. One is built upon Chromium, an open-source project backed by Google, Intel, Opera, and Samsung. The other stems from the Firefox open-source browser.
Key Chromium-based browsers include Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Opera, Vivaldi, and Brave. The Firefox family encompasses Firefox itself, Tor Browser, and Librewolf.
Chromium browsers utilize the Blink rendering engine, while Firefox programs employ Gecko. Since Microsoft and Opera discontinued their proprietary engines (EdgeHTML and Presto, respectively), Blink and Gecko remain the dominant rendering engines. The rendering engine is the core component responsible for visually displaying a website’s HTML code. Our comparison focuses on Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, and Vivaldi.
| Browser | Google Chrome | Microsoft Edge | Mozilla Firefox | Opera | Vivaldi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automatic Updates | + | + | + | + | + |
| Sandbox | + | + | + | + | + |
| Password Manager | + | + | + | + | + |
| Anti-Phishing | + | + | + | + | + |
| Anti-Malware | + | + | + | + | + |
| VPN | – | 5 GB/month | Paid | Free | – |
| Incognito Mode | + | + | + | + | + |
| Do Not Track | + | + | + | + | + |
| Tracking Blocker | + | + | + | + | Via URLs |
| Anti-Fingerprinting | Add-on Only | Add-on Only | Integrated | Add-on Only | Add-on Only |
| Synchronization | + | + | + | + | + |
| Sync Encryption | + | + | + | + | Password |
| Android Version | + | + | + | + | + |
| iOS Version | + | + | + | + | + |
| Integrated AI | – | + | – | + | – |
Security Features: Browsers Compared
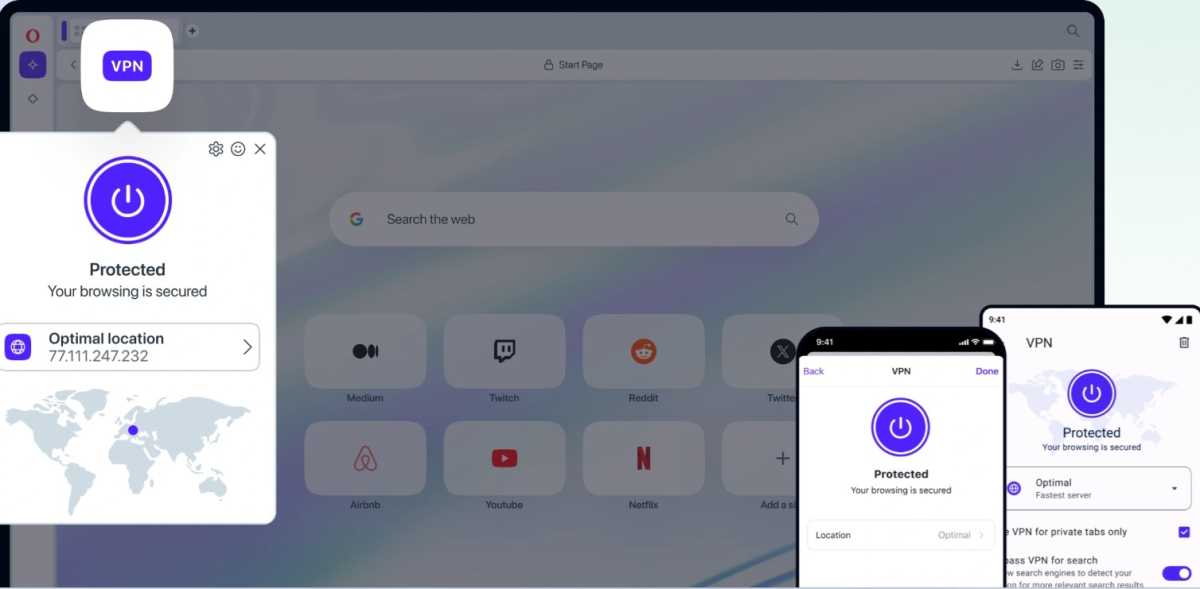 Opera VPN
Opera VPN
Security is paramount. All browsers in our comparison incorporate essential features like sandboxing to isolate malicious code, automatic updates, integrated password managers, and phishing/malware protection based on blacklists.
Opera stands out with its free, unlimited built-in VPN, enhancing security, especially on public Wi-Fi. Opera VPN Pro, a paid tier, offers a wider selection of server locations. Microsoft Edge includes a limited VPN (Edge Secure Network) capped at 5GB per month without location selection. Firefox offers a paid VPN service and supports VPN add-ons. Chrome and Vivaldi rely solely on third-party VPN extensions.
Security Verdict: Opera’s free and unlimited VPN gives it a significant edge in security.
