Corsair recently discussed its power supply units (PSUs) and cooling solutions in the context of upcoming graphics cards, offering insights into the power demands of the next generation. While the company didn’t reveal specific details about Nvidia’s RTX 50-series or other upcoming GPUs, the information suggests that power requirements may not drastically increase from the current generation.
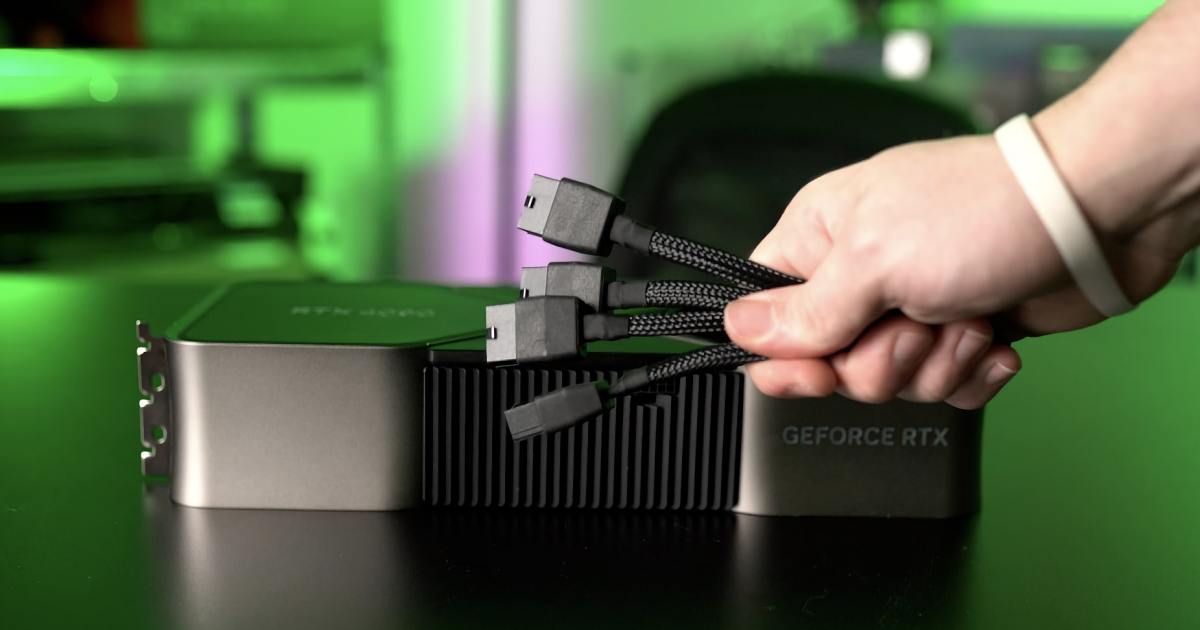
Corsair’s statement indicates that existing PSUs will likely suffice for next-gen GPUs, as long as they provide adequate wattage. The company emphasizes the continued use of the 12V-2×6 GPU power connector, a standard expected to persist with upcoming graphics cards.
 Corsair PSU
Corsair PSU
However, Corsair acknowledges the potential for increased power demands, stating that high-end next-gen GPUs could surpass the 450-watt draw of current models. When combined with high-end CPUs and other power-hungry components, this suggests a growing need for higher-wattage PSUs.
The RTX 5090 and Power Consumption
Much of the speculation around next-gen GPU power requirements centers on Nvidia’s flagship RTX 5090. While AMD’s RDNA 4 and Intel’s Battlemage architectures are also on the horizon, they are less likely to feature enthusiast-level cards with similarly high power demands. Nvidia, on the other hand, is expected to continue pushing the boundaries of high-end performance.
Previous rumors suggested the RTX 5090 might require 600 watts, a significant increase over its predecessor. Some even speculated about the use of two 12V-2×6 power connectors. However, Corsair’s statement seems to dispel these rumors, suggesting that the RTX 5090 will likely stay within the 600-watt limit of a single 12V-2×6 connector.
AMD, Intel, and the Future of GPU Power
While Corsair’s focus was primarily on Nvidia, the information about the 12V-2×6 connector raises questions about AMD and Intel’s upcoming GPUs. While their high-end offerings may not reach the same power levels as Nvidia’s, it’s possible they will also adopt the same power connector.
In conclusion, while next-gen GPUs are expected to demand more power, the increase may not be as dramatic as some rumors suggested. The continued use of the 12V-2×6 connector points to a power ceiling of around 600 watts for the most demanding cards. As more information becomes available, it will be interesting to see how AMD and Intel approach power consumption in their next-gen GPUs.