Privacy: Protecting Your Online Footprint
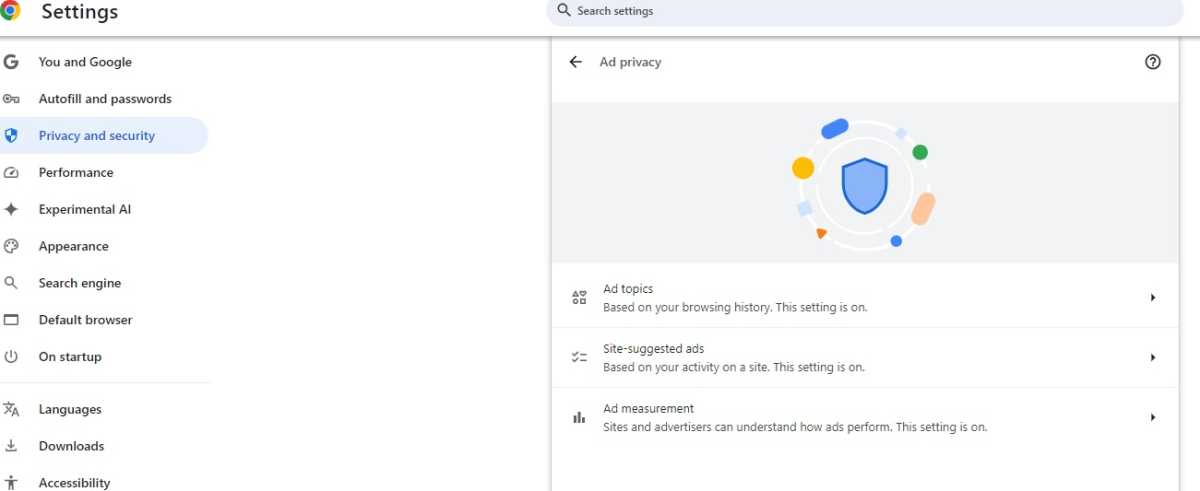 Chrome ad privacy
Chrome ad privacy
Privacy is another crucial aspect. All browsers support “Do Not Track” requests, although websites are not obligated to honor them. Incognito mode, which deletes local browsing history upon closing, is also standard.
Each browser offers tracking protection and third-party cookie management, though implementation varies. Edge and Firefox use profiles, potentially impacting clarity. Chrome’s settings could also be more user-friendly. Opera and Vivaldi provide more intuitive privacy controls.
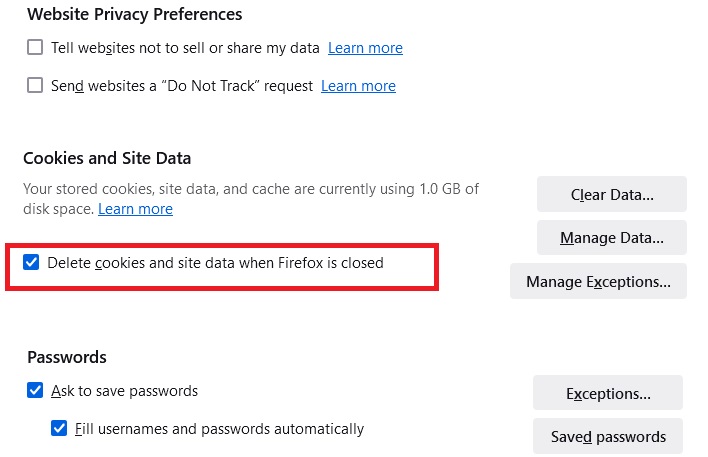 Firefox cookies
Firefox cookies
Chrome, by default, tracks user activity for targeted advertising, though this can be disabled. Edge also has tracking capabilities, but it’s off by default. Opera enables tracking for advertising post-installation. Vivaldi suggests blocking trackers during setup. Firefox stands out by blocking tracking scripts and third-party cookies by default.
Crucially, Firefox is the only browser that significantly mitigates fingerprinting—a technique that identifies users based on browser configuration, hardware, and software details. Other browsers require extensions for similar protection.
Privacy Verdict: Firefox’s comprehensive and user-friendly privacy features make it the privacy leader.
Additional Features and Mobile Versions
All reviewed browsers offer synchronization across devices via a user account. Synchronized data is encrypted, with Vivaldi offering an extra layer of security with a separate encryption password. All browsers have mobile versions for Android and iOS, supporting synchronization with their desktop counterparts.
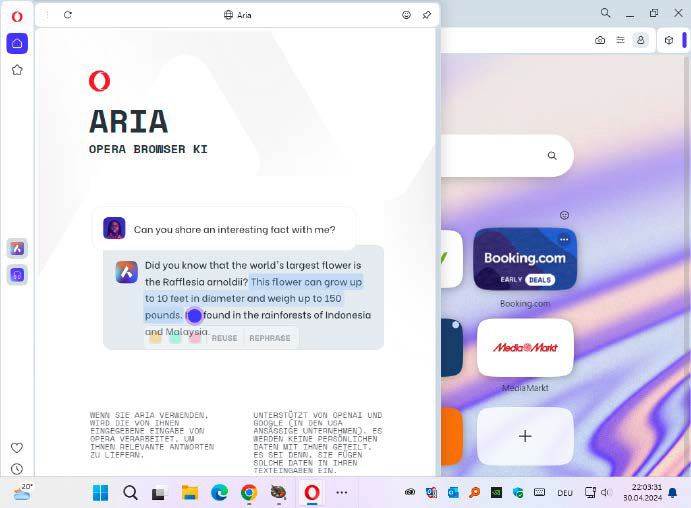 Opera AI
Opera AI
Microsoft Edge integrates the AI-powered Copilot, leveraging Bing search for assistance. Opera also offers AI functionality with Aria, designed for web browsing support, including contextual explanations and free-form prompts. It also links to ChatGPT and ChatSonic.
Features Verdict: While all browsers offer valuable features, Edge and Opera’s integrated AI assistants offer a unique advantage.
Conclusion
Choosing the right browser depends on your priorities. Opera excels in security with its free VPN, while Firefox champions privacy with its robust default settings and anti-fingerprinting measures. Edge and Opera offer unique AI integration. Ultimately, the best browser is the one that best meets your individual needs and preferences